Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Task Parallel Library in C# with Examples (TPL in C#)
In this article, I am going to give you an overview of Parallel Programming and Task Parallel Library in C# with Examples. Please read our previous section articles where we discussed Asynchronous Programming in C#. The Task Parallel Library is also referred to as TPL in C#. At the end of this article, you will understand What Task Parallel Library is and why we need it in C# applications.
Introduction to Parallelism
It is time for us to start talking about parallelism. With parallelism, we can use our processor to perform several actions simultaneously. So, with parallelism, we have the opportunity to improve the speed of certain processes of our programs.
We will start this module by talking about what parallelism is. Later, we will see different tools for parallelization like Parallel.For, Parallel.Foreach and Parallel.Inoke. We will also talk about when not to use parallelism. We will also see concepts such as Atomic Methods, Thread safety, and race conditions. Then we will see mechanisms to integrate race conditions such as interlocked and locks. Finally, we’ll talk about PLINQ (Parallel LINQ)
What is Parallel Programming in C#?
Parallel Programming in C# helps us divide a task into different parts and work those parts simultaneously. An example might be that we have a set of credit cards and we want to process them simultaneously. Or if we have a set of images and we want to apply a series of filters to each one, we can do this by taking the advantage of parallelism.
The main benefit of parallelism is saving time. Time is saved by maximizing the use of computer resources. The idea is that if the computer allows the use of multi-threading, we can use these threads when we have a task to solve. So, instead of underusing our processor using a single thread, we can use as many threads as we can to speed up the processing of the task.
In general, an exception to the benefits of using parallelism using ASP.NET and ASP.NET Core since those scenarios are already parallelized. That is because every thread serves an HTTP request. And therefore, if you have one HTTP request that occupies several threads, then the Web server will have fewer resources to serve other HTTP requests.
In general, we use parallelism in CPU-bound operations, CPU bound operations are those operations whose resolution depends on the processor, not on services external to the application. Doing an arithmetic operation will be an example of a CPU-bound operation. Taking a set of images and applying filters and transformations through them will be another CPU-bound operation.
It is these types of operations, those that are CPU bound, which are candidates for us to use parallelism. It is important to know that parallelism is not always beneficial in terms of performance, since using parallelism has a cost, so we must always make measurements to prove that the cost of parallelism is not greater than not using it. That is sometimes when we use parallelism, the result is a slower application. One reason for this is that when we want to parallelize is very small or doesn’t require enough work for justifying the use of parallelism.
The benefit of parallelism depends on the amount of work to be parallelized. So, Parallel Programming in C# is very important for systems that must process a huge amount of data. For example, on Facebook, approximately two hundred and fifty thousand photos are uploaded per minute. As you can imagine, it takes a lot of power to process such a high volume of information. However, the processors are not getting much faster because of the physical limitations. What is being done then mainly is to include more cores in the processors. In this way, we can take advantage of parallelism to accomplish more tasks in less time.
It is not recommended to occupy several threads for one HTTP request. If you have a long task to do, then it is recommended to use background services or some server technology.
Finally, parallelism shows benefits, if the computer where the program is running has parallelism capabilities. If you try to use parallelism on a computer that cannot use parallelism, then the code will run in sequential. That is, it will not throw any errors, but it will not be faster either. So, the objective is that not all computers can perform parallelism.
