Back to: ASP.NET Core Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Non-Primary Key Table in EF Core using Fluent API
In this article, I will discuss Creating a Table without Primary Key in EF Core using Fluent API with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing Property Configurations using Entity Framework Core Fluent API with Examples.
When Should We Create a Table Without a Primary Key?
In relational databases, it is recommended that every table has a primary key to identify each record uniquely. However, there are scenarios where we might encounter tables without primary keys, especially when dealing with:
- Logging or Audit Data: When storing log entries or application activities, where each entry may be unique, but we don’t need a specific key to identify it. For example, if we log API requests and their response times, we might want to insert log entries quickly without enforcing a unique key constraint.
- Historical Data: When keeping track of historical records, each row is unique based on the timestamp, and no particular column or combination of columns serves as a primary key.
- Read-Only Reference Tables: Sometimes, tables are used just for reference or to hold denormalized data from other sources, such as data from external systems, where we may not need a primary key.
How Do We Create a Table Without a Primary Key in EF Core Using Fluent API?
EF Core typically expects entities to have primary keys for tracking and updating. However, EF Core supports keyless entities primarily used for read-only operations. To create a table without a primary key, we need to tell the DbContext to ignore the primary key requirement. This is a two-step process as follows:
- Define the entity without a primary key. The Entity should not have an Id or EntityName + Id property and don’t specify any property with the Key Attribute.
- Use the Fluent API HasNoKey() in the OnModelCreating method to inform EF Core that the entity is keyless.
Example to Understand Key Less Entity in EF Core Using Fluent API:
Let’s create a real-time example: a Log table that stores application logs without using a primary key using Entity Framework core.
Define the Log Entity
The Log entity will represent a table without a primary key. This table will store log entries, such as API requests, response times, log levels, etc. So, create a class file named ApplicationLog.cs within the Entities folder and copy and paste the following code. You can see that this entity has no property that can be considered a Primary key by default.
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class ApplicationLog
{
public DateTime LoggedAt { get; set; } // Time of the log entry
public string LogLevel { get; set; } // Log level (e.g., Information, Warning, Error)
public string Message { get; set; } // Log message content
}
}
Configure the Entity in the DbContext
We need to configure the ApplicationLog entity in the DbContext class using the Fluent API to specify that it does not have a primary key. So, modify the EFCoreDbContext class as follows. In the OnModelCreating method, we use modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationLog>().HasNoKey() to specify that the Log entity has no primary key.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities
{
public class EFCoreDbContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// Configuring the Connection String
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EFCoreDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;");
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// Configure ApplicationLog entity to have no primary key
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationLog>()
.HasNoKey(); // Specifies that the ApplicationLog entity does not have a primary key
// Optionally map the entity to a specific table name
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationLog>().ToTable("Logs");
}
// DbSet for keyless table
public DbSet<ApplicationLog> ApplicationLogs { get; set; }
}
}
Generating the Migration:
With the above changes, open the Package Manager Console and Execute the Add-Migration and Update-Database commands as follows.
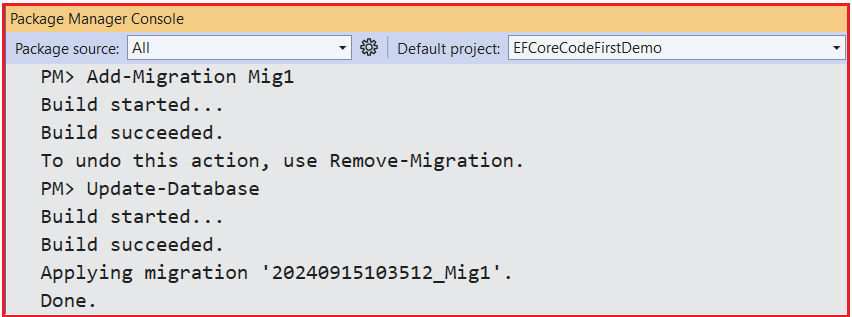
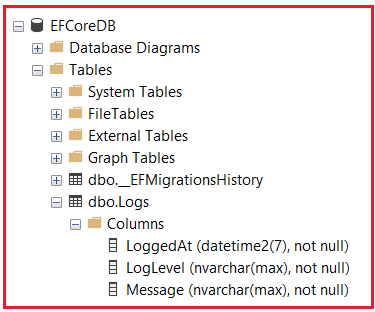
Once you execute the above commands, the database should be created with the Required Logs table. However, as shown in the image below, the Logs table is created without the Primary Key column.
