Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
MaxLength and MinLength Attribute in Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss MaxLength and MinLength Data Annotation Attributes in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing the Required Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples.
What is MaxLength Attribute in Entity Framework Core?
The MaxLength attribute in Entity Framework Core is a Data Annotation Attribute used to specify the maximum allowable length of array or string data allowed in a property. This attribute serves two primary purposes:
- Database Schema Configuration: When we apply the MaxLength attribute to a property, EF Core sets the maximum size of the corresponding column in the database schema. For example, if you set MaxLength(50) on a string property, the generated database column will be configured to hold a maximum of 50 characters.
- Data Validation: It enforces validation rules at the model level, ensuring that the data inserted into the database does not exceed the specified length. If the data exceeds the maximum length, an exception will be thrown.
What is MinLength Attribute in Entity Framework Core?
The MinLength attribute in Entity Framework Core is a data annotation attribute used to specify the minimum length of array or string data that must be present in the property for the model to be considered valid.
Unlike MaxLength, the MinLength attribute does not affect the database schema. In this case, it will set the size of the corresponding database table column to the max. This attribute is primarily used for model validation. For example, [MinLength(3)] requires the string to be at least three characters long to pass validation checks in the application layer.
Example to Understand MaxLength and MinLength Attribute in EF Core
Let us understand the default convention with an example, and then we will see how to use MinLength and MaxLength Data Annotation Attributes in EF Core.
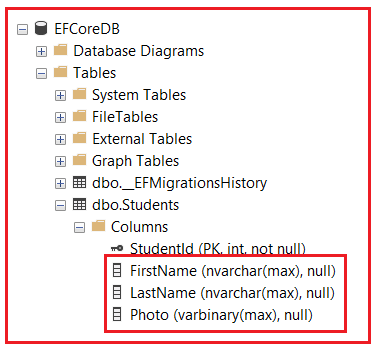
Please modify the Student Entity as follows. Here, we have created the Student Entity with four properties. One Integer Property, two string properties, and one byte[] property. In this case, for string properties, the corresponding database column will be set as nvarchar(max). For the byte[] property, it will set the corresponding database column as varbinary(max).
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
public string? LastName { get; set; }
public byte[]? Photo { get; set; }
}
}
Next, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as shown below. As you can see, we have registered the Student model within the context class using DbSet.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EFCoreDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
With the above changes, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows. You can give your migration any name. Here, I am giving it DBMig1. The name you are giving it should not be given earlier.

If you check the Students database table, you will see that the corresponding database columns with the maximum size are created, as shown in the image below.
How to Set the Max Length and Min Length in EF Core?
We can set the maximum and minimum lengths in our model class using the MaxLength and MinLength data annotation Attributes. Now, we need to provide some restrictions on the data that we are going to store in the database. Our requirement is that the maximum length for the First Name value is 50 Characters, and the minimum length for the Last Name value is 5 Characters.
So, modify the Student Entity Class as follows. We have applied the MaxLength(50) Data Annotation Attribute on the FirstName Property, which will also set the corresponding database column length as 50. If we enter the FirstName value of more than 50 characters, it will throw an exception.
Then, we applied the MinLength(5) Data Annotation Attribute with the LastName Property, which will throw an exception if we enter a value of less than five characters at the time of model validation. It does not have any impact on the database. For the MinLength Attribute, Entity Framework will set the maximum length of the corresponding database column.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(50)]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
[MinLength(5)]
public string? LastName { get; set; }
}
}
With the above changes, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands. Once you execute the commands, verify the database. You will see that the FirstName column will be created with size 50, and the LastName column will be created with size max, as shown in the image below.

