Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
User Input and Output in C# with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss User Input and Output in C# with Examples. Please read our previous article where we discussed Recursion in C# with Examples. At the end of this article, you will understand how to accept input from the user and display output to the users in the C# Console application.
Console Class in C#
One really useful class that handles input from a user is called the Console class. Console class is present in the “System” namespace. So, first, we import this System namespace into our program. It also converts the Bytes (from the input stream) into characters using the platform’s default charset. To use the Console class, you need to reference it in your code. This is done with the keyword using.
using System;
The using System; statement needs to go just above the Class statement or above namespace: The Syntax is given below.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
Or
namespace FirstProgram
{
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
This tells the C# compiler that you want to use the Console class that is located in the System namespace. This Console class provides a number of built-in methods which we can use the get the user input and also to print output on the Console window. If you go to the definition of Console class then you will see that all the methods and properties are defined as static. That means without creating an object, using the class name only we can access the members of the Console class.
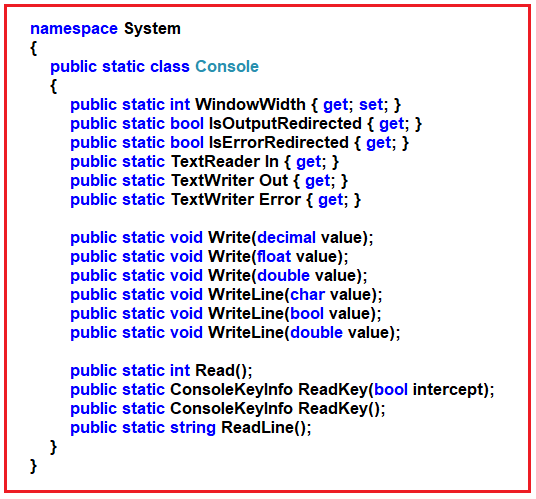
Output in C#:
In order to print something on the console, we can use the following two methods
System.Console.WriteLine();
System.Console.Write();
Here, System is the namespace, Console is the class within the namespace System, and WriteLine and Write are static methods of the Console class. There are many overloaded versions available of the Write and WriteLine methods in the Console. Let us discuss them.
Examples to Print a string on the Console in C#
Let us see a simple example to print a string on the Console window in C#.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}
}
When you run the above code, you will get the following output in the console.
![]()
Difference between WriteLine() and Write() method of Console Class in C#
The main difference between WriteLine() and Write() method of Console Class in C# is that the Write() method only prints the string provided to it, while the WriteLine() method prints the string and moves to the start of the next line as well. Let us see an example to understand the difference between WriteLine() and the Write() method.
Example to understand the use of WriteLine() and Write() method in C#.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Prints on ");
Console.WriteLine("New line");
Console.Write("Prints on ");
Console.Write("Same line");
}
}
}
When you run the above code, you will get the following output in the console.