No Tracking for Non-Primary Key Column by Context Class in EF Core:
Since the ApplicationLog entity does not have a primary key, EF Core does not track changes for entities, and it can only be used for read-only operations (queries). That means we can retrieve data using the DbContext object, but we cannot perform insert, update, and delete operations using DbContext as the Entity Framework core does not track it.
Remember that Entity Framework Tracking only works when the Entity has a primary key. To resolve this, we need to use the non-tracking mechanism to insert, update, and delete data. For such operations, we can execute raw SQL commands or Stored Procedures.
Program Class
Now, modify the Program class as follows to store and fetch data from the Logs table. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using EFCoreCodeFirstDemo.Entities;
namespace EFCoreCodeFirstDemo
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create an instance DbContext
using var context = new EFCoreDbContext();
// Ensure the database and tables are deleted
context.Database.EnsureDeleted();
// Ensure the database and tables are created based on the model
context.Database.EnsureCreated();
// Insert sample data using raw SQL since ApplicationLog is keyless
context.Database.ExecuteSqlRaw(@"
INSERT INTO Logs (LoggedAt, LogLevel, Message) VALUES
('2024-04-01 10:00:00', 'INFO', 'Application started.'),
('2024-04-01 10:05:00', 'WARN', 'Low disk space.'),
('2024-04-01 10:10:00', 'ERROR', 'Unhandled exception occurred.')
");
// Query and display the audit logs
var logs = context.ApplicationLogs.ToListAsync().Result;
Console.WriteLine("Application Logs:");
foreach (var log in logs)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{log.LoggedAt} [{log.LogLevel}] {log.Message}");
}
// Example: Update a specific log entry using raw SQL
context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolated($@"
UPDATE Logs
SET Message = 'Disk space critically low.'
WHERE LoggedAt = '2024-04-01 10:05:00'
");
// Example: Delete a specific log entry using raw SQL
context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolated($@"
DELETE FROM Logs
WHERE LoggedAt = '2024-04-01 10:10:00'
");
// Query again to see the updates
logs = context.ApplicationLogs.ToListAsync().Result;
Console.WriteLine("\nUpdated Application Logs:");
foreach (var log in logs)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{log.LoggedAt} [{log.LogLevel}] {log.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Code Explanation:
- Ensure Database Deletion: The EnsureDeleted method checks if the database exists; it will delete the database.
- Ensure Database Creation: The EnsureCreated method checks if the database exists; if not, it creates it along with the necessary tables.
- Insert Data: Use ExecuteSqlRaw to insert three log entries into the Logs table.
- Query Logs: Retrieves and displays all log entries.
- Update a Log Entry: Modifies the message of a specific log entry identified by its LoggedAt.
- Delete a Log Entry: Removes a log entry based on its LoggedAt.
- Query Updated Logs: Retrieves and displays the updated log entries to reflect changes.
Now, run the application, and you should see the following output:

Does EF Core Track Non-Primary Key Entities?
EF Core relies on primary keys to track entities during changes. Without a primary key:
- Change Tracking: EF Core cannot track changes to entities without primary keys.
- CRUD Operations: You cannot use Add(), Update(), or Remove() methods on entities without primary keys.
Note: Starting with EF Core 5.0, entities without keys are known as keyless entities and are intended for read-only query mapping.
Performing Database Operations on a Non-Primary Key Table
Since EF Core doesn’t support direct modifications on keyless entities, you need to:
- Use Raw SQL Commands: Execute SQL commands directly for insert, update, and delete operations.
- Stored Procedures: Call stored procedures if your database logic is encapsulated there.
In the next article, I will discuss How to Perform Asynchronous Operations using Entity Framework Core with Examples. In this article, I explain how to Configure the Non-Primary Key Table in Entity Framework (EF Core) Core using Fluent API with Examples. I hope you enjoyed this article on configuring the Non-Primary key table and identity column in Entity Framework (EF Core) Core using Fluent API.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
