Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Many-to-Many Relationships in Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss How to Configure Many-to-Many Relationships between two Entities in Entity Framework Core with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing How to Configure One-to-Many Relationships in EF Core with Examples.
What is a Many-to-Many Relationship in Entity Framework Core?
A Many-to-Many relationship in Entity Framework Core represents a scenario where multiple instances of one entity can be associated with multiple instances of another entity. This type of relationship is commonly used when both sides of the relationship can have multiple records linked to each other.
For example, consider an application that manages Students and Courses. A student can enroll in many courses, and a course can have many students enrolled. This is a classic Many-to-Many relationship.
Another real-time example is an application that manages Projects and Employees. An employee can work on multiple projects, and each project can have multiple employees working on it. This creates a Many-to-Many relationship between Employees and Projects.
Guidelines to Implement Many-to-Many Relationships in Entity Framework Core
In EF Core, a Many-to-Many relationship is typically implemented with the help of a join table that holds the foreign keys of both related entities. EF Core can create this join table implicitly. The following are the key guidelines for implementing Many-to-Many relationships in Entity Framework Core:
- Principal and Dependent Entities: Both entities involved in a Many-to-Many relationship can be considered as principals, as they can exist independently.
- Join Table: In the database, Many-to-Many relationships are represented by an additional table known as a “join table” that contains foreign keys pointing to the primary keys of both related entities. EF Core automatically creates this table when the Many-to-Many relationship is configured.
- Navigation Properties: Both entities involved in the relationship will contain collection navigation properties that point to each other.
Real-Time Example to Understand Many-to-Many Relationships in EF Core
Let’s consider a real-time example where we need to implement a Many-to-Many relationship between Student and Course entities. In this scenario, a student can enroll in multiple courses, and each course can have multiple students. I will show you two approaches to implementing Many-to-Many Relationships in EF Core. They are as follows:
- Implementing Many-to-Many Relationships without Data Annotations or Fluent API
- Implementing Many-to-Many Relationships with Fluent API
Implementing Many-to-Many Relationships Without Data Annotations or Fluent API
Entity Framework Core 5.0+ automatically handles Many-to-Many relationships by introducing a join table when it detects collection navigation properties on both sides. Let’s understand how to implement the One-to-Many relationship with default EF Core conventions.
Creating Entities:
We want to establish a Many-to-Many relationship between Student and Course entities.
Student Entity
Create a class file named Student.cs within the Entities folder with the following code. The Student entity contains a collection of Courses, meaning each student can enroll in multiple courses.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<Course> Courses { get; set; } // Navigation property for many-to-many
}
}
Course Entity
Next, create a class file named Course.cs within the Entities folder. The Course entity contains a collection of Students, meaning each course can have many students.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Course
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string CourseName { get; set; }
public List<Student> Students { get; set; } // Navigation property for many-to-many
}
}
With Default Convention:
- EF Core detects the Many-to-Many relationship based on the presence of navigation properties (Courses in Student and Students in Course).
- EF Core will automatically create a join table between Students and Courses, including foreign keys for both Student and Course.
DbContext Class:
Next, modify the EFCoreDbContext class to include these entities as DbSet properties.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Configuring the Connection String
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
}
Generating the Migration:
After the changes, run the following commands in the Package Manager Console:
- Add-Migration CreateStudentCourseTables
- Update-Database
Once these commands are executed, EF Core will automatically create a join table named CourseStudent (or something similar) that links Students to Courses, as shown in the image below.
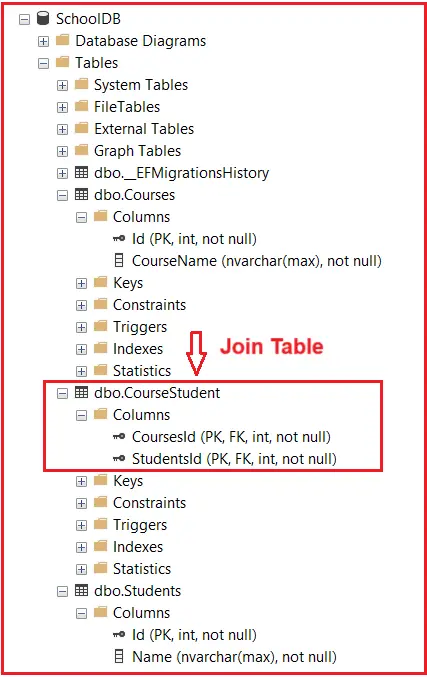
Implementing Many-to-Many Relationships Using Fluent API in EF Core
For more complex configurations, Fluent API provides a powerful way to explicitly configure the Many-to-Many relationship. So, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows to configure Many-to-Many Relationships using Fluent API. In this configuration, we use the HasMany, WithMany, and UsingEntity methods to define the many-to-many relationship between Student and Course.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Configuring the Connection String
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.HasMany(s => s.Courses) // Student can enroll in many Courses
.WithMany(c => c.Students) // Course can have many Students
.UsingEntity(j => j.ToTable("StudentCourses")); //Explicitly set the join table name
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
}
In this Fluent API configuration:
- HasMany(s => s.Courses): Specifies that a Student can have many Courses.
- WithMany(c => c.Students): Specifies that a Course can have many Students.
- UsingEntity(j => j.ToTable(“StudentCourses”)): Explicitly names the join table. If you don’t specify this, EF Core will use a default name based on the two entity names.
Generating Migration:
With the above changes, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands. Now, if you verify the database, you should see the following.

