Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Required Attribute in Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss the Required Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing NotMapped Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples.
What is the Required Attribute in Entity Framework Core?
The Required Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core can be applied to one or more properties of an entity class. If we apply the Required Attribute to a Property, Entity Framework will create a NOT NULL column for that Property in the database. A NOT NULL Column means the database will not accept a NULL Value.
By applying this attribute, we can also enforce validation on the model properties at both the application and database levels. If you go to the definition of the Required Data Annotation Attribute definition, you will see the following signature.

The Required Attribute belongs to the System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations namespace. This class has one parameterless constructor, one property, AllowEmptyStrings, and one overridden method, IsValid.
- Constructor: Initializes the RequiredAttribute with a default error message used if validation fails.
- Property AllowEmptyStrings: This property allows the developer to specify whether empty strings should be considered valid when applying the RequiredAttribute. It has no Impact on the database schema and will be part of Model validation only.
- Method IsValid: Performs validation by ensuring the value is not null.
Default Entity Framework Core Behavior (Nullable and Non-nullable Columns)
By default, when we define a property as a nullable type (e.g., string?, int?, bool?, etc.), EF Core will generate a NULL column for that property. EF Core will generate a NOT NULL column in the database if we define the property without a ? (e.g., string, int, bool, etc.).
Let us first understand this default Entity Framework Core behavior and then see how to use the Required Data Annotation Attribute. First, modify the Student.cs entity class file as follows. As you can see, we have created the Student Entity with four properties: two integer properties and two string properties.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; } // This will create a NOT NULL column
public string? Name { get; set; } // This will create a NULL column
public string? Address { get; set; } // This will create a NULL column
public int RollNumber { get; set; } // This will create a NOT NULL column
}
}
Explanation:
- StudentId and RollNumber: Since these are non-nullable value types (integers), EF Core will generate NOT NULL columns for these fields.
- Name and Address: As these are nullable reference types (because of the ?), EF Core will create NULL columns for these fields in the database.
Modifying the Context Class:
Next, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows. As you can see, we have registered the Student model class within the context class using the DbSet property.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EFCoreDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
Generation Migration:
Now, open Package Manager Console and Execute Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows:
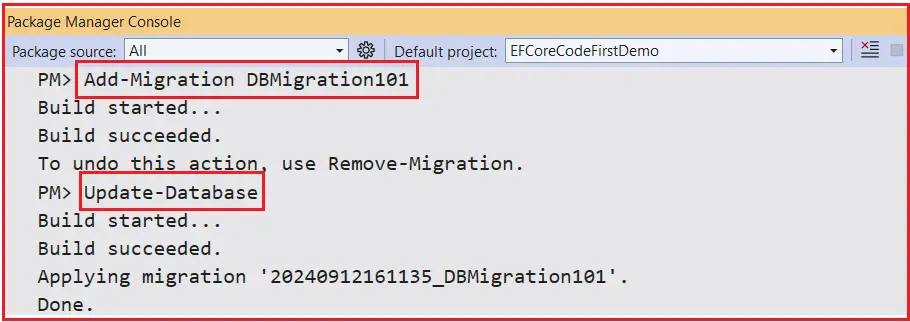
Now, verify the database. You will see NOT NULL columns for StudentId and RollNumber and NULL columns for Address and Name, as shown in the image below.

How to make the Name Column a NOT NULL Column?
Now, what is our requirement, we need to accept a NULL value for the Address column, but we do not want to accept NULL Value for the Name column. To enforce that the Name property should be NOT NULL, we can either:
- Remove the ? from the property definition.
- Use the [Required] attribute.
Let’s modify the Student entity to make the Name column as a NOT NULL column using the [Required] attribute. So, modify the Student.cs class file as follows. By applying the [Required] attribute, EF Core will apply the NOT NULL constraint on the Name column in the database. The Address property is still marked as nullable (string?), so it will remain a NULL column.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; } // This will create a NOT NULL column
[Required]
public string? Name { get; set; } // Name is now NOT NULL due to Required Attribute
public string? Address { get; set; } // This will create a NULL column
public int RollNumber { get; set; } // This will create a NOT NULL column
}
}
Generating Migration and Syncing with Database:
Now, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands. Once you execute the commands, verify the Students table. You will see that the Name column is created using the NOT NULL constraint, as shown in the below image.

Testing the Required Attribute:
Now, let us test the Required attribute by inserting a Student object without providing a value for the Name property. If we attempt to save an entity that violates any of the Required constraints (for example, if you try to save a Student entity without a Name), EF Core will throw a DbUpdateException.
So, please modify the Program class as shown below. As you can see, we are not providing any value for the Name property, and hence, it will take the default value NULL, and when we call the SaveChanges method, it will throw a runtime exception.
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Attempting to add a student without a name...");
// Creating a Student object without setting the Name property
Student student = new Student
{
Address = "123 Main St",
RollNumber = 101
};
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Adding the student to the context
context.Add(student);
// Attempting to save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Student added successfully.");
}
catch (DbUpdateException dbEx)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Update Error: {dbEx.InnerException?.Message ?? dbEx.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Output:

Note: If there are any database-related issues, such as saving a NULL value where it’s not allowed, the DbUpdateException is thrown, and the detailed error message is displayed in its inner exception property.
What happens if we store an Empty String in the Not Null Column:
By default, the Required attribute in Entity Framework Core ensures that a property is NOT NULL but does not automatically validate empty strings for string properties. So, let us try to create a student with Name as an Empty. To better understand, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Attempting to add a student with an empty name...");
// Creating a Student object with an empty Name
Student student = new Student
{
Name = string.Empty, // Empty string is allowed
Address = "456 Main St",
RollNumber = 102
};
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Adding the student to the context
context.Add(student);
// Attempting to save changes to the database
context.SaveChanges();
Console.WriteLine("Student added successfully with an empty name.");
}
catch (DbUpdateException dbEx)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {dbEx.InnerException?.Message ?? dbEx.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Output:

How Do We Restrict Empty Strings in NOT NULL Properties?
Let us modify the Student Entity class as follows to use Required Attribute with AllowEmptyStrings property and let us set its value to false.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; } // This will create a NOT NULL column
// Allows empty strings, but disallows NULL
[Required(AllowEmptyStrings = false)]
public string? Name { get; set; } // Name is now NOT NULL due to Required Attribute
public string? Address { get; set; } // This will create a NULL column
public int RollNumber { get; set; } // This will create a NOT NULL column
}
}
Next, generate the Migration, Update the database, and rerun the application. You will still see that the application accepts the empty string.
Why AllowEmptyStrings is not working to restrict empty strings:
This is because the AllowEmptyStrings does not impact the database schema. This property only provides validation to model properties. We will discuss this concept in detail in our ASP.NET Core MVC and Web API sessions, where we will get the data from the client and validate the data in our application.
When Should We Use the Required Attribute in EF Core?
The Required attribute should be used to ensure data integrity at the database level for any property that should not accept NULL values. The following are some of the Common scenarios:
- You want to ensure a property always contains a value.
- When you want to enforce NOT NULL constraints at the database level.
- The application logic requires a field always to be populated (e.g., a name or an ID that should never be missing).
- When establishing a relationship that must not be null, ensure that the foreign key property is not nullable.
In the next article, I will discuss the MaxLength and MinLength Attributes in Entity Framework Core with Examples. In this article, I explain the Required Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples. I hope you enjoyed this article on the Required Attribute in EF Core with Examples.
