Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Table Per Hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance in Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss Table-Per-Hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance, how to implement it in Entity Framework Core, and provide a step-by-step real-time example. Entity Framework Core (EF Core) supports different types of inheritance mapping strategies to represent inheritance hierarchies in the database. One of the most commonly used strategies is Table-Per-Hierarchy (TPH).
Table Per Hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance in Entity Framework Core
Table Per Hierarchy (TPH), also known as Single-Table Inheritance, is an inheritance mapping strategy where all classes in an inheritance hierarchy are stored in a single database table. This approach uses a discriminator column to distinguish between different entity types. All properties, both base and derived, are represented in a single table, which may result in some columns being null for certain entities if those properties are specific to a derived class.
This approach simplifies the database schema and can offer performance benefits due to fewer joins, but it may introduce null columns for properties that are not shared across all types. The following are the Key Features of Table Per Hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance in EF Core:
- Single Table: All entities in the inheritance hierarchy are stored in a single database table.
- Discriminator Column: This column differentiates between entity types. For example, a “PaymentType” column can indicate whether a record is for a CardPayment, UPIPayment, or CashOnDeliveryPayment.
- Nullable Columns: Properties specific to derived types may result in null values in the database for other entity types
How to Implement Table Per Hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance in Entity Framework Core
We need to follow the below steps to implement TPH inheritance in Entity Framework Core:
- Create a Base Class and Derived Classes: Create a base class for the shared properties and derived classes for specific entities.
- Configure the Discriminator Column (Optional): EF Core automatically adds a discriminator column, but you can customize it using Fluent API.
- Configure TPH using Fluent API: Use the Fluent API to specify how the inheritance mapping should occur. Use the HasDiscriminator() method to define the discriminator column and values for each derived class.
Real-time Example: Implementing TPH Inheritance in a .NET Application
Let’s implement a scenario with a base class, Payment, and three derived classes: CardPayment, UPIPayment, and CashOnDeliveryPayment. We will create a console application that simulates processing different types of payments, using TPH inheritance to store them in a single table using Entity Framework Core. Let us proceed and define the Parent and Child Entities:
Payment Entity
Create a new file named Payment.cs within the Entities folder and then copy and paste the following code. The Payment class serves as the base class for all types of payments in your e-commerce application. It contains the common properties shared across all payment methods, such as the amount, date, and currency of the payment.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
// Base Class representing a general payment
public abstract class Payment
{
public int PaymentId { get; set; } // Primary Key, Unique identifier for each payment record in the database.
[Column(TypeName = "decimal(18,2)")]
public decimal Amount { get; set; } // The total amount of the payment
public DateTime PaymentDate { get; set; } // The date and time when the payment was made
public string Currency { get; set; } // The currency in which the payment was made (e.g., INR, USD)
}
}
CardPayment Entity
Create a new file named CardPayment.cs within the Entities folder, then copy and paste the following code. The CardPayment class is a derived class of Payment that represents payments made using cards (credit and debit). It includes properties specific to card transactions, such as card details and billing information.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
// Derived Class representing a card payment (credit or debit)
public class CardPayment : Payment
{
public string? CardNumber { get; set; } // The 16-digit (or appropriate length) number printed on the card used for the transaction.
public string? CardHolderName { get; set; } // The full name of the person to whom the card is issued.
public DateTime? ExpiryDate { get; set; } // The date after which the card is no longer valid.
public string? CVV { get; set; } // The Card Verification Value, a security code typically found on the back of the card.
public CardType? CardType { get; set; } // An enumeration indicating whether the card is a credit or debit card.
}
// Enumeration to specify the type of card
public enum CardType
{
Credit,
Debit
}
}
Note: All properties are marked as nullable (?) because they are specific to this derived class and will result in nullable columns in the database when using TPH inheritance.
UPIPayment Entity
Create a new class file named UPIPayment.cs within the Entities folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The UPIPayment class is a derived class of Payment representing payments made via UPI (Unified Payments Interface), a popular payment method in India. It includes properties specific to UPI transactions.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
// Derived Class representing a UPI payment
public class UPIPayment : Payment
{
public string? UPIId { get; set; } // The UPI ID (e.g., user@bank) associated with the payer's bank account.
public string? UPITransactionId { get; set; } // A unique identifier assigned to the UPI transaction for tracking purposes.
}
}
CashOnDeliveryPayment Entity
Create a new file named CashOnDeliveryPayment.cs within the Entities folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The CashOnDeliveryPayment class is a derived class of Payment that represents payments made via Cash on Delivery (COD). It includes properties related to the status of the delivery and payment receipt.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
// Derived Class representing a Cash On Delivery payment
public class CashOnDeliveryPayment : Payment
{
public DateTime? ExpectedDeliveryDate { get; set; } // The anticipated date when the product will be delivered to the customer.
public bool? PaymentReceived { get; set; } // A flag indicating whether the payment has been collected upon delivery.
public DateTime? PaymentReceivedDate { get; set; } // The date and time when the payment was actually received.
