Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
How Computer Programs Works
In this article, I am going to discuss How Computer Programs Work in detail. Please read our previous article where we give a brief Introduction to Programming Languages. At the end of this article, you will mostly understand what is program and detailed information about Translators.
What is a Program?
We already talked about the program files and data files in our How does the computer work article. Here let us talk about what exactly a program means. A program is just a set of instructions for a computer to perform a specific task. For example, I instruct my computer to open the application, close the application, etc.
Student: Hey Teacher… you said the program is an instruction to a computer and you also said the computer thinks in binary 0’s and 1’s but I am learning here is C# whose syntax is similar to English. I feel awkward about your explanation.
Teacher: Hey wait, I think you are in hurry…! Can you talk with the computer in 0’s and 1’s?
Student: No!
Teacher: Then can you teach machine English?
Student: NO. From your explanations what I understand is the computer can only understand 0’s and 1’s just like me I understand only English.
Teacher: That is why we need compilers and interpreters when we talk with computers.
Example to understand this better:
Teacher: Suppose you have a client from Spain who knows only Spanish and you know only English then how do you interact with them?
Student: I appoint a translator when I had a meeting with a Spain client where he/she could translate for me and vice-versa.
Teacher: Exactly the same thing happens in the case of Computers also. Computers cannot learn our language or we cannot learn the computer language. So, we need a translator who could translate our instructions to the computer and vice versa. Compilers and Interpreters act as a translator here.
What is a Translator?
Always the user’s given instructions are in English, which is called source code. But the computer is not able to understand this source code and the computer’s understandable code is binary / machine. To convert this source code into binary code we are using the interface software called translators.
Translators are system software that converts programming language code into binary format. The translators are classified into three types:
- Compiler
- Interpreter
- Assembler
For a better understanding please have a look at the following image.
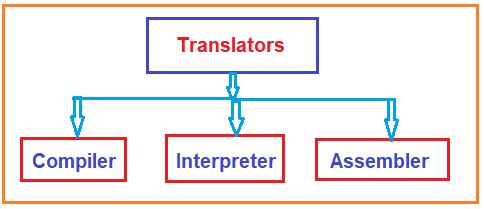
Compiler and interpreter are both used to convert high-level programs to machine code. Assembler is used to convert low-level programs to machine code.
Compiler and Interpreter:
From Definition Compilers and Interpreters transform code written in High-level language (Human understandable language) to Machine Code (Binary code or Machine understandable language). From the Interview Point of View and Exam Point of View, it is important to know the difference between a Compiler and an Interpreter.
Compilers:
The compiler translates High-level code (Source code) to Machine code All at once. Let us take an example: Say you have written a program in a high-level language that does simple arithmetic operations like addition, multiplication, etc. When you give this program to the compiler, the compiler translates all the instructions written in the program into machine code. Then after it gives a full-translated machine code to computers.
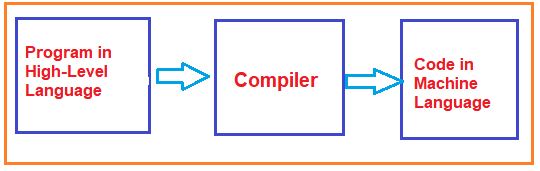
A compiler is the system software that translates High-level programming language code into binary format in a single step except for those lines which are having errors. It checks all kinds of limits, ranges, errors, etc. But its execution time is more and occupies the largest part of the memory.

Advantage: It is faster when compared to the interpreter as the entire translation happens in one go.
Interpreter:
The interpreter translates each High-level instruction to machine code One by one. We can take the above example, which we used, for compilers. When we give the program to the interpreter, it translates the first instruction and generates the machine code, and gives it to the computer. Thereafter second instruction translation goes on until all the instructions were converted to machine code.

It is the system software that converts programming language code into binary format step by step i.e. line by line compilation takes place. It reads one statement and then executes it until it proceeds further to all the statements. If an error occurs it will stop the compilation process.

Advantage: If there is a problem in one instruction then the program will be executed till the previous instruction.
Note: The compiler converts the total source code at once by leaving the error lines. Whereas the interpreter is line by line. C & C++ are compiler-based languages. Java / .Net / Python, etc. are compiler-based interpreted languages. The assembler’s working style is similar to the compiler.
Assembler:
It is the system software that converts assembly language instructions into binary formats.

Difference between Compilers and Interpreters:

Operating System:
An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An Operating system is a software that performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and Printers.
Operating System (OS) is a master program, which uses all available resources of the computer, and provides a service to the end user.
Student: OS is a program? But I never ran the OS or I never instructed the computer to run this master program.
Teacher: Yes, OS is also an instruction maybe you can call it a bunch of instructions to the computer. This is the program that gets autoloaded when you trigger the Switch On button of your PC (which means it is an auto-loaded program).
To run any program or instruction in the main memory or on the computer you need a master program that got loaded to the main memory so that it handles all the resources like HDD, Keyboard monitor, etc. In addition, this program runs in the main memory unless you trigger it to shut down on your computer.
Commonly used OS for PC is Linux, windows, and mac. Commonly used OS for mobile are Android, Windows, and iOS.
Loader:
A loader is a program that loads the machine codes of a program into system memory. And a locator is a program that assigns specific memory addresses for each machine code of a program that is to be loaded into system memory.
Linker:
Usually, a longer program is divided into a number of smaller subprograms called modules. It is easier to develop, test, and debug smaller programs. A linker is a program that links smaller programs to form a single program. The linker links the machine codes of the program. Therefore, it accepts the user’s programs after the editor has edited the program, and the compiler has produced machine codes of the program. The Process is called Linking.
Difference between High-level Program Code and Low-Level Program Code

In the next article, I am going to discuss Different Types of Applications in detail. Here, in this article, I try to explain How Computer Programs Works, and I hope you enjoy this How Computer Programs Works article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.

C, C++, C#, Scala, Java all use complier. PHP, Perl, Ruby uses an interpreter.
Thank you for your great efforts.
You said “Java / .Net / Python, etc. are compiler-based interpreted languages”, well, Java is considered a compiler-based and interpreted-based language, .Net is compiler-based, and Python is interpreter-based.
Thank you!
Keep Going (y)