Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing the Non-Primary Key Table and Identity Column in EF Core using Fluent API with Examples.
Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core
Asynchronous programming enables applications to handle multiple tasks concurrently without blocking the main execution thread. When combined with Entity Framework Core (EF Core), asynchronous programming can significantly enhance the performance, scalability, and responsiveness of .NET applications. Now, I will explore asynchronous programming and its benefits with EF Core and present a real-time example of implementing asynchronous CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in a .NET Console Application.
What is Asynchronous Programming?
Asynchronous programming is a programming approach that allows a program to perform tasks concurrently without blocking the main execution thread. When we execute a method asynchronously, it runs in the background, allowing the application to continue with other work instead of waiting for that method to finish. When the work is complete, it notifies the main thread about its completion, failure, or progress. This is important for improving applications’ performance, responsiveness, and scalability, especially when dealing with I/O-bound operations such as database Calls, File I/O, or external API calls.
Why Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core?
Asynchronous programming is highly beneficial when dealing with database operations that are inherently time-consuming, particularly for applications where performance, scalability, and responsiveness are important.
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) supports asynchronous operations to enhance performance, responsiveness, and scalability. By default, database operations (e.g., queries, inserts, updates, deletes) are I/O-bound operations and can benefit significantly from asynchronous programming.
- Prevent Blocking the Main Thread: Asynchronous programming prevents the main thread from blocking, allowing it to handle concurrent requests.
- Improved User Experience: Asynchronous database operations can help keep the user interface responsive, which is important for any user-facing application.
- Scalable Applications: With async operations, servers can handle more requests since threads aren’t held up by database operations, making the application scalable.
- Non-Blocking Operations: Prevents the application from freezing or becoming unresponsive during database operations.
How Do We Implement Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core?
Entity Framework Core provides several asynchronous methods to interact with databases, such as:
- ToListAsync()
- FindAsync()
- AddAsync()
- SaveChangesAsync()
- FirstOrDefaultAsync()
- SingleOrDefaultAsync()
These methods are equivalent to their synchronous versions but run asynchronously. The key difference is that they return a Task or Task<T> object, allowing the code to continue executing without waiting for the database operation to complete. To implement asynchronous programming in EF Core, we need to follow the below steps:
- Use async and await: Mark methods with the async keyword and use await when calling asynchronous methods.
- Use Asynchronous Methods: Use the asynchronous versions of EF Core methods (e.g., SaveChangesAsync, FindAsync, ToListAsync).
- Return Task-Based Results: Methods should return Task or Task<T> instead of void or the direct result.
Real-Time Example of Asynchronous CRUD Operations with Entity Framework
Let’s create a simple console application to manage a Product entity using EF Core with asynchronous methods. In this example, I will cover how to perform Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations asynchronously.
Define the Entity Class
In this example, we will use a Product entity. So, create a new class file named Product.cs within the Entities folder and then copy and paste the following code:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Product
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(100)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[MaxLength(500)]
public string Description { get; set; }
[Required]
[Column(TypeName ="decimal(18,2)")]
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
}
Define the DbContext
Create a Context class that inherits from DbContext. This class will manage the database operations. So, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Configuring the Connection String
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=ProductDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
}
}
Generating the Migration and Creating the Database:
Open the Package Manager Console and execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows.
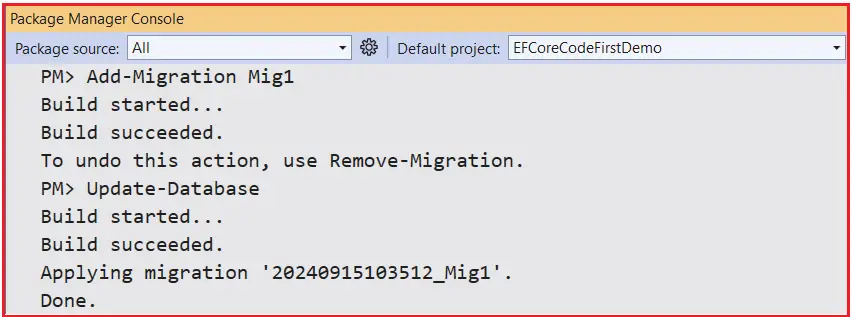
Once you execute the above commands, it should create the database with the Required Products table, as shown in the below image:
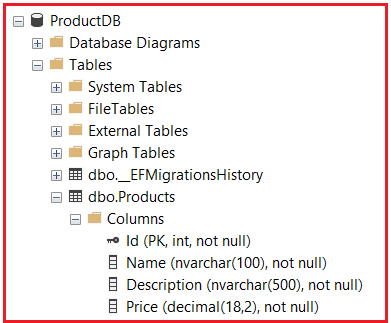
Implement Asynchronous CRUD Operations using EF Core.