}
}
Create the DbContext
Modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows. The EFCoreDbContext class represents the session with the database, allowing us to query and save instances of our entities. It includes the configuration necessary for Entity Framework Core to map entities to the database using TPH inheritance.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
//// Configuring the connection string to the SQL Server database
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=PaymentDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
// Configures the model and mappings between entities and database
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// Configuring Table-Per-Hierarchy (TPH) inheritance for Payment entities
modelBuilder.Entity<Payment>()
.HasDiscriminator<string>("PaymentType") // Adds a discriminator column named 'PaymentType'
.HasValue<CardPayment>("Card") // Sets discriminator value 'Card' for CardPayment entities
.HasValue<UPIPayment>("UPI") // Sets discriminator value 'UPI' for UPIPayment entities
.HasValue<CashOnDeliveryPayment>("COD"); // Sets discriminator value 'COD' for CashOnDeliveryPayment entities
}
// DbSet representing the Payments table in the database
public DbSet<Payment> Payments { get; set; }
}
}
Generate Migration and Update Database:
With the above changes, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows.
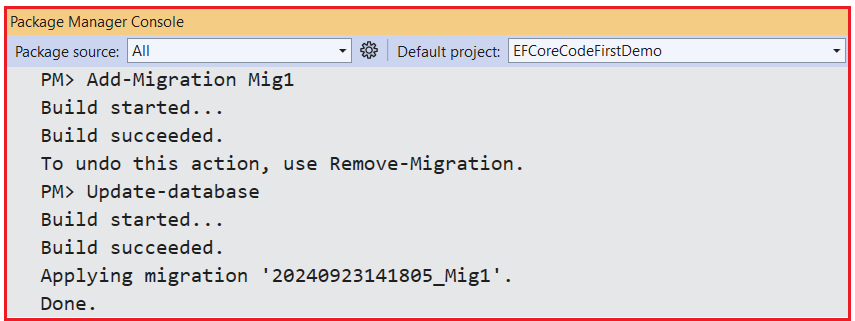
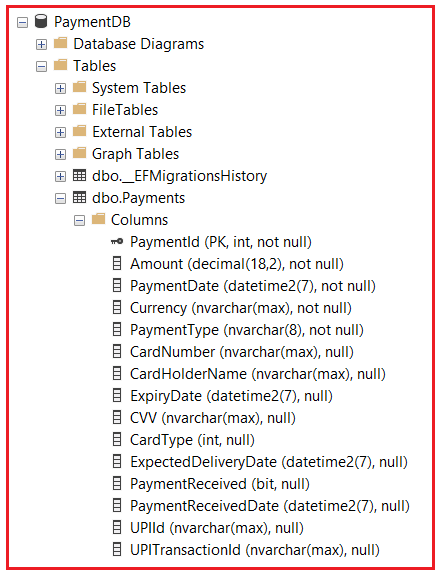
Now, verify the database, and you should see one table containing all the columns along with the discriminator column named PaymentType, as shown in the below image:
Write Operations with TPH in EF Core:
When inserting or updating entities, EF Core sets the discriminator value appropriately based on the entity’s actual type. This ensures that the correct type information is stored in the PaymentType column, enabling EF Core to map the data back to the appropriate derived class upon retrieval.
Read Operations with TPH in EF Core:
When we query the database, EF Core automatically uses the discriminator column to determine the entity type and return the appropriate derived class instances. For example, when querying the Payments DbSet, EF Core automatically uses the discriminator column (PaymentType) to determine the correct derived class to instantiate. This means you can write queries against the base Payment class and receive a collection of different payment types.
Example to Perform Create and Read Operations using TPH in EF Core:
Please modify the Program class to perform Create and Read operations using the entities and EFCoreDbContext. Here, I have provided inline comments for a better understanding. After the code, I will explain how TPH (Table Per Hierarchy) performs these operations in Entity Framework Core.
