Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Bulk Operations in Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss Bulk Operations (Bulk Insert, Update, and Delete) in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. Please read our previous article on Asynchronous Programming with Entity Framework Core.
Why Bulk Operations?
When working with databases, applications often need to handle large volumes of data efficiently. Performing operations like inserting, updating, or deleting multiple records individually can lead to significant performance bottlenecks due to the overhead of multiple database round trips. Bulk operations address this by allowing multiple records to be processed in a single database round trip, enhancing performance and scalability. Bulk operations optimize this process by:
- Reducing Round Trips: Sending multiple records in a single batch.
- Minimizing Overhead: Avoiding the overhead of change tracking for individual entities.
- Ensuring Consistency: Wrapping operations in a single transaction to maintain data integrity.
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) provides mechanisms to handle bulk operations, but understanding how these operations work under the hood can help you optimize your application’s performance.
Bulk Operations with Standard Entity Framework Core Methods?
EF Core offers some support for bulk operations through command batching, which reduces the number of database round trips by grouping multiple SQL commands into one batch. However, it does not natively provide true bulk operations where a single SQL statement affects multiple rows (e.g., INSERT INTO … SELECT, UPDATE … WHERE, or DELETE … WHERE). Instead, EF Core employs command batching to improve performance by grouping multiple SQL commands into a single database round trip.
What is Command Batching in EF Core?
Command Batching allows EF Core to send multiple SQL commands to the database in a single round trip. This reduces the number of database round trips and improves performance compared to executing each command individually. For example, EF Core can batch these insert commands together when inserting multiple records, minimizing the communication overhead with the database.
How EF Core Generates and Executes Queries During Bulk Operations
When using methods like AddRange, UpdateRange, or RemoveRange, EF Core tracks changes to entities. Upon calling SaveChanges() or SaveChangesAsync(), EF Core generates the necessary SQL commands to apply those changes:
- Bulk Insert (MERGE Statement): EF Core uses the MERGE statement to insert multiple entities efficiently. This statement combines the insertions into a single SQL command, reducing database round trips and improving performance. The MERGE statement is available in EF Core 7.0 and later.
- Bulk Update (Individual UPDATE Statements): EF Core generates individual UPDATE statements for each entity being updated. These statements are batched together to minimize database interactions.
- Bulk Delete (Individual DELETE Statements): Similar to updates, EF Core generates individual DELETE statements for each entity to be deleted, batching them together for efficiency.
Using External Libraries for Enhanced Bulk Operations
While EF Core’s command batching improves performance, it may not be optimal for handling very large datasets due to the generation of individual SQL statements for each entity during updates and deletes. To achieve fully optimized bulk operations that can handle thousands of records efficiently with a single SQL command, external libraries such as EFCore.BulkExtensions or Z.EntityFramework.Extensions can be integrated with EF Core. These libraries provide set-based SQL commands (e.g., BULK INSERT, MERGE, or bulk UPDATE/DELETE) to perform bulk operations in a single SQL statement, significantly improving performance for large datasets.
Example to Understand Bulk Insert, Update, and Delete Operations in EF Core:
Let’s understand how Entity Framework Core (EF Core) performs Bulk Operations with a few examples. In this article, I will show you how to use the EF core Bulk Operations method, and in our upcoming article, I will show you how to use external libraries. Let’s start by defining a simple Student entity and setting up our DbContext.
Student Entity
To demonstrate how to perform bulk operations using Entity Framework Core (EF Core), we will use the following Student Entity. Create a class file named Student.cs and add the following code. We define the Student entity with properties StudentId, FirstName, LastName, and Branch.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; } = string.Empty; // Ensure non-null values
public string LastName { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string Branch { get; set; } = string.Empty;
}
}
EFCoreDbContext
Next, create the EFCoreDbContext class, inheriting from DbContext, and configure it to use SQL Server and log generated SQL statements. So, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Log the SQL queries to the console
optionsBuilder.LogTo(Console.WriteLine, LogLevel.Information);
// Set up SQL Server with the appropriate connection string
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EFCoreDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
Generating Migration and Updating Database
After setting up the Student entity and EFCoreDbContext, we need to create the database and apply migrations. So, open the Package Manager Console and execute the following commands:
- Add-Migration Mig1
- Update-Database
This will create the Students table in the EFCoreDB database.