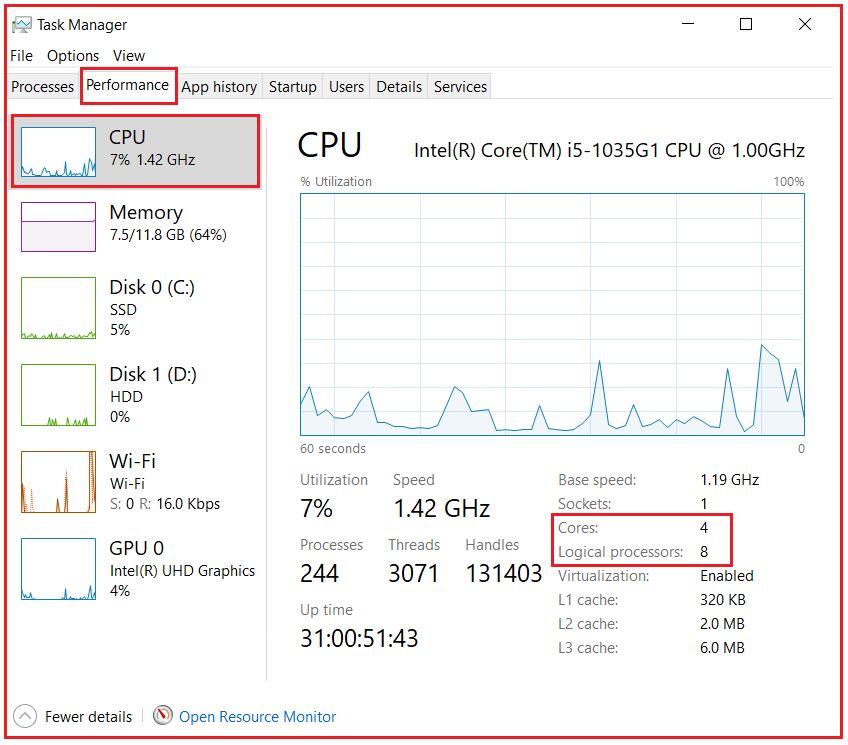
Modern processors are typically multicore. In windows, you can see if your computer is multicore by going to task manager, then selecting the performance tab, and having look at the CPU. Here, you can look at the number of available cores and also have a look at the logical processors. In my case, I have 4 cores and 8 logical processors as shown in the below image. This means that each core can do two operations simultaneously.
In C#, we mainly use two tools to work with parallelism. They are as follows:
- The Task Parallel Library (TPL)
- Parallel LINQ (PLINQ)
The Task Parallel Library is a library that makes life easier for us. When we see parallelism in our programs that TPL (Task Parallel Library) abstracts the low-level detail of thread handling, allowing us to run programs that run parallel without having to work with these threads manually.
On the other hand, PLINQ or Parallel LINQ is an implementation of LINQ that allows us to work in parallel. For example, in LINQ, we can filter the elements of an array. Then with Parallel LINQ, we can filter the same array in parallel. This allows us to use the cores of our processor to perform the evaluations of the elements of the array simultaneously.
Why do we need Task Parallel Library in C#?
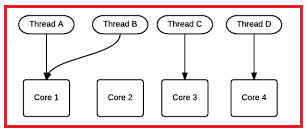
We can’t expect our sequential program to run faster on the new processors as we know the processor technology advances means the focus is on Multicore-processors. Today’s desktop typically has 4 cores but the latest experimental multi-core chips have up to 1000 cores.
So in simple words, we can say that the multicore processor machines are now becoming standard and the aim is to improve the performance by running a program on multiple processors in parallel. So by considering the above scenario, the .NET Framework 4 introduces Task Parallel Library (TPL) that makes it easier for developers to write parallel programs that target multi-core machines (automatically use multiple processors) which improves the performance.
Using the Task Parallel Library (TPL), we can express the parallelism in the existing sequential code, which means we can express the code as a Parallel task, which will be run concurrently on all the available processors.
What is Parallel Programming in C#?
Parallel Programming in C# is a type of programming in which many calculations or the execution of processes are carried out simultaneously. The Points to Remember while working with Parallel Programming:
- The Tasks must be independent.
- The order of the execution does not matter
C# Supports Two Types of Parallelism:
Data Parallelism: In Data Parallelism, we have a collection of values and we want to use the same operation on each of the elements in the collection. The examples will be to filter the elements of an array in parallel or find the inverse of each matrix in a collection. This means each process does the same work on unique and independent pieces of data.
Example:
Task Parallelism: Task Parallelism occurs when we have a set of independent tasks that we want to perform in parallel. An example would be if we want to send an email and SMS to a user, we can perform both operations in parallel if they are independent. This means each process performs a different function or executes different code sections that are independent.
Just because we have the concept of parallelism, that doesn’t mean we should use parallelism. We will see later that there are times when it is better to not use parallelism because in certain cases using parallelism is slower than not using it.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Parallel For Method in C# with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to give you an overview of the Task Parallel Library (TPL) in C#. I hope you enjoy this Parallel Programming in C# article.


Guys,
Please give your valuable feedback. And also, give your suggestions about this Task Parallel Library (TPL) in C# concept. If you have any better examples, you can also put them in the comment section. If you have any key points related to Task Parallel Library (TPL) in C#, you can also share the same.