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Perform INSERT and READ operations
CreatePayments();
ReadPayments();
}
// Creates sample payment records and saves them to the database.
static void CreatePayments()
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Create a new CardPayment (Credit Card)
var cardPaymentCredit = new CardPayment
{
Amount = 1500.00m,
PaymentDate = DateTime.Now,
Currency = "INR",
CardNumber = "4111111111111111",
CardHolderName = "Ravi Kumar",
ExpiryDate = new DateTime(2024, 12, 31),
CVV = "123",
CardType = CardType.Credit
};
// Create a new CardPayment (Debit Card)
var cardPaymentDebit = new CardPayment
{
Amount = 2000.00m,
PaymentDate = DateTime.Now,
Currency = "INR",
CardNumber = "5111111111111111",
CardHolderName = "Anjali Mehta",
ExpiryDate = new DateTime(2025, 11, 30),
CVV = "456",
CardType = CardType.Debit
};
// Create a new UPIPayment
var upiPayment = new UPIPayment
{
Amount = 750.00m,
PaymentDate = DateTime.Now,
Currency = "INR",
UPIId = "ravi@upi",
UPITransactionId = "TXN1234567890"
};
// Create a new CashOnDeliveryPayment
var codPayment = new CashOnDeliveryPayment
{
Amount = 500.00m,
PaymentDate = DateTime.Now,
Currency = "INR",
ExpectedDeliveryDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays(3),
PaymentReceived = false
};
// Add payments to the context
context.Payments.AddRange(cardPaymentCredit, cardPaymentDebit, upiPayment, codPayment);
// Save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Payments have been created and saved to the database.\n");
}
}
//Reads and displays all payment records from the database.
static void ReadPayments()
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Retrieve all payments from the database
var payments = context.Payments.ToList();
Console.WriteLine("Displaying all payments:");
foreach (var payment in payments)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Payment ID: {payment.PaymentId}, Amount: {payment.Amount}, Payment Date: {payment.PaymentDate}, Currency: {payment.Currency}, Payment Type: {payment.GetType().Name}");
// Use pattern matching to access derived class properties
if (payment is CardPayment cardPayment)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\tCard Type: {cardPayment.CardType}, Card Number: {cardPayment.CardNumber}");
Console.WriteLine($"\tCard Holder Name: {cardPayment.CardHolderName}, Expiry Date: {cardPayment.ExpiryDate?.ToShortDateString()}");
}
else if (payment is UPIPayment upi)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\tUPI ID: {upi.UPIId}, UPI Transaction ID: {upi.UPITransactionId}");
}
else if (payment is CashOnDeliveryPayment cod)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\tExpected Delivery Date: {cod.ExpectedDeliveryDate?.ToShortDateString()}");
Console.WriteLine($"\tPayment Received: {cod.PaymentReceived}, Payment Received Date: {cod.PaymentReceivedDate?.ToShortDateString()}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
}
Output:

How Does TPH Handle Create Operations in EF Core?
- Entity Tracking: When we create a new instance of a derived class (e.g., CardPayment), EF Core tracks it as an entity to be added.
- Discriminator Value Assignment: EF Core automatically sets the PaymentType discriminator value based on the entity type.
- Database Insert: Upon calling SaveChanges(), EF Core generates an INSERT statement for the Payments table. All properties, including those from the base and derived classes, are inserted. Columns not applicable to the entity (i.e., properties from other derived classes) are set to NULL.
- Example: Creating a CardPayment sets the PaymentType to ‘Card’. The CardNumber, CardHolderName, etc., are populated. The UPI and COD-specific columns are set to NULL.
Now, if you verify the Payments table, then you should see the following:

How Does TPH Handle Read Operation in EF Core?
- Query Execution: When querying the Payments DbSet, EF Core fetches records from the Payments table.
- Derived Entity Instantiation: EF Core reads the PaymentType discriminator value for each record. Based on the discriminator, EF Core instantiates the appropriate derived class, and properties specific to the derived class are populated.
- Type Casting: In code, we can use pattern matching (is) to work with specific payment types. For example, a record with PaymentType ‘UPI’ is materialized as a UPIPayment object. You can safely access the UPIId and UPITransactionId properties.
Example to Understand Update Operation using TPH in EF Core:
Let us see how to perform the Update operation using TPH in EF Core. So, please modify the Program class as follows. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Perform Update operation
UpdatePayment();
}
// Updates a specific payment record in the database.
static void UpdatePayment()
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Prompt user to enter the Payment ID to update
Console.Write("Enter the Payment ID to update: ");
if (int.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out int paymentId))
{
// Retrieve the payment with the specified Payment ID
var paymentToUpdate = context.Payments.Find(paymentId);
// Since all payments are in one table, the Find method looks up the record by PaymentId.