Bulk Insert in Entity Framework Core
Bulk Insert efficiently inserts multiple records into a database table. In EF Core, the AddRange or AddRangeAsync methods add a collection of entities at once. Upon calling SaveChanges() or SaveChangesAsync(), EF Core generates optimized SQL commands to insert all entities in a single database round trip. For a better understanding, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Step 1: Create a list of new students to insert
List<Student> newStudents = new List<Student>()
{
new Student() { FirstName = "Pranaya", LastName = "Rout", Branch = "CSE" },
new Student() { FirstName = "Hina", LastName = "Sharma", Branch = "CSE" },
new Student() { FirstName = "Anurag", LastName = "Mohanty", Branch = "CSE" },
new Student() { FirstName = "Prity", LastName = "Tiwary", Branch = "ETC" }
};
// Step 2: Perform a bulk insert of the students
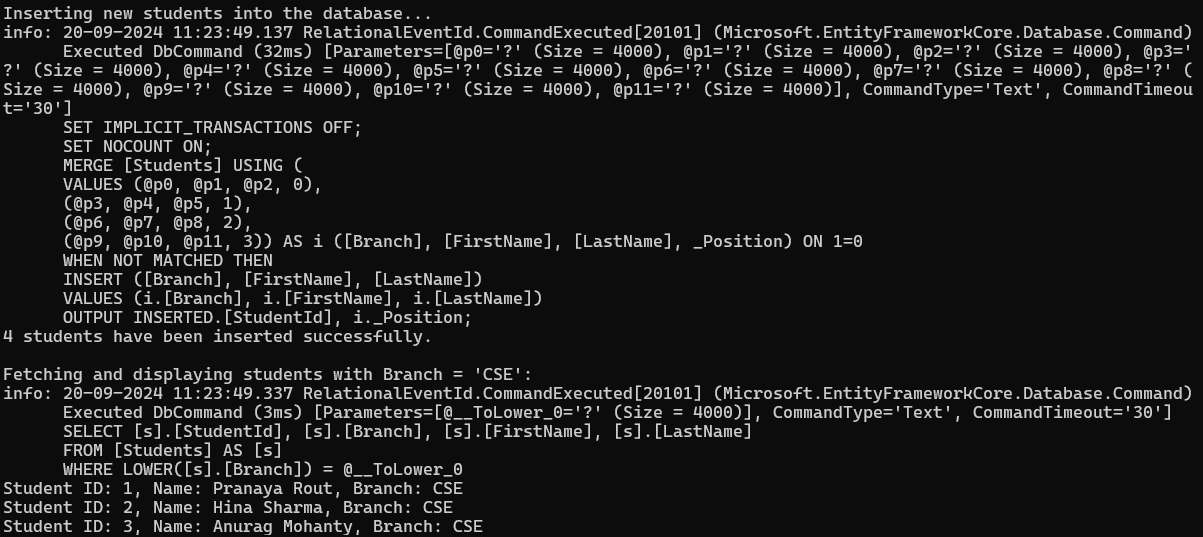
Console.WriteLine("Inserting new students into the database...");
BulkInsert(newStudents);
// Step 3: Display students with the branch "CSE"
Console.WriteLine("\nFetching and displaying students with Branch = 'CSE':");
GetStudents("CSE");
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Method to perform bulk insert operation
public static void BulkInsert(IList<Student> newStudents)
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Add the list of students to the context
context.Students.AddRange(newStudents);
// Save changes to the database (generates MERGE statement)
context.SaveChanges();
// Confirm successful insertion
Console.WriteLine($"{newStudents.Count} students have been inserted successfully.");
}
}
// Method to fetch and display students based on their branch
public static void GetStudents(string branch)
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Fetch students with the specified branch (case-insensitive)
var studentsList = context.Students
.Where(std => EF.Functions.Like(std.Branch, branch))
.ToList();
// Display fetched students or notify if none are found
if (studentsList.Any())
{
foreach (var student in studentsList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Student ID: {student.StudentId}, Name: {student.FirstName} {student.LastName}, Branch: {student.Branch}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch.");
}
}
}
}
}
Explanations:
- AddRange Method: Adds multiple entities to the context in one operation.