Program to Understand Many to Many Relationships in Entity Framework Core:
Please modify the Program class as follows. The following code demonstrates adding entities into the Student and Course tables using a Many-to-Many relationship. It also shows how to fetch and display the data.
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Initialize the database context
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Adding new Students and Courses
AddStudentsAndCourses(context);
// Fetching and displaying the data
DisplayStudentsAndCourses(context);
}
}
// Method to add students and courses
static void AddStudentsAndCourses(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Creating new courses
var course1 = new Course { CourseName = "ASP.NET Core" };
var course2 = new Course { CourseName = "Machine Learning" };
var course3 = new Course { CourseName = "Cloud Computing" };
// Creating new students
var student1 = new Student { Name = "Pranaya Rout", Courses = new List<Course> { course1, course2 } };
var student2 = new Student { Name = "Rakesh Kumar", Courses = new List<Course> { course2, course3 } };
var student3 = new Student { Name = "Anurag Mohanty", Courses = new List<Course> { course1, course3 } };
// Adding the students (EF Core will automatically add the courses due to the relationship)
context.Students.AddRange(student1, student2, student3);
// Save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Students and Courses have been added to the database.\n");
}
// Method to fetch and display students with their enrolled courses
static void DisplayStudentsAndCourses(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Fetch all students and their related courses using Include for eager loading
var students = context.Students
.Include(s => s.Courses) //Eager Load the Related Courses
.ToList();
// Iterate through each student and display the courses they are enrolled in
foreach (var student in students)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Student Id: {student.Id}, Name: {student.Name}");
// If the student is enrolled in any courses, display them
if (student.Courses.Any())
{
Console.WriteLine("Enrolled in the following courses:");
foreach (var course in student.Courses)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\tCoure Id:{course.Id}, Name:{course.CourseName}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No courses enrolled.");
}
Console.WriteLine(); // For spacing
}
}
}
}
Output:

Now, if you verify the database tables, then you should see the data as expected, as shown in the below image:

How Do We add a New Column to the Join Table?
Now, we need to add a column named EnrollmentDate to the Joining table. To include the EnrollmentDate column in the joining table StudentCourses, we will need to create an explicit join entity that represents the many-to-many relationship between Student and Course. This approach allows us to add additional properties (like EnrollmentDate) to the join table.
Create the StudentCourse Entity
Define a class that represents the join table, including the EnrollmentDate property. So, create a new class file named StudentCourse.cs within the Entities folder and copy and paste the following code:
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class StudentCourse
{
public int StudentId { get; set; } // Foreign Key to Student
public Student Student { get; set; } // Navigation property
public int CourseId { get; set; } // Foreign Key to Course
public Course Course { get; set; } // Navigation property
public DateTime EnrollmentDate { get; set; } // Additional Property
}
}
Modify the Student and Course Classes:
Add the StudentCourse collection to the Student and Course entities. Modify the Student class to reference the StudentCourse entity instead of the Course entity.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<StudentCourse> StudentCourses { get; set; } // Navigation property to join entity
}
}
Similarly, modify the Course class as follows:
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Course
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string CourseName { get; set; }
public List<StudentCourse> StudentCourses { get; set; } // Navigation property to join entity
}
}
Configure Many to Many Relationships in EFCoreDbContext:
Now, we need to configure the StudentCourse entity as the join table using Fluent API and set up the Many-to-Many relationship between Student and Course via this join table. So, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Configuring the Connection String
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<StudentCourse>()
.HasKey(sc => new { sc.StudentId, sc.CourseId }); // Composite Key for Join Table
modelBuilder.Entity<StudentCourse>()
.HasOne(sc => sc.Student)
.WithMany(s => s.StudentCourses) // Navigation Property in Student
.HasForeignKey(sc => sc.StudentId); //Foreign Key
modelBuilder.Entity<StudentCourse>()
.HasOne(sc => sc.Course)
.WithMany(c => c.StudentCourses) // Navigation Property in Course
.HasForeignKey(sc => sc.CourseId); //Foreign Key
// Explicitly configure the join table name
modelBuilder.Entity<StudentCourse>().ToTable("StudentCourses");
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; }
public DbSet<StudentCourse> StudentCourses { get; set; }
}
}
With the introduction of the StudentCourse entity, we create an explicit join table to which we can add additional properties like EnrollmentDate. The HasKey method sets a composite primary key using StudentId and CourseId. The HasOne and WithMany methods configure the relationships between StudentCourse, Student, and Course. The ToTable method ensures that the table is named StudentCourses.
Generate Migration and Update Database
Open the Package Manager Console and execute the following commands to apply the changes:
- Add-Migration AddEnrollmentDateToStudentCourses
- Update-Database
This will create a new migration that includes the EnrollmentDate column in the StudentCourses table and updates the database schema accordingly. Once you execute the above commands, verify the database, and you should see the following:

Clearing the Data:
Before proceeding, please execute the following SQL Statements in the SchoolDB database to clear all the data and reset the Identity column values.
TRUNCATE TABLE StudentCourses;
DELETE FROM Courses;
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('Courses', RESEED, 0);
DELETE FROM Students;
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('Students', RESEED, 0);
Testing the Many to Many Relationships:
Next, modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Initialize the database context
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Adding new Students and Courses
AddStudentsAndCourses(context);
// Fetching and displaying the data
DisplayStudentsAndCourses(context);
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException dbex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {dbex.InnerException?.Message ?? dbex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error Occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Method to add students and courses
static void AddStudentsAndCourses(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Creating new courses
var course1 = new Course { CourseName = "ASP.NET Core" };
var course2 = new Course { CourseName = "Machine Learning" };
var course3 = new Course { CourseName = "Cloud Computing" };
// Creating new students
var student1 = new Student { Name = "Pranaya Rout" };
var student2 = new Student { Name = "Rakesh Kumar" };
var student3 = new Student { Name = "Anurag Mohanty" };
// Creating StudentCourse join entities with EnrollmentDate
var studentCourses = new List<StudentCourse>
{
new StudentCourse { Student = student1, Course = course1, EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Now },
new StudentCourse { Student = student1, Course = course2, EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Now },
new StudentCourse { Student = student2, Course = course2, EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Now },
new StudentCourse { Student = student2, Course = course3, EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Now },
new StudentCourse { Student = student3, Course = course1, EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Now },
new StudentCourse { Student = student3, Course = course3, EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Now }
};
// Adding the students and courses via the join table
context.StudentCourses.AddRange(studentCourses);
// Save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Students, Courses, and Enrollments have been added to the database.\n");
}
// Method to fetch and display students with their enrolled courses and enrollment dates
static void DisplayStudentsAndCourses(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Fetch all students and their related courses using Include for eager loading
var students = context.Students //Fetch the Students Data
.Include(s => s.StudentCourses) // Eager Load the Related StudentCourses
.ThenInclude(sc => sc.Course) // Then Load the related Courses
.ToList();
// Iterate through each student and display the courses they are enrolled in
foreach (var student in students)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Student Id: {student.Id}, Name: {student.Name}");
// If the student is enrolled in any courses, display them
if (student.StudentCourses.Any())
{
Console.WriteLine("Enrolled in the following courses:");
foreach (var studentCourse in student.StudentCourses)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\tCourse Id:{studentCourse.Course.Id}, Name:{studentCourse.Course.CourseName}, Enrollment Date: {studentCourse.EnrollmentDate}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No courses enrolled.");
}
Console.WriteLine(); // For spacing
}
}
}
}
Key Changes:
- StudentCourse Entity: The join entity is now explicitly used to manage the many-to-many relationship, and the EnrollmentDate property has been added.
- AddStudentsAndCourses Method: Instead of adding courses directly to the Courses property in Student, we have added StudentCourse objects to link the students and courses, along with the EnrollmentDate.
- DisplayStudentsAndCourses Method: We have updated the Include statement to load the StudentCourses and then the related Course. This allows access to both the EnrollmentDate and the course information.
Now, run the application to ensure that students and courses are added to the database with the EnrollmentDate. Verify that the output displays the students, the courses they are enrolled in, and the enrollment dates correctly, as shown in the image below.

Now, if you verify the StudentCourses database table, then it should have the enrolment date along with the Course ID and Student ID as shown in the below image:

When Should We Use Many-to-Many Relationships in Entity Framework Core?
Many-to-many relationships are suitable when:
- Multiple Associations Between Entities: When both entities need to reference multiple instances of the other entity. For example, students enroll in multiple courses, or employees work on multiple projects.
- Efficient Querying: In situations where you need to query associations between two entities frequently, like finding all courses a student is enrolled in or all employees working on a project.
This type of relationship is useful in scenarios where each entity can have multiple links with the other entity, creating a more complex data structure.
In the next article, I will discuss Self-Referencing Relationships in Entity Framework Core using Fluent API with Examples. In this article, I explain how to Configure Many-to-Many Relationships in Entity Framework Core with Examples. I hope you enjoyed this article on Configuring Many-to-Many Relationships in EF Core.
