Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core (EF Core)
In this article, I will discuss Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing Disconnected Entity Graph in Entity Framework Core with Examples. At the end of this article, you will understand how to perform database CRUD operations using Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core.
What is a Stored Procedure?
A Stored Procedure is a precompiled collection of SQL statements stored in the database under a specific name and processed as a unit. They can accept both input and output parameters, execute complex logic involving loops, conditions, transactions, and error handling, and handle SQL commands such as INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT. Stored procedures are designed to encapsulate reusable database logic, improve performance, and enhance security.
How a Stored Procedure Execute in SQL Server:
Understanding the execution flow of a stored procedure helps optimize its performance and helps in knowing how SQL Server handles its execution. To understand how a stored procedure is executed in SQL Server, please have a look at the following diagram:
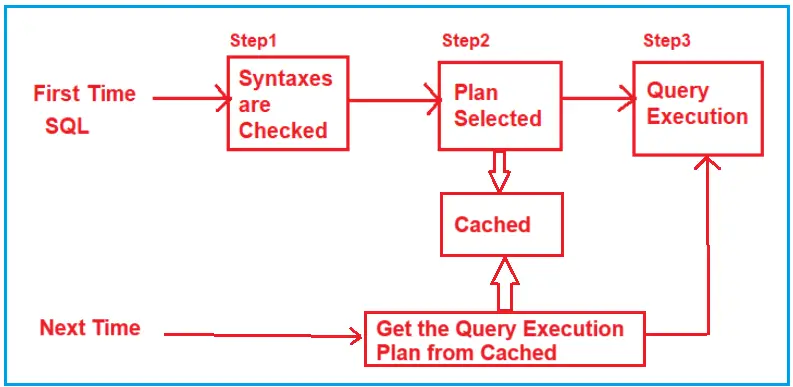
Let us understand what happens when we execute for the first and what happens for the subsequent executions.
First Execution:
Step 1: Syntax Check
- When the stored procedure is executed for the first time, SQL Server checks the syntax of the SQL statements inside the procedure. If there are any syntax errors, they are reported immediately.
Step 2: Query Plan Compilation
- SQL Server parses the SQL statements inside the stored procedure and creates a Query Plan.
- During this step, SQL Server analyzes the queries, evaluates different execution strategies, and selects the most efficient one based on available indexes and statistics.
- A Query Execution Plan is generated, containing detailed instructions on how the queries will access the data (e.g., full table scan or index scan).
Step 3: Caching the Query Plan
- After creating the Query Execution Plan, it is stored in the cache to avoid recompiling the SQL statements and regenerating the Query Plan every time the procedure is executed, saving time during subsequent executions.
Step 4: Query Execution
- The stored procedure is executed using the cached Query Execution Plan, and the required data is retrieved and returned to the user.
Subsequent Executions:
- The next time the stored procedure is executed, the SQL Server first checks if an existing Query Execution Plan is already there in the cache.
- If it finds the Query Execution Plan in the Cache, SQL Server skips the syntax checking and Query Generation plan steps.
- The stored procedure proceeds directly to execution using the cached query plan, which speeds up execution.
Why do we need Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core?
- Performance Improvement: Stored procedures reduce network traffic by executing SQL statements on the server side. The execution plans are cached, reducing compilation overhead for repetitive tasks.
- Security: They provide an additional security layer by restricting direct access to underlying tables. Permissions can be granted on stored procedures without exposing table structures.
- Reusability and Maintainability: Encapsulate complex logic in a single location, which can be reused across multiple applications or services, promoting code reusability. Changes to the logic require updates only to the stored procedure, not the application code.
- Reduced Network Traffic: Reduce network traffic by sending only procedure execution commands, i.e., minimizing the amount of data sent over the network.
- Transaction Management: Facilitate complex transaction handling within the database, ensuring data integrity.
Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core:
While EF Core is generally used with LINQ-based queries and entity modeling, it also supports the execution of stored procedures for performing complex operations and improving performance and security within the EF Core context. The following benefits we will get by Using Stored Procedures in EF Core:
- Performance Boost: Stored procedures execute directly on the database server, reducing the need to transfer complex logic or operations over the network.
- Advanced SQL: They allow us to use advanced SQL concepts like transactions, loops, conditions, and error handling, which are not always easy to express in LINQ.
Example to Understand How to Call Stored Procedure in Entity Framework Core:
We will create a console application that performs CRUD operations on a Student entity using stored procedures. This example demonstrates how to integrate stored procedures with EF Core. First, define the Student entity representing the Students table in the database.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Branch { get; set; }
public string Gender { get; set; }
}
}
DbContext Configuration
Configure the DbContext to interact with the database. So, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
//Configuring the Connection String
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EFCoreDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
Generate and Apply Migrations
Open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows.
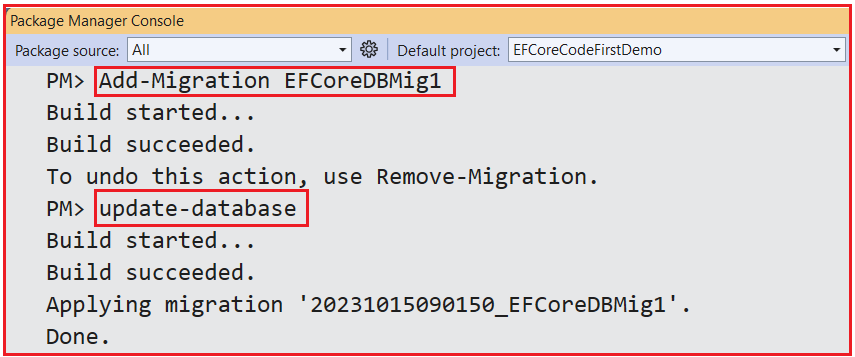
Once you execute the above commands, the database EFCoreDB is created with a Students table reflecting the Student entity properties, as shown in the image below.

Creating Stored Procedures in SQL Server
Let us create stored procedures to perform CRUD Operations with the Students database table. Stored procedures encapsulate SQL logic for various database operations. The following are the stored procedures for inserting, updating, deleting, and retrieving student records.
Creating a Stored Procedure for Inserting a Student:
The following Stored Procedure will take the First Name, Last Name, Gender, and Branch as input parameters and then INSERT the student data into the student database table. Then it will return the newly generated StudentId using the SCOPE_IDENTITY() function via the output parameter.
-- Insert Student Stored Procedure
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE spInsertStudent
@FirstName NVARCHAR(100),
@LastName NVARCHAR(100),
@Branch NVARCHAR(100),
@Gender NVARCHAR(50),
@StudentId INT OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO Students (FirstName, LastName, Branch, Gender)
VALUES (@FirstName, @LastName, @Branch, @Gender);
-- Retrieve the newly inserted StudentId
SET @StudentId = SCOPE_IDENTITY();
END
Creating a Stored Procedure for Updating an Existing Student:
The following Stored Procedure will take the StudentId, First Name, Last Name, Gender, and Branch as input parameters and then update the First Name, Last Name, Gender, and Branch data into the Student database table based on the StudentId. This stored procedure does not return anything.
-- Updates the specified student record based on StudentId.
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE spUpdateStudent
@StudentId INT,
@FirstName NVARCHAR(100),
@LastName NVARCHAR(100),
@Branch NVARCHAR(100),
@Gender NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
UPDATE Students
SET
FirstName = @FirstName,
LastName = @LastName,
Branch = @Branch,
Gender = @Gender
WHERE StudentId = @StudentId;
END
Creating a Stored Procedure for Deleting an Existing Student:
The following stored procedure is used to delete an existing student from the Students table based on the Student ID.
-- Delete the specified student record based on StudentId.
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE spDeleteStudent
@StudentId int
AS
BEGIN
DELETE FROM Students WHERE StudentId = @StudentId
END
Creating a Stored Procedure to Fetch All Students:
The following Stored Procedure fetches all Student data from the Students Table.