- SaveChanges Method: This method commits all changes to the database and generates a MERGE statement for bulk inserts in EF Core 7.0+.
- EF.Functions.Like: Used for case-insensitive searches (more efficient and reliable than ToLower() comparisons).
EF Core generates a single MERGE statement to insert all new student records efficiently after running the application. The console output will confirm the number of students inserted and display the inserted students in the “CSE” branch. Now, run the application, and you should see the following output:
Bulk Update in Entity Framework Core:
Bulk Update involves modifying multiple records in the database efficiently. In EF Core, this is typically done by fetching the relevant entities, updating their properties, and calling SaveChanges(), which generates individual UPDATE statements batched together. For a better understanding, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Step 1: Perform a bulk update for students in the "CSE" branch
Console.WriteLine("Updating all students with Branch = 'CSE'...");
BulkUpdate("CSE");
// Step 2: Display the updated students in the "CSE" branch
Console.WriteLine("\nFetching and displaying updated students with Branch = 'CSE':");
GetStudents("CSE");
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Method to perform bulk update of students based on their branch
public static void BulkUpdate(string branch)
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Fetch students with the specified branch
var studentsList = context.Students
.Where(std => EF.Functions.Like(std.Branch, branch))
.ToList();
// Check if any students were found before updating
if (studentsList.Any())
{
// Update properties for each student
foreach (var student in studentsList)
{
student.FirstName += "Changed";
student.LastName += "Changed";
}
// Save changes to the database (generates individual UPDATE statements)
context.SaveChanges();
// Confirm successful update
Console.WriteLine($"{studentsList.Count} students have been updated successfully.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch to update.");
}
}
}
// Method to fetch and display students based on their branch
public static void GetStudents(string branch)
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Fetch students with the specified branch (case-insensitive)
var studentsList = context.Students
.Where(std => EF.Functions.Like(std.Branch, branch))
.ToList();
// Display fetched students or notify if none are found
if (studentsList.Any())
{
foreach (var student in studentsList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Student ID: {student.StudentId}, Name: {student.FirstName} {student.LastName}, Branch: {student.Branch}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch.");
}
}
}
}
}
Explanations:
- Fetching Entities: Retrieves all students in the specified branch.
- Updating Properties: Modifies the FirstName and LastName of each fetched student.
- SaveChanges Method: Commits all updates, generating individual UPDATE statements batched together.
Now, run the application, and you should see the following output:

Performance Considerations:
EF Core generates individual UPDATE SQL statements for each entity but batches them together to send in a single round trip. While batching reduces the number of round trips, generating individual UPDATE statements for each entity can be inefficient for large datasets. To handle thousands of records, consider using external libraries like EFCore.BulkExtensions or Z.EntityFramework.Extensions for more efficient bulk updates.
Bulk Delete in Entity Framework Core:
Bulk Delete involves efficiently removing multiple records from the database. In EF Core, this is typically achieved by fetching the entities to be deleted, marking them for deletion using RemoveRange, and calling SaveChanges(), which generates individual DELETE statements batched together. For a better understanding, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Step 1: Perform bulk delete for students in the "CSE" branch
Console.WriteLine("Deleting all students with Branch = 'CSE'...");
BulkDelete("CSE");
// Step 2: Attempt to fetch and display students in the "CSE" branch post-deletion
Console.WriteLine("\nFetching students with Branch = 'CSE' after deletion attempt:");
GetStudents("CSE");
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Method to perform bulk delete of students based on their branch
public static void BulkDelete(string branch)
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Fetch students with the specified branch
var studentsList = context.Students
.Where(std => EF.Functions.Like(std.Branch, branch))
.ToList();
// Check if any students were found before deleting
if (studentsList.Any())
{
// Remove the fetched students from the context
context.Students.RemoveRange(studentsList);
// Save changes to the database (generates individual DELETE statements)
context.SaveChanges();
// Confirm successful deletion
Console.WriteLine($"{studentsList.Count} students with Branch = '{branch}' have been deleted.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch to delete.");
}
}
// Method to fetch and display students based on their branch
public static void GetStudents(string branch)
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Fetch students with the specified branch (case-insensitive)
var studentsList = context.Students
.Where(std => EF.Functions.Like(std.Branch, branch))
.ToList();
// Display fetched students or notify if none are found
if (studentsList.Any())
{
foreach (var student in studentsList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Student ID: {student.StudentId}, Name: {student.FirstName} {student.LastName}, Branch: {student.Branch}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch.");
}
}
}
}
Explanations:
- RemoveRange Method: Marks multiple entities for deletion in one operation.
