Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Introduction to ASP.NET Core Framework
In this article, I will give you a brief introduction to the ASP.NET Core Framework. Nowadays, when it comes to software development, everyone is talking about Free, Open-Source, and Cross-Platform Development. As we all know, Microsoft is well known for its Windows-based products. Now, we are in a new age of software development. For this, Microsoft introduced a new revolutionary product, ASP.NET Core or .NET.
History of ASP.NET Core
For years, ASP.NET was the go-to framework for building data-driven web applications. Since then, the ASP.NET Framework has undergone steady evolutionary change, and finally, the most decent evolution is ASP.NET Core (you can also call it .NET).
However, ASP.NET Core is not a continuation of the ASP.NET Framework but rather a complete redesign. It represents a significant shift, introducing a more modular, cross-platform framework that can be used to build modern, cloud-based applications.
- ASP.NET Core is not just a continuation of ASP.NET but rather a completely new framework. It’s a rewrite with a more modular design and support for cross-platform development.
- It retains some familiar concepts but introduces fundamental changes, especially in its handling of performance, deployment, and modularity.
What is ASP.NET Core?
ASP.NET Core is a Cross-Platform, Open-Source, High-Performance framework used for building modern, cloud-based, and internet-connected applications that run on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Docker. According to Microsoft:
- ASP.NET Core is the modern, high-performance web development framework for .NET, that runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Docker.
- ASP.NET is a popular web development framework for building web apps on the .NET platform.
- ASP.NET Core is the open-source version of ASP.NET that runs on macOS, Linux, and Windows. It was first released in 2016 and is a redesign of earlier Windows-only versions of ASP.NET.
For more information, visit the official ASP.NET Core page: https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/aspnet/what-is-aspnet-core
Why ASP.NET Core?
Nowadays, the ASP.NET Core framework is becoming more and more popular among developers. There are a number of reasons why developers are using it, and some of them are listed below:
High Performance:
ASP.NET Core is optimized for high performance. Its modular architecture allows developers to include only necessary dependencies, resulting in faster and more efficient applications. Benchmarks demonstrate that applications developed with ASP.NET Core are significantly faster than those built with previous versions of ASP.NET and are ideal for high-traffic, cloud-native applications. For a better understanding, please look at the following image, which is provided on the Official Microsoft Site:
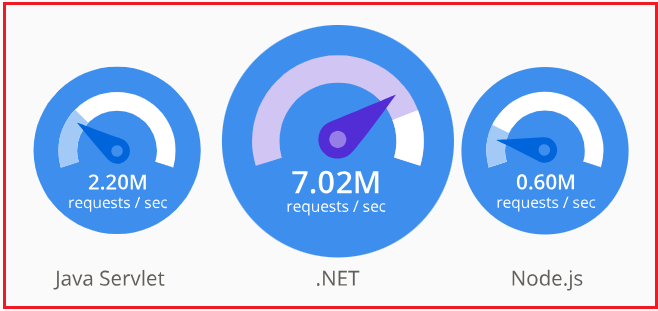
Open Source
ASP.NET Core framework is open-source, which is the main reason for its popularity. The entire source code for ASP.NET Core Framework is available on GitHub at https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore, and allows developers to:
- Download and inspect the source code.
- Modify and customize it as needed.
- Contribute to its development, benefiting from a huge community with over 100,000 contributions from more than 3,700 companies.
All aspects of .NET are open source, including class libraries, runtime, compilers, languages, the ASP.NET Core web framework, Windows desktop frameworks, the Entity Framework Core data access library, and more.
The ASP.NET Core team is always there to support your effort in developing the application. It receives bug fixing and improvement updates on a regular basis, usually within a short time period. You don’t have to wait longer for updates. For more information, visit the official ASP.NET Core page: https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/platform/open-source
Cross-Platform:
The ASP.NET Core Framework is designed from scratch to be Cross-Platform, meaning ASP.NET apps can be developed and run on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Docker. This means we can build applications that run across different operating systems without needing to build different applications for different platforms using different frameworks.
Compared with Traditional ASP.NET Framework, earlier versions of ASP.NET Framework applications can only run on Windows platforms. On the other hand, ASP.NET Core applications can be developed and run on different platforms, such as Windows, Mac, or Linux operating systems. We can host the earlier ASP.NET Framework applications only on IIS, whereas we can host the ASP.NET Core applications on IIS, Nginx, Apache, or within Docker containers.
Lightweight and Modular:
The framework is built to be modular, which allows developers to include only the necessary libraries. This reduces the application’s overall size and improves performance. Dependencies are managed via NuGet packages, making it easy to add or remove features.
Built-in Dependency Injection:
ASP.NET Core includes a built-in dependency injection (DI) container. This feature simplifies the management of service lifetimes and dependencies, leading to more maintainable and testable code.