//EF Core reads the PaymentType discriminator column to determine the actual type of the payment(CardPayment, UPIPayment, or CashOnDeliveryPayment
//F Core instantiates the correct derived class based on the discriminator value.
if (paymentToUpdate != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Updating Payment ID: {paymentToUpdate.PaymentId}, Type: {paymentToUpdate.GetType().Name}");
// Update common properties
Console.Write("Enter new amount (leave blank to keep current): ");
var amountInput = Console.ReadLine();
if (decimal.TryParse(amountInput, out decimal newAmount))
{
paymentToUpdate.Amount = newAmount;
}
// Update properties based on payment type
// Uses is pattern matching to check if paymentToUpdate is a CardPayment.
if (paymentToUpdate is CardPayment cardPayment)
{
Console.Write("Enter new Card Holder Name (leave blank to keep current): ");
var newName = Console.ReadLine();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(newName))
{
cardPayment.CardHolderName = newName;
}
//If you want you can also update other properties as required
}
else if (paymentToUpdate is UPIPayment upiPayment)
{
Console.Write("Enter new UPI ID (leave blank to keep current): ");
var newUPIId = Console.ReadLine();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(newUPIId))
{
upiPayment.UPIId = newUPIId;
}
}
else if (paymentToUpdate is CashOnDeliveryPayment codPayment)
{
Console.Write("Has payment been received? (y/n): ");
var paymentReceivedInput = Console.ReadLine();
if (paymentReceivedInput?.ToLower() == "y")
{
codPayment.PaymentReceived = true;
codPayment.PaymentReceivedDate = DateTime.Now;
}
}
// Save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Payment has been updated successfully.\n");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Payment not found for update.\n");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid Payment ID.\n");
}
}
}
}
}
Code Explanation:
The UpdatePayment method is designed to update payment records in the database. It handles different types of payments (CardPayment, UPIPayment, and CashOnDeliveryPayment) by leveraging TPH inheritance in EF Core. The method performs the following steps:
- Prompt the User for Payment ID: It asks users to enter the PaymentId of the payment they wish to update.
- Retrieve the Payment: It retrieves the payment record from the database using the provided PaymentId.
- Update Common Properties: It allows users to update properties common to all payment types (e.g., Amount).
- Update Type-Specific Properties: It uses pattern matching to determine the payment’s actual type and allows properties specific to that type to be updated.
- Save Changes: It saves the updated payment record and sends it back to the database.
For a better understanding, please have a look at the following output:

Example to Understand Delete Operation using TPH in EF Core:
Let us see how to perform the Delete operation using TPH in EF Core. So, please modify the Program class as follows. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Perform Delete operations
DeletePayment();
}
// Deletes a specific payment record from the database.
static void DeletePayment()
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Prompt user to enter the Payment ID to delete
Console.Write("Enter the Payment ID to delete: ");
if (int.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out int paymentId))
{
// Retrieve the payment with the specified Payment ID
var paymentToDelete = context.Payments.Find(paymentId);
if (paymentToDelete != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Deleting Payment ID: {paymentToDelete.PaymentId}, Type: {paymentToDelete.GetType().Name}");
// Remove the payment from the context
context.Payments.Remove(paymentToDelete);
// Save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Payment has been deleted successfully.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Payment not found for deletion.");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid Payment ID.");
}
}
}
}
}
Code Explanation:
The DeletePayment method is designed to delete a specific payment record from the database. It interacts with the user to obtain the PaymentId of the payment to be deleted and then performs the deletion if the payment exists. Here’s what the method does:
- Prompt for Payment ID: Asks the user to enter the PaymentId of the payment they wish to delete.
- Retrieve the Payment: Retrieve the payment record from the database using the provided PaymentId.
- Delete the Payment: If the payment exists, it removes it from the context.
- Save Changes: Persists the deletion to the database.
- Provide Feedback: Informs the user about the success or failure of the operation.
For a better understanding, please have a look at the following output:

Advantages of TPH in EF Core
- Simplified Schema: Only one table to manage for all payment types.
- Easier Maintenance: Adding a new payment type involves creating a new class and updating the model configuration.
- Performance on Read Operations: Minimizing joins can improve read performance.
Drawbacks of TPH in EF Core
- Null Values: Columns specific to one payment type are null for other types.
- Database Constraints: It is harder to enforce NOT NULL constraints on derived type properties.
- Table Sparsity: As more derived types are added with unique properties, the Payments table may accumulate numerous nullable columns, leading to sparsity. This results in wasted storage space and performance degradation due to the increased width of the table.
- Discriminator Overhead: To determine the entity type, each query must evaluate the discriminator column (PaymentType). Additional processing can affect query performance, especially on large datasets.
Table-Per-hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance provides a simple and efficient way to implement inheritance in Entity Framework Core. However, unused columns may result in performance challenges. It is best suited for scenarios where inheritance hierarchies are not overly complex, and performance needs are moderate.
In the next article, I will discuss Table Per Type (TPT) Inheritance in Entity Framework Core with Examples. In this article, I explain Table Per Hierarchy (TPH) Inheritance in Entity Framework Core with Examples. I hope you enjoy this TPH Inheritance in EF Core article.