- SaveChanges Method: Commits all deletions, generating individual DELETE statements batched together.
Now, run the application, and you should see the following output:

Performance Considerations:
Like bulk updates, generating individual DELETE statements can be inefficient for large datasets. For optimal performance with large volumes, consider using external libraries that support true bulk deletes with set-based SQL commands.
Asynchronous Bulk Operations with EF Core:
Asynchronous operations enhance application responsiveness and scalability by allowing tasks to run without blocking the main thread. EF Core provides asynchronous methods like AddRangeAsync, SaveChangesAsync, ToListAsync, and RemoveRangeAsync to perform bulk operations asynchronously. Let us see how to perform asynchronous bulk operations in Entity Framework core. So, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Step 1: Perform a bulk insert of students asynchronously
Console.WriteLine("Inserting students into the database asynchronously...");
await BulkInsertAsync();
// Step 2: Perform a bulk update of students asynchronously
Console.WriteLine("\nUpdating students in the 'CSE' branch asynchronously...");
await BulkUpdateAsync("CSE");
// Step 3: Perform a bulk delete of students asynchronously
Console.WriteLine("\nDeleting students in the 'CSE' branch asynchronously...");
await BulkDeleteAsync("CSE");
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Method to perform bulk insert asynchronously
public static async Task BulkInsertAsync()
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Create a list of new students to insert
var newStudents = new List<Student>
{
new Student() { FirstName = "John", LastName = "Doe", Branch = "CSE" },
new Student() { FirstName = "Jane", LastName = "Smith", Branch = "CSE" },
new Student() { FirstName = "Mark", LastName = "Johnson", Branch = "CSE" },
new Student() { FirstName = "Sara", LastName = "Connor", Branch = "IT" }
};
// Asynchronously add the list of students to the context
await context.Students.AddRangeAsync(newStudents);
// Asynchronously save changes to the database
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Confirm successful insertion
Console.WriteLine($"{newStudents.Count} students have been inserted successfully.");
}
// Method to perform bulk update asynchronously
public static async Task BulkUpdateAsync(string branch)
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Asynchronously fetch students from the specified branch
var studentsList = await context.Students
.Where(s => EF.Functions.Like(s.Branch, branch))
.ToListAsync();
if (studentsList.Any())
{
// Update properties for each student
foreach (var student in studentsList)
{
student.FirstName += "Updated";
student.LastName += "Updated";
}
// Asynchronously save updated student details to the database
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Confirm successful update
Console.WriteLine($"{studentsList.Count} students in the '{branch}' branch have been updated successfully.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch to update.");
}
}
// Method to perform bulk delete asynchronously
public static async Task BulkDeleteAsync(string branch)
{
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Asynchronously fetch students from the specified branch
var studentsList = await context.Students
.Where(s => EF.Functions.Like(s.Branch, branch))
.ToListAsync();
if (studentsList.Any())
{
// Mark the fetched students for deletion
context.Students.RemoveRange(studentsList);
// Asynchronously save changes to the database
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Confirm successful deletion
Console.WriteLine($"{studentsList.Count} students in the '{branch}' branch have been deleted.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"No students found in the '{branch}' branch to delete.");
}
}
}
}
Asynchronous Methods:
- Bulk Insert: We create a list of students and add them to the Students table using AddRangeAsync(). We then use SaveChangesAsync() to commit the bulk insert to the database.