Cloud-Ready:
ASP.NET Core is designed for cloud deployment. It provides configuration features that simplify deploying and scaling applications in cloud environments like Microsoft Azure.
ASP.NET Core Support Policy and Release Lifecycle:
The latest stable version of .NET Core is .NET 8, released in November 2023. Starting with .NET 5, the term “Core” was removed, and it is now simply called .NET (e.g., .NET 6, .NET 7, .NET 8). Microsoft releases new major versions every year in November, alternating between Long-Term Support (LTS) and Short-Term Support (STS) releases:
- Long-Term Support (LTS) Releases: Even-numbered releases (e.g., .NET 6, .NET 8) are designated as LTS releases. They receive support and patches for three years, making them ideal for production environments.
- Standard-Term Support (STS) Releases: Odd-numbered releases (e.g., .NET 5, .NET 7) receive support and patches for 18 months, suitable for projects that can adopt newer versions more frequently.
For a better understanding, please have a look at the following image:
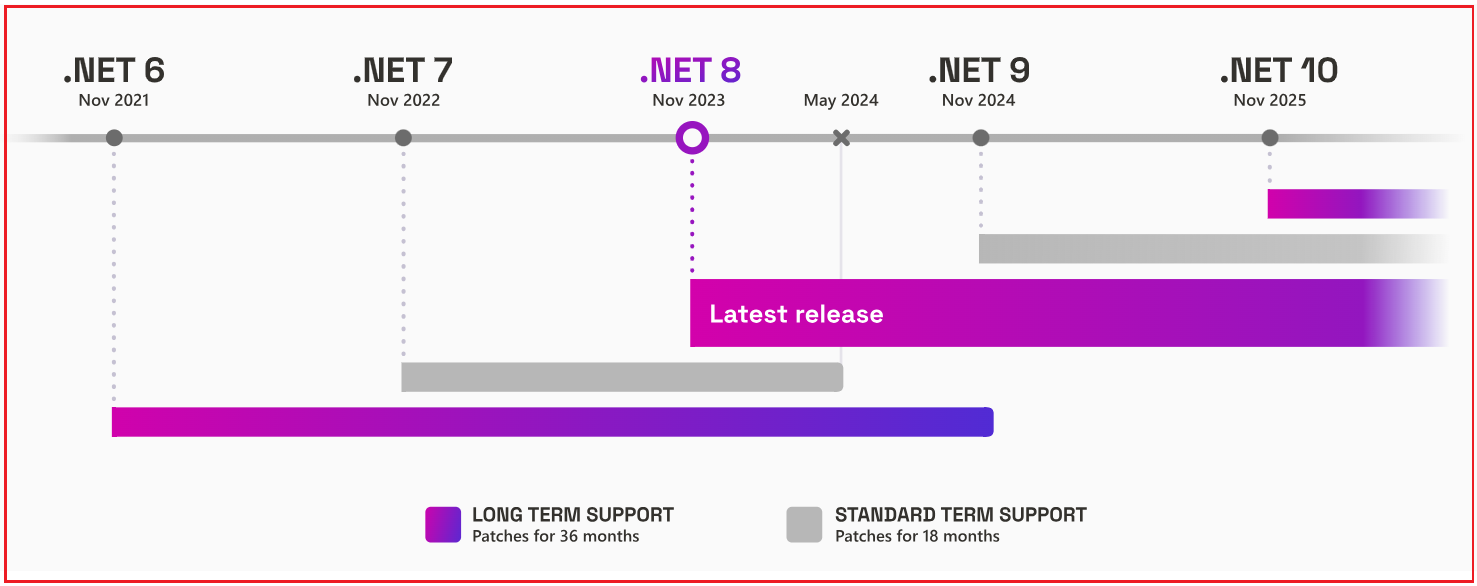
Note: Customers can choose Long Term Support (LTS) releases or Standard Term Support (STS) releases. The quality of all releases is the same. The only difference is the length of support. LTS releases get free support and patches for 3 years. STS releases get free support and patches for 18 months.
For more information, visit the official ASP.NET Core page: https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/platform/support/policy/dotnet-core
What the ASP.NET Core Doesn’t Have?
If you are familiar with ASP.NET, here are some features that are no longer part of ASP.NET Core:
- Global.asax File: This has been replaced by the Program.cs file, which is used to configure the application’s startup process.
- Web.config File: Configuration is now handled using appsettings.json, appsettings.{Environment}.json, environment variables, and other configuration providers.
- HTTP Handlers and HTTP Modules: Replaced by Middleware Components in the ASP.NET Core request pipeline.
Differences Between .NET Framework vs .NET Core Framework
The following are the Differences Between .NET Framework and .NET Core
.NET Framework
- Platform: Designed exclusively for Windows.