-- Get All Student Stored Procedure
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE spGetAllStudents
AS
BEGIN
SELECT StudentId, FirstName, LastName, Branch, Gender
FROM Students;
END
Creating a Stored Procedure to Fetch a Student by ID:
The following Stored Procedure is used to fetch a particular Student data from the Student Database Table based on the StudentId.
-- Get Student by Student Id
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE spGetStudentByStudentId
@StudentId INT
AS
BEGIN
SELECT StudentId, FirstName, LastName, Branch, Gender
FROM Students
WHERE StudentId = @StudentId;
END
Verifying the Stored Procedures:
Once the stored procedures are created, we can verify the same within the Programmability/Stored Procedures folder of the EFCoreDB database, as shown in the below image:

Different Ways to Call Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core:
EF Core allows us to execute stored procedures and raw SQL queries using FromSqlRaw, FromSqlInterpolated, ExecuteSqlRaw, and ExecuteSqlInterpolated methods. The choice between these methods depends on whether you expect a result set. Let us first understand these methods:
ExecuteSqlRaw
- The ExecuteSqlRaw method in EF Core executes raw SQL commands or stored procedures that perform data manipulation operations (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) or execute commands without returning entities. Parameters are passed separately to prevent SQL injection.
- Return Type: Returns the number of rows affected.
ExecuteSqlInterpolated
- The ExecuteSqlInterpolated method is similar to ExecuteSqlRaw, but it does not return data. It uses interpolated strings for safer parameter handling. It is preferred over ExecuteSqlRaw when using user inputs or dynamic parameters.
- Return Type: Returns the number of rows affected.
FromSqlRaw
- The FromSqlRaw method in EF Core executes raw SQL queries or stored procedures that return data, mapping the results to entity types. It is ideal for retrieving data that maps directly to entities.
- Return Type: Returns an IQueryable<TEntity>, allowing further querying or enumeration.
FromSqlInterpolated
- The FromSqlInterpolated method returns data similar to FromSqlRaw, but it uses interpolated strings for safer parameter handling. It is preferred over FromSqlRaw when using user inputs or dynamic parameters.
- Return Type: Returns an IQueryable<TEntity>.
Note: ExecuteSqlRaw and ExecuteSqlInterpolated are Used for commands that do not return data (e.g., INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). On the other hand, FromSqlRaw and FromSqlInterpolated are used for queries that return data and map results to entity types.
Example to Understand Calling Stored Procedure with EF Core:
In Entity Framework Core (EF Core), we can work with stored procedures to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on our database. Let us see how to perform each of these operations using stored procedures in EF Core:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.Data;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Initialize sample student data
var student1 = new Student
{
FirstName = "Pranaya",
LastName = "Rout",
Branch = "CSE",
Gender = "Male"
};
var student2 = new Student
{
FirstName = "Hina",
LastName = "Sharma",
Branch = "CSE",
Gender = "Female"
};
// Add new students to the database
int id1 = AddStudent(student1);
Console.WriteLine($"Newly Added Student Id: {id1}");
int id2 = AddStudent(student2);
Console.WriteLine($"Newly Added Student Id: {id2}");
// Retrieve a single student by ID
var retrievedStudent = GetStudentById(id1);
if (retrievedStudent != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("\nRetrieved Student by Id {id1}:");
Console.WriteLine($"Id: {retrievedStudent.StudentId}, Name: {retrievedStudent.FirstName} {retrievedStudent.LastName}, Branch: {retrievedStudent.Branch}, Gender: {retrievedStudent.Gender}");
}
// Retrieve all students
var allStudents = GetAllStudents();
Console.WriteLine("\nAll Students:");
foreach (var student in allStudents)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Id: {student.StudentId}, Name: {student.FirstName} {student.LastName}, Branch: {student.Branch}, Gender: {student.Gender}");
}
// Update an existing student
if (retrievedStudent != null)
{
retrievedStudent.FirstName = "Prateek";
retrievedStudent.LastName = "Sahoo";
UpdateStudent(retrievedStudent);
// Retrieve updated student
var updatedStudent = GetStudentById(retrievedStudent.StudentId);
Console.WriteLine("After Update:");
Console.WriteLine($"Id: {updatedStudent?.StudentId}, Name: {updatedStudent?.FirstName} {updatedStudent?.LastName}, Branch: {updatedStudent?.Branch}, Gender: {updatedStudent?.Gender}");
}
// Delete a student
if (id2 > 0)
{
DeleteStudent(id2);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Adds a new student to the database using the spInsertStudent stored procedure.