- Bulk Update: We fetch students asynchronously using ToListAsync() from a specific branch. After modifying the FirstName and LastName, we save the changes asynchronously using SaveChangesAsync().
- Bulk Delete: We fetch students asynchronously, then use RemoveRange() to mark them for deletion. Finally, we call SaveChangesAsync() to delete the students from the database asynchronously.
What is the Default Batch size when performing Bulk Operations using EF Core?
Batch Size determines how many SQL statements EF Core sends to the database in a single round trip during bulk operations. Efficient batching can significantly improve performance by reducing the number of network calls. In EF Core, the default maximum batch size for SQL Server is 42 records. EF Core will send up to 42 SQL statements in a single batch when performing operations like Insert, Update, or Delete. For a better understanding, please modify the Program class as follows:
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
List<Student> newStudents = new List<Student>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 200; i++)
{
newStudents.Add(new Student() { FirstName = $"Pranaya-{i}", LastName = $"Rout-{i}", Branch = "CSE" });
}
// Step 2: Perform a bulk insert of the students
Console.WriteLine("Inserting new students into the database...");
BulkInsert(newStudents);
Console.WriteLine("Inserting new students into the database completed...");
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database Error: {ex.InnerException?.Message ?? ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Method to perform bulk insert operation
public static void BulkInsert(IList<Student> newStudents)
{
using (var context = new EFCoreDbContext())
{
// Step 1: Add the list of students to the context
context.Students.AddRange(newStudents);
// Step 2: Save the changes to the database (MERGE statement generated)
context.SaveChanges();
// Output confirmation of successful insertion
Console.WriteLine($"{newStudents.Count} students have been inserted successfully.");
}
}
}
}
Expected Behavior:
- EF Core generates multiple MERGE statements, each containing up to 42 insert operations.
- For 200 records, EF Core will create approximately 5 batches (4 batches of 42 and 1 batch of 32).
- Each batch is sent in a single database round trip, optimizing performance.
Note: The default batch size may vary depending on the database provider. For instance, providers other than SQL Server might have different defaults or handle batching differently.
How Do We Customize the Batch Size in Entity Framework Core?
We can customize the batch size by setting the MaxBatchSize option when configuring DbContext. This can be done in the OnConfiguring method of DbContext or when configuring services in dependency injection. For a better understanding, please modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows to Set Custom Batch Size:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Log the SQL queries to the console
optionsBuilder.LogTo(Console.WriteLine, LogLevel.Information);
string _connectionString = @"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EFCoreDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;";
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(_connectionString, sqlOptions =>
{
sqlOptions.MaxBatchSize(100); // Set the batch size to 100
});
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
Explanations:
- MaxBatchSize Option: Specifies the maximum number of commands in a single batch.
- Setting to 100: Increases the batch size from the default of 42 to 100, allowing more operations per round trip.
Effect of Custom Batch Size:
- Performance: Larger batch sizes can reduce the number of round trips, improving performance for large datasets.
- Memory Usage: Increasing batch size may lead to higher memory consumption during operations.
- Optimal Value: Choose a batch size that balances performance improvements with resource constraints, potentially through performance testing.
After setting MaxBatchSize to 100, running the bulk insert example with 200 students will result in:
- 2 batches of 100 insert operations each.
- Each batch is sent in a single database round trip, further optimizing performance.
Understanding how EF Core handles bulk operations is essential for optimizing application performance when working with large datasets. While EF Core provides mechanisms to improve efficiency through command batching and the MERGE statement for inserts, it may not be sufficient for all scenarios, especially with updates and deletes involving many records. By using external libraries like EFCore.BulkExtensions or Z.EntityFramework.Extensions, we can perform true bulk operations that execute set-based SQL commands, providing significant performance benefits.
In the next article, I will discuss Bulk Operations using Entity Framework Core Extension with Examples for Performance Improvement. In this article, I try to explain Bulk Operations (INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE) using Entity Framework Core with Examples. I hope you enjoyed this article on Bulk Operations using Entity Framework Core.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