Testing the Application:
Next, modify the Program class as follows. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Initialize the DbContext (using a 'using' statement ensures proper resource disposal)
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Display an informative message for user input
Console.WriteLine("Please enter the student information:");
// Capture the student's first name
Console.Write("First Name (Max 50 characters): ");
string? firstName = Console.ReadLine();
// Capture the student's last name
Console.Write("Last Name (Min 5 characters): ");
string? lastName = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
// Validate the Student entity manually before saving to ensure it meets constraints
var student = new Student
{
FirstName = firstName,
LastName = lastName
};
// Perform validation using the DataAnnotationsValidator
ValidateStudent(student); // This method will throw an exception if validation fails
// If validation passes, add the student to the DbSet and save changes to the database
context.Students.Add(student);
context.SaveChanges();
// Inform the user that the data has been successfully saved
Console.WriteLine("Student information has been saved successfully!");
}
catch (ValidationException ex) // Catch validation errors (MaxLength, MinLength, etc.)
{
// Display the validation error message to the user
Console.WriteLine($"Validation error: {ex.Message}");
}
catch (DbUpdateException dbEx) // Catch any database update errors
{
// Handle potential database errors and provide a meaningful message
Console.WriteLine($"Database update error: {dbEx.InnerException?.Message ?? dbEx.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex) // Catch any other general exceptions
{
// Display a general error message
Console.WriteLine($"An error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
// Output the list of all students to show the saved records
var students = context.Students.ToList();
Console.WriteLine("\nList of Students in Database:");
foreach (var stud in students)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Student ID: {stud.StudentId}, First Name: {stud.FirstName}, Last Name: {stud.LastName}");
}
}
}
// Custom method to perform validation on the Student entity
public static void ValidateStudent(Student student)
{
// Create a ValidationContext object.
// This object contains information about the object being validated (student in this case).
// It is used by the Validator to perform validation according to the attributes (like MaxLength, MinLength) applied on the Student entity.
// The 'null' values are placeholders for services or items that could be used by the ValidationContext (we don’t need them here, hence null).
var validationContext = new ValidationContext(student, null, null);
// Create a list to hold the results of the validation.
// Each item in this list will be a ValidationResult,
// which will contain information about any validation errors that occur.
var validationResults = new List<ValidationResult>();
// TryValidateObject is a method from the Validator class that checks if the given object (student)
// satisfies the validation rules specified by the data annotations (MaxLength, MinLength, etc.).
// - The 'true' flag at the end ensures that all properties of the object (student) are validated.
// - If validation fails, the validation errors are added to the 'validationResults' list.
if (!Validator.TryValidateObject(student, validationContext, validationResults, true))
{
// If validation results contain errors (i.e., TryValidateObject returns false),
// throw a ValidationException to indicate that validation failed.
// We extract the first validation error from the 'validationResults' list and use its error message.
throw new ValidationException(validationResults.First().ErrorMessage);
}
// If no validation errors occur, the method simply completes, allowing the caller to proceed without error.
}
}
}
With Valid Data:

With Invalid Data:

How Can We Set the MaxLength and MinLength Attributes in a Single Property?
We need to apply both attributes on the same property to set both maximum and minimum lengths on a single property. Each attribute enforces its respective constraint independently. For example, we need to set the maximum length of the student’s first name to 10 characters and the minimum length for the student’s first name to 5 characters. Then, we need to use both MaxLength and MinLength Attributes in the FirstName property of the Student Entity, as follows:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(10)]
[MinLength(5)]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
public string? LastName { get; set; }
}
}
In this case, FirstName must be between 5 and 10 characters long. The MaxLength constraint is enforced at the database level, while the MinLength is usually enforced at the application level (e.g., during model validation.
When to Use MaxLength and MinLength Attributes in Entity Framework Core
The MaxLength and MinLength attributes serve important roles in various scenarios:
- Data Validation: These attributes help ensure that data meets expected size limits before it is processed or stored in the database. Defining constraints helps prevent data-related errors and reduces the risk of accepting invalid or malicious inputs.
- Database Schema Configuration: The MaxLength attribute directly influences the database column definitions. This is especially important for optimizing database performance and storage, as it controls the maximum data size stored in specific columns, like VARCHAR or NVARCHAR fields.
- Client-Side Validation: In applications that use frameworks supporting data annotations (such as ASP.NET or ASP.NET Core), MaxLength and MinLength attributes can automatically enforce validation on the client side. This provides users with instant feedback and improves user experience by preventing invalid data submission before it reaches the server.
In the next article, I will discuss DatabaseGenerated Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples. In this article, I try to explain the MaxLength and MinLength Data Annotation Attributes in Entity Framework Core with Examples. I hope you enjoyed this article’s MaxLength and MinLength Attribute in EF Core with Examples.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