- Architecture: Monolithic, including all features by default, leading to larger applications.
- Performance: Does not match the performance optimizations of .NET Core due to its older architecture.
- Support and Development: In maintenance mode with Microsoft primarily releasing security updates and critical fixes; no new features are being added.
- Open Source: It is not open source.
- Use Cases: Ideal for applications tightly integrated with the Windows ecosystem, such as desktop applications, or for maintaining large existing applications built on the .NET Framework.
.NET Core
- Platform: Cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Architecture: Modular, allowing developers to include only necessary packages via NuGet, resulting in lighter and more efficient applications.
- Performance: Optimized for high performance and scalability.
- Support and Development: Actively developed with regular additions of new features, performance improvements, and enhancements.
- Open Source: It is open source and hosted on GitHub with over 100,000 contributions from more than 3,700 companies.
- Use Cases: Perfect for building modern web applications, microservices, and applications requiring cross-platform functionality.
.NET Core (.NET) vs ASP.NET Core:
Many people are confused between ASP.NET Core and .NET Core. Please note that ASP.NET Core and .NET Core are not the same. They are different, just like ASP.NET and .NET Framework are different.
ASP.NET Core is a web framework for building web applications, services, and APIs. .NET Core is the runtime that supports running ASP.NET Core applications. It is also the foundation for other types of applications like console, desktop, and mobile apps (through .NET MAUI). So, .NET Core provides the runtime environment, while ASP.NET Core is the web application framework that runs on it. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following diagram:

.NET Core (.NET):
- .NET Core (.NET) is the cross-platform software. It provides the Runtime Environment where the ASP.NET Core Web Applications will run.
- Install .NET Core Runtime to run applications and install .NET Core SDK to build applications.
- .NET 8 is the latest stable version.
ASP.NET Core:
- ASP.NET Core is an Open-Source, Cross-Platform Framework using which we can develop different types of Web Applications, such as MVC, Web API, Razor Pages, etc.
- If you want to develop and run .NET Core Applications, you need to install the .NET Core SDK, which will automatically install the .NET Runtime. If you only want to run .NET Core Applications, you only need to install the .NET Core Runtime.
- ASP.NET Core 8 is the latest stable version.
Note: ASP.NET Core does not have a separate versioning system; it is the same as the other .NET Core versions.
In the next article, I will discuss the ASP.NET Core Environment Setup Required for Developing ASP.NET Core Web Applications using Visual Studio. In this article, I will try to give a brief introduction to the ASP.NET Core Framework. I hope this Introduction to ASP.NET Core Framework article will help you with your needs.

Thanks to the author of this article. It was awesome
Thanks for this tutorial. Very well explained
i am beginner and now these days i enjoy these tutorials
Thanks, this tutorials help me a lotm very nice article!
Thanks, this tutorials help me a lot very nice article!
very nice article among the top most sites
Thanks
I am beginner and this tutorial very helpful for me . Thanks a lot dotnettutorials.
This tutorial are really amazing.Grateful to the author.
very informative and realistic article
Nice article. I am very happy to read this
Please update to .NET 5
Very soon we are going to update the tutorials using the latest DOT NET Core as well as we are going to finish the course.
This tutorials really help me, very informative and nice article
Thanks you
Great tutorial
Love these tutorials!
EXCELLENT
Great explanation. Thanks
Sometimes you say, ASP.NET is .NET, and other times you say its a framework on top of .NET. Very confusing.
EXAMPLE:
Note: ASP.NET Core was initially launched as ASP.NET 5, but later, it was renamed to ASP.NET Core, and now it is called .NET.
ANOTHER EXAMPLE:
ASP.NET Core:
1. ASP.NET Core is Open Source and Cross Platform Framework.
2. ASP.NET Core is a Web Application Development Framework to build Web Applications, IoT Applications, and Mobile Applications, which is going to be run on the top of the .NET Core Platform. If you are developing an application using ASP.NET Core 1.x or 2.z, then you can run the ASP.NET Core Application using both .NET Framework and .NET Core Platform.
#2 above says ‘ASP.NET Core is a web application development framework……. which is going to be run on the top of the .NET core platform’.
A simple one liner explanation would be great.
.NET Core (.NET) and ASP.NET Core are two different things. .NET Core (.NET) provides the runtime environment where the ASP.NET Core Web Applications are going to be run. ASP.NET Core is the Web Application Development Framework using which you can develop different kinds of Web Applications.
Both .NET Core (.NET) and ASP.NET Core are cross-platform and Open Source.
This article started pretty well but became very confusing at the end with terminologies of .NET,.NET Core,ASP.NET and ASP.NET core. Would like to have more simple explanations.
I actually liked this article but needs a little brush up.