public static int AddStudent(Student student)
{
int newStudentId = 0;
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Define parameters for the stored procedure
//Input Parameter
var firstNameParam = new SqlParameter("@FirstName", student.FirstName);
var lastNameParam = new SqlParameter("@LastName", student.LastName);
var branchParam = new SqlParameter("@Branch", student.Branch) ;
var genderParam = new SqlParameter("@Gender", student.Gender);
//Output Parameter
var studentIdOutParam = new SqlParameter
{
ParameterName = "@StudentId",
SqlDbType = SqlDbType.Int,
Direction = ParameterDirection.Output
};
// Execute the stored procedure
context.Database.ExecuteSqlRaw(
"EXEC spInsertStudent @FirstName, @LastName, @Branch, @Gender, @StudentId OUTPUT",
firstNameParam, lastNameParam, branchParam, genderParam, studentIdOutParam
);
// Retrieve the output parameter value
newStudentId = (int)studentIdOutParam.Value;
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database AddStudent Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"AddStudent Error: {ex.Message}");
}
return newStudentId;
}
// Retrieves a single student by StudentId using the spGetStudentByStudentId stored procedure.
public static Student? GetStudentById(int studentId)
{
Student? student = null;
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Define parameter for the stored procedure
var studentIdParam = new SqlParameter("@StudentId", studentId);
// Execute the stored procedure and map the result to the Student entity
// Execute the non-composable part of the query first using FromSqlRaw and
// materialize the results by calling ToList, ToArray, or AsEnumerable to ensure the data is retrieved from the database
student = context.Students
.FromSqlRaw("EXEC spGetStudentByStudentId @StudentId", studentIdParam)
.AsEnumerable()
.FirstOrDefault();
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database GetStudentById Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"GetStudentById Error: {ex.Message}");
}
return student;
}
// Retrieves all students using the spGetAllStudents stored procedure.
public static List<Student> GetAllStudents()
{
var students = new List<Student>();
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Execute the stored procedure and map results to the Student entity
students = context.Students
.FromSqlRaw("EXEC spGetAllStudents")
.AsNoTracking() // Optional: No tracking for read-only operations
.ToList();
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database GetAllStudents Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"GetAllStudents Error: {ex.Message}");
}
return students;
}
//Updates an existing student using the spUpdateStudent stored procedure.
public static void UpdateStudent(Student student)
{
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Define parameters for the stored procedure
var studentIdParam = new SqlParameter("@StudentId", student.StudentId);
var firstNameParam = new SqlParameter("@FirstName", student.FirstName);
var lastNameParam = new SqlParameter("@LastName", student.LastName);
var branchParam = new SqlParameter("@Branch", student.Branch);
var genderParam = new SqlParameter("@Gender", student.Gender);
// Execute the stored procedure
int rowsAffected = context.Database.ExecuteSqlRaw(
"EXEC spUpdateStudent @StudentId, @FirstName, @LastName, @Branch, @Gender",
studentIdParam, firstNameParam, lastNameParam, branchParam, genderParam
);
// Output the result
if (rowsAffected > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nStudent with ID {student.StudentId} successfully updated.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nNo student found with ID {student.StudentId} to update.");
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database UpdateStudent Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"UpdateStudent Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Deletes a student by StudentId using the spDeleteStudent stored procedure.