Now that the database is set up let’s implement asynchronous CRUD operations in the Program.cs file using Entity Framework core. So, modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Create a DbContext instance for the database interaction, using 'await using' to ensure proper disposal after the operations are completed
await using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
await CreateProductAsync(context);
await ReadProductsAsync(context);
await UpdateProductAsync(context);
await DeleteProductAsync(context);
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
// Handle database update exceptions
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error Occurred: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle any other exceptions
Console.WriteLine($"Error Occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Asynchronous method for creating products in the database
private static async Task CreateProductAsync(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Check if products already exist, this ensures we don't insert duplicates
if (context.Products.Any())
return;
// Define two new products
var product1 = new Product
{
Name = "Laptop",
Description = "A high-performance laptop",
Price = 1200.00m
};
var product2 = new Product
{
Name = "Desktop",
Description = "A high-performance Desktop",
Price = 1500.00m
};
// Add products asynchronously to the DbSet
await context.Products.AddAsync(product1);
await context.Products.AddAsync(product2);
// Save the changes asynchronously to the database
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Products Added Successfully.\n");
}
// Asynchronous method for reading all products from the database
private static async Task ReadProductsAsync(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Fetch the list of all products asynchronously
var products = await context.Products.ToListAsync();
// Display each product's details
Console.WriteLine("Products in database:");
foreach (var product in products)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\tProduct Id: {product.Id}, Name: {product.Name}, Price: ${product.Price}");
}
}
// Asynchronous method for updating the price and description of a specific product
private static async Task UpdateProductAsync(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Find the first product with the name "Laptop" asynchronously
var product = await context.Products.FirstOrDefaultAsync(prd => prd.Name == "Laptop");
if (product != null)
{
// Update the product's price and description
product.Price += 100.00m;
product.Description = "A high-performance laptop with Core i7 Processor";
// Save changes to the database asynchronously
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
Console.WriteLine("\nProduct with Name 'Laptop' Price and Description Updated.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nProduct with Name 'Laptop' not found.\n");
}
}
// Asynchronous method for deleting a specific product by Id
private static async Task DeleteProductAsync(EFCoreDbContext context)
{
// Find the product with ID 1 asynchronously
var product = await context.Products.FindAsync(1);
if (product != null)
{
// Remove the product from the context
// No RemoveAsync Method available
context.Products.Remove(product);
// Save changes to the database asynchronously
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
Console.WriteLine("\nProduct with ID 1 deleted.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nProduct with ID 1 not found.\n");
}
}
}
}
Understanding Each Asynchronous CRUD Operation Method:
CreateProductAsync:
This method is used to create new products in the database asynchronously. The following things are happening with this method:
- First, it checks if any products exist in the database (context.Products.Any()).
- If the product list is empty, it creates two new Product instances (product1 and product2).
- The method then adds these products to the database using AddAsync(), ensuring non-blocking execution.
- Finally, it saves the changes to the database using SaveChangesAsync(), which commits the transaction to the database in an asynchronous manner.
ReadProductsAsync:
The method retrieves and displays all products from the database asynchronously. The following things are happening with this method:
- It retrieves all products from the database by asynchronously querying the Products table with ToListAsync().
- The products are then printed out, displaying their ID, name, and price. This is useful to see the current state of the data in the database without blocking the Main Thread.
UpdateProductAsync:
This method is used to update the details (price and description) of a product based on its name asynchronously. The following things are happening with this method:
- It searches for the first product in the database with the name “Laptop” using FirstOrDefaultAsync().
- If the product is found, the method updates its Price and Description fields.
- The changes are then saved asynchronously with SaveChangesAsync().
- If no product is found with the name “Laptop”, it prints a message indicating that no matching product was found.
DeleteProductAsync:
The method is used to delete a specific product (by ID) from the database asynchronously. The following things are happening inside this method:
- It looks for a product with ID 1 using FindAsync().
- If a matching product is found, the product is removed from the context using the Remove() method.
- It then commits the deletion to the database using SaveChangesAsync().
- If the product is not found, it prints a message indicating that no product with ID 1 was found.
Now run the application, and you should see the following:

When Should We Use Asynchronous Programming with EF Core?
Asynchronous programming with EF Core is beneficial in the following scenarios:
- Web Applications: In web applications where multiple concurrent requests are being processed, async operations can help ensure that threads are not blocked, allowing for more efficient request handling.
- Time-Consuming Database Queries: If your database operations are slow or take more time to complete, asynchronous operations can help keep your application responsive.
- Scalable Backends: Async programming can help improve scalability for backend services that need to handle many simultaneous requests.
However, asynchronous programming is not always necessary. Using synchronous methods might perform better for small applications, CPU-bound operations, or scenarios where the database response time is minimal, as async programming can add overhead in certain situations.
Conclusion:
Asynchronous programming with Entity Framework Core provides a way to make database operations non-blocking, improving your application’s responsiveness and scalability. By using asynchronous methods like ToListAsync(), AddAsync(), SaveChangesAsync(), etc., we ensure that the main thread remains free to handle other tasks.
In the next article, I will discuss Bulk Operations in Entity Framework Core with Examples. In this article, I will try to explain Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core with examples. I hope you enjoyed this article on Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core.

Very good learning material, explained in a very easy example to understand. Thank you sir.