Printing Variables and Literals using WriteLine() and Write() Method in C#
The WriteLine() and Write() method of the Console class in C# can also be used to print variables and literals. Let us see an example to see how we can use the WriteLine() and Write() methods to print Variables and Literals in C#.
Example Printing Variables and Literals using WriteLine() and Write() Method in C#.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Printing Variable
int number = 10;
Console.WriteLine(number);
// Printing Literal
Console.WriteLine(50.05);
}
}
}
When you run the above code, you will get the following output in the console.
![]()
Combining two strings using the + operator and printing them in C#
Strings can also be combined or concatenated using the + operator while printing inside the WriteLine() and Write() Method in C#. Let us understand this with an example.
Example to Print Concatenated String using + operator in C#
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int number = 55;
Console.WriteLine("Hello " + "C#");
Console.WriteLine("Number = " + number);
}
}
}
When you run the above code, you will get the following output in the console.
![]()
Printing concatenated string using Formatted String in C#
A better alternative for printing concatenated strings is using a formatted string instead of the + Operator in C#. In the case of formatted strings, we need to use placeholders for variables.
For example, The following line,
Console.WriteLine(“Number = ” + number);
can be replaced as,
Console.WriteLine(“Number = {0}”, number);
Here, {0} is the placeholder for the variable number which will be replaced by the value of the number. Since only one variable is used so there is only one placeholder. Multiple variables can be used in the formatted string. That we will see in our example.
Example to Print Concatenated string using String formatting in C#
In the below example, {0} is replaced by number1, {1} is replaced by number2 and {2} is replaced by sum. This approach to printing output is more readable and less error-prone than using the + operator.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int number1 = 15, number2 = 20, sum;
sum = number1 + number2;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", number1, number2, sum);
}
}
}
Output: 15 + 20 = 35
User Input in C#
In C#, the simplest method to get input from the user is by using the ReadLine() method of the Console class. However, Read() and ReadKey() are also available for getting input from the user. They are also included in the Console class. The most important thing is all these three methods are static methods of the Console class, and hence we can call these methods using the class name.
Example to Get String Input from User in C#:
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str;
Console.Write("Enter a string - ");
str = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine($"You entered {str}");
}
}
}
Output:
![]()
Difference between ReadLine(), Read() and ReadKey() methods in C#:
The difference between ReadLine(), Read() and ReadKey() method in C# are as follows:
- ReadLine(): The ReadLine() method of Console class in C# reads the next line of input from the standard input stream. It returns the same string.
- Read(): The Read() method of Console class in C# reads the next character from the standard input stream. It returns the ASCII value of the character.
- ReadKey(): The ReadKey() method of the Console class in C# obtains the next key pressed by the user. This method is usually used to hold the screen until the user press a key.
Following are also the differences that I have taken from Stack Overflow:
ReadKey() (returns a character): reads only one single character from the standard input stream or command line. Usually used when you’re giving options to the user in the console to select from, such as select A, B, or C. Another prominent example is Press Y or n to continue.
ReadLine() (returns a string): or Console.Readline() reads a single line from the standard input stream or the command line. As an example, it can be used to ask the user to enter their name or age. It reads all the characters till we press enter.
Read() (returns an int): or Console.Read() reads only one single character from the standard input stream. Similar to ReadKey except that it returns an integer. It returns the next character from the input stream, or returns (-1) if there is no more character to be read.
Note: The Console.Read() reads only the next character from standard input and Console.ReadLine() reads the next line of characters from the standard input stream. Standard input in the case of Console Application is input from the user typed words in the console UI of your application.
Example to show the Difference between Read() and ReadKey() method in C#
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int userInput;
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("Input using Read() - ");
userInput = Console.Read();
Console.WriteLine("Ascii Value = {0}", userInput);
}
}
}
Output:

From this output, it must be clear how ReadKey() and Read() method works. While using ReadKey(), as soon as the key is pressed, it is displayed on the screen. When Read() is used, it takes a whole line but only returns the ASCII value of the first character. Hence, 104 (ASCII value of h) is printed on the Console.
Reading Integer and floating Numbers (Numeric Values)
In C#, it is very easy to read a character or string. All we need to do is call the corresponding methods as required like Read, ReadKey, and ReadLine. But it is not that straightforward while read the numeric values. Here, we will use the same ReadLine() method we used for getting string values. But since the ReadLine() method receives the input as a string, we need to typecast it into an integer or floating-point type as per our requirement. The simplest approach for converting user input to integer or floating-point type is by using the methods of the Convert class.
Example to Read Numeric Values from User Using Convert class in C#:
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string userInput;
int intVal;
double doubleVal;
Console.Write("Enter integer value: ");
userInput = Console.ReadLine();
// Converts to integer type
intVal = Convert.ToInt32(userInput);
Console.WriteLine("You entered {0}", intVal);
Console.Write("Enter double value: ");
userInput = Console.ReadLine();
// Converts to double type
doubleVal = Convert.ToDouble(userInput);
Console.WriteLine("You entered {0}", doubleVal);
}
}
}
Output:

Note: The ToInt32() and ToDouble() method of the Convert class converts the string input to integer and double type respectively. Similarly, you can convert the input to other types. If you go to the definition of Convert class, then you will find the list of convert methods as shown in the below image.

Another way of Reading Numeric Values in C#:
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Enter integer value: ");
int intVal = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("You entered {0}", intVal);
Console.Write("Enter double value: ");
double doubleVal = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("You entered {0}", doubleVal);
}
}
}
Output:

In the next article, I am going to discuss Command Line Arguments in C# with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain Input and Output in C# with Examples. I hope you enjoy this User Input and Output in C# with Examples article. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.