public static void DeleteStudent(int studentId)
{
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Define parameter for the stored procedure
var studentIdParam = new SqlParameter("@StudentId", studentId);
// Execute the stored procedure
int rowsAffected = context.Database.ExecuteSqlRaw("EXEC spDeleteStudent @StudentId", studentIdParam);
// Output the result
if (rowsAffected > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nStudent with ID {studentId} successfully deleted.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nNo student found with ID {studentId} to delete.");
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database DeleteStudent Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"DeleteStudent Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Output:

Example Using ExecuteSqlInterpolated and FromSqlInterpolated Methods in EF Core
Microsoft recommends using ExecuteSqlInterpolated and FromSqlInterpolated for safer parameter handling, especially when dealing with user input. These methods prevent SQL injection by automatically parameterizing inputs.
In our previous example, we used the ExecuteSqlRaw and FromSqlRaw methods to call the Stored Procedures. To call the Stored Procedures, let us rewrite the same example using ExecuteSqlInterpolated and FromSqlInterpolated Methods in EF Core. For a better understanding, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.Data;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Initialize sample student data
var student1 = new Student
{
FirstName = "Pranaya",
LastName = "Rout",
Branch = "CSE",
Gender = "Male"
};
var student2 = new Student
{
FirstName = "Hina",
LastName = "Sharma",
Branch = "CSE",
Gender = "Female"
};
// Add new students to the database using ExecuteSqlInterpolated
int id1 = AddStudent(student1);
Console.WriteLine($"Newly Added Student Id: {id1}");
int id2 = AddStudent(student2);
Console.WriteLine($"Newly Added Student Id: {id2}");
// Retrieve a single student by ID using FromSqlInterpolated
var retrievedStudent = GetStudentById(id1);
if (retrievedStudent != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nRetrieved Student by Id {id1}:");
Console.WriteLine($"Id: {retrievedStudent.StudentId}, Name: {retrievedStudent.FirstName} {retrievedStudent.LastName}, Branch: {retrievedStudent.Branch}, Gender: {retrievedStudent.Gender}");
}
// Retrieve all students using FromSqlInterpolated
var allStudents = GetAllStudents();
Console.WriteLine("\nAll Students:");
foreach (var student in allStudents)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Id: {student.StudentId}, Name: {student.FirstName} {student.LastName}, Branch: {student.Branch}, Gender: {student.Gender}");
}
// Update an existing student using ExecuteSqlInterpolated
if (retrievedStudent != null)
{
retrievedStudent.FirstName = "Prateek";
retrievedStudent.LastName = "Sahoo";
UpdateStudent(retrievedStudent);
// Retrieve updated student
var updatedStudent = GetStudentById(retrievedStudent.StudentId);
Console.WriteLine("After Update:");
Console.WriteLine($"Id: {updatedStudent?.StudentId}, Name: {updatedStudent?.FirstName} {updatedStudent?.LastName}, Branch: {updatedStudent?.Branch}, Gender: {updatedStudent?.Gender}");
}
// Delete a student using ExecuteSqlInterpolated
if (id2 > 0)
{
DeleteStudent(id2);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
/// Adds a new student to the database using the spInsertStudent stored procedure with ExecuteSqlInterpolated.
public static int AddStudent(Student student)
{
int newStudentId = 0;
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
var StudentIdOutParam = new SqlParameter
{
ParameterName = "StudentId",
SqlDbType = SqlDbType.Int,
Direction = ParameterDirection.Output
};
// Execute the stored procedure using ExecuteSqlInterpolated for automatic parameterization
int NumberOfRowsAffected = context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolated($@"
EXEC spInsertStudent
@FirstName = {student.FirstName},
@LastName = {student.LastName},
@Branch = {student.Branch},
@Gender = {student.Gender},
@StudentId = {StudentIdOutParam} OUTPUT"
);
if (NumberOfRowsAffected > 0)
{
// Retrieve the value of the OUT parameter
newStudentId = (int)StudentIdOutParam.Value;
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database AddStudent Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"AddStudent Error: {ex.Message}");
}
return newStudentId;
}
// Retrieves a single student by StudentId using the spGetStudentByStudentId stored procedure with FromSqlInterpolated.
