Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Column Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss Column Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. Please read our previous article, discussing the Table Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples.
Column Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core:
The [Column] attribute in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) allows developers to customize how entity class properties are mapped to columns in the database. EF Core follows convention-based mapping by default, but the [Column] attribute can override these defaults. The [Column] attribute is part of the System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema namespace. This attribute can be used to specify important details such as:
- Column Name: Allows mapping a property to a column with a different name.
- Data Type: Maps the property to a specific database provider data type (e.g., DateTime2 in SQL Server).
- Column Order: Specifies the order in which columns are created in the table (note: this is only applicable when the table is first created and is generally not recommended for use with migrations in EF Core).
Default Mapping Behavior in EF Core Without the [Column] Attribute
By default, EF Core uses convention-based mapping, where the column names in the database are the same as the property names, and columns are created in the order in which the properties are defined in the class. So, When the [Column] attribute is not applied:
- Column Names: EF Core uses the property names as column names.
- Column Order: Columns appear in the order they are defined within the class.
- Data Types: EF Core automatically maps .NET types to appropriate database types based on the database provider.
Example:
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
public string? LastName { get; set; }
}
In this example, EF Core will create a table with columns StudentId, FirstName, and LastName in that order, using default data types mapped from their respective .NET types.
Definition of Column Attribute Class in EF Core
The ColumnAttribute class inherits from the abstract Attribute class. Now, if you go to the definition of Column Attribute, then you will see the following.
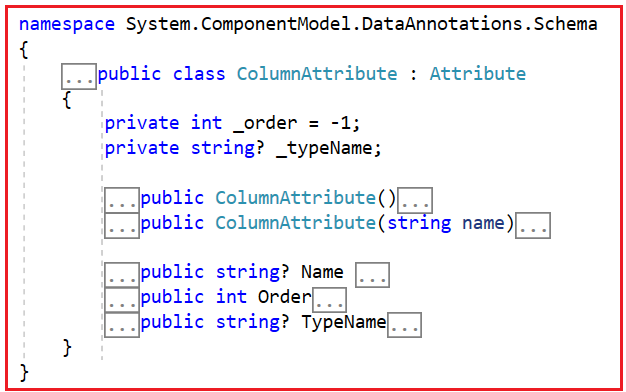
Properties of the Column Attribute in EF Core
The [Column] attribute has three primary properties that developers can configure:
- Name: Specifies the name of the column in the database. By default, EF Core uses the property name as the column name. The Name property allows us to specify a different name if required.
- TypeName: Specifies the database-specific data type for the column. For example, in SQL Server, the DateTime2 data type might be preferred over DateTime for better precision. This is useful when you want more control over how a column is represented in the database.
- Order: Defines the order in which columns appear in the table when it’s first created. The order is zero-based, meaning the first column will have an order of 0, the second column will have an order of 1, and so on. This property only affects the schema during the creation of the table, and it is ignored for updates to existing tables. Defaults to -1, which means EF Core ignores the order.
Constructors of the [Column] Attribute in EF Core
There are two constructors for the [Column] attribute:
- Default Constructor: When no parameters are provided, EF Core uses the property name for the column name, and the default conventions are applied to column order and type.
- Overloaded Constructor (with name parameter): This constructor allows us to explicitly specify a different column name.
Examples to understand Column Data Annotation Attribute in EF Core:
Let us understand the Column Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core with an example. Let us modify the Student Entity class as follows. As you can see, we have specified the Column Attribute with the FirstName and LastName properties. FirstName will map to a column named FirstName, while LastName will map to a column named LName in the database.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
[Table("StudentInfo", Schema = "Admin")]
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
// Default column name will be FirstName
[Column]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
// Column name will be LName in the database
[Column("LName")]
public string? LastName { get; set; }
}
}
Here,
- With the FirstName property, we have not provided the string name, i.e., using the 0-Argument constructor, so in this case, it will create the database table column with the same name as the Property name.
- With the LastName property, we have specified the name as LName, i.e., using the constructor, which takes one string parameter. In this case, it will create the database table column with the name LName, which is mapped to the LastName property.
Migration Process:
As we already discussed, whenever we add or update domain classes or configurations, we need to sync the database with the model using the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands in the Package Manager Console or .NET Core CLI. So, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as shown in the image below. You can give your migration any name. Here, I am giving it Mig3. The name that you are giving it should not be given earlier.
Now, verify the database, and you should see the following. As you can see, the FirstName property is created as FirstName, but the LastName property is created as the LName column in the database, as expected.

Column Data Type in EF Core:
As we see, the Column Attribute class has a property called TypeName, and that TypeName property is used to get or set the data type of a database column. For a better understanding, please modify the Student Entity as follows. Here, you can see that we have set the DateOfBirth column name as DOB and Data type as DateTime2 using the TypeName Property.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
[Table("StudentInfo", Schema = "Admin")]
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
// Default column name will be FirstName
[Column]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
// Column name will be LName in the database
[Column("LName")]
public string? LastName { get; set; }
//This ensures that the DateOfBirth property is stored as DateTime2 in SQL Server,
[Column("DOB", TypeName = "DateTime2")]
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
}
}
So, again, open the Package Manager Console and execute the add-migration and update-database commands as follows as we modify the Student Entity.

Now, if you verify the database, it should create a column with the name DOB and the data type DateTime2 instead of DateTime, as shown in the image below.

Column Order in Entity Framework Core:
The Order property is relevant only when creating a new table. If you’re updating an existing table, the order will be ignored, and you will receive warnings indicating that the order applies only to table creation.
It is a 0-based order, i.e., it will start from 0. As per the default convention, the Primary Key columns will come first, followed by the rest of the columns based on the order we specified in the Column Attribute Order Property.
The most important point you need to remember is that the Order Property of the Column Attribute must be applied to all the properties of an Entity with a different index, starting from zero. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following example.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
[Table("StudentInfo", Schema = "Admin")]
public class Student
{
//Primary Key: Order Must be 0
[Column(Order = 0)]
public int StudentId { get; set; }
// Default column name will be FirstName
[Column(Order = 2)]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
// Column name will be LName in the database
[Column("LName", Order = 4)]
public string? LastName { get; set; }
//This ensures that the DateOfBirth property is stored as DateTime2 in SQL Server
[Column("DOB", Order = 3, TypeName = "DateTime2")]
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
[Column(Order = 1)]
public string? Mobile { get; set; }
}
}
So, again, open the Package Manager Console and execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows as we modify the Student Entity.

Here, you need to observe one thing. We are getting warnings, and the warnings say that Column orders are only used when the table is first created. In our example, we are not creating the table but updating the table structure in the database.
Note: When we apply the Order Property of Column Attribute of an existing Entity, it is ignored.
So, to understand the Order Property of Column Attribute, delete the database and the Migration folder, generate the Migration again, and apply the migration. It should work.
When Should We Use Column Attribute in EF Core?
The [Column] attribute is particularly useful when:
- Custom Column Names: You need to map a property to a column with a name different from the property itself.
- Custom Data Types: You want to specify a specific data type for a column, such as DateTime2, to optimize precision, performance, or compatibility with the database provider.
- New Table Column Order: You want to control the order in which columns appear when a table is first created (though this is generally discouraged).
In the next article, I will discuss the Key Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples. I explain Column Data Annotation Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples in this article. I hope you enjoyed this Column Attribute in the EF Core with Examples article. Please provide your valuable feedback and suggestions for this article.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