public static Student? GetStudentById(int studentId)
{
Student? student = null;
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Execute the stored procedure using FromSqlInterpolated for automatic parameterization
student = context.Students
.FromSqlInterpolated($@"
EXEC spGetStudentByStudentId
@StudentId = {studentId}")
.AsNoTracking() // No Tracking
.AsEnumerable() // Materialize the results by calling ToList, ToArray, or AsEnumerable to ensure the data is retrieved from the database
.FirstOrDefault();
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database GetStudentById Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"GetStudentById Error: {ex.Message}");
}
return student;
}
// Retrieves all students using the spGetAllStudents stored procedure with FromSqlInterpolated.
public static List<Student> GetAllStudents()
{
var students = new List<Student>();
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Execute the stored procedure using FromSqlInterpolated
students = context.Students
.FromSqlInterpolated($@"
EXEC spGetAllStudents")
.AsNoTracking() // Optional: No tracking for read-only operations
.ToList();
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database GetAllStudents Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"GetAllStudents Error: {ex.Message}");
}
return students;
}
// Updates an existing student using the spUpdateStudent stored procedure with ExecuteSqlInterpolated.
public static void UpdateStudent(Student student)
{
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Execute the stored procedure using ExecuteSqlInterpolated for automatic parameterization
int rowsAffected = context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolated($@"
EXEC spUpdateStudent
@StudentId = {student.StudentId},
@FirstName = {student.FirstName},
@LastName = {student.LastName},
@Branch = {student.Branch},
@Gender = {student.Gender}"
);
// Output the result
if (rowsAffected > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nStudent with ID {student.StudentId} successfully updated.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nNo student found with ID {student.StudentId} to update.");
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database UpdateStudent Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"UpdateStudent Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Deletes a student by StudentId using the spDeleteStudent stored procedure with ExecuteSqlInterpolated.
public static void DeleteStudent(int studentId)
{
try
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Execute the stored procedure using ExecuteSqlInterpolated for automatic parameterization
int rowsAffected = context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolated($@"
EXEC spDeleteStudent
@StudentId = {studentId}"
);
// Output the result
if (rowsAffected > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nStudent with ID {studentId} successfully deleted.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nNo student found with ID {studentId} to delete.");
}
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database DeleteStudent Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"DeleteStudent Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Before executing the application, clear all the data from the Students table by executing the TRUNCATE Table Statement below.
TRUNCATE TABLE Students;
Now, run the application, and you should see the following output:

ExecuteSqlRaw vs. ExecuteSqlInterpolated in EF Core
Both ExecuteSqlRaw and ExecuteSqlInterpolated are methods EF Core provides to execute raw SQL commands against the database. The key difference lies in how they handle parameterization and prevent SQL injection.
ExecuteSqlRaw
This method executes a raw SQL command with parameters specified separately. We need to manually create SqlParameter objects for any parameters used in the SQL command.
- Parameters are passed separately.
- Requires manual handling of SqlParameter objects.
- There is a higher risk of SQL injection if parameters are concatenated into the SQL string.
- Slightly faster due to less overhead.
ExecuteSqlInterpolated
This method executes a raw SQL command using string interpolation, where EF Core automatically handles parameterization. Parameters are embedded directly into the interpolated string, and EF Core ensures they are safely parameterized.
- Uses string interpolation for parameters.
- EF Core automatically parameterizes inputs, reducing SQL injection risks.
- It is more convenient and leads to cleaner code.
- Preferred when using user inputs or dynamic parameters.
In the next article, I will discuss Entity Framework Core (EF Core) Inheritance (TPH, TPT, and TPC) with Examples. In this article, I try to explain Stored Procedures in Entity Framework Core with Examples. I hope you enjoyed this Stored Procedures in EF Core article.
