Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Introduction to Programming Languages
In this article, I will give a brief Introduction to Programming Languages. Please read our previous article discussing how a computer works and the number system. At the end of this article, you will understand what a language is, computer language, programming languages, why we need a programming language, and what a programmer’s job is. Also, we will discuss software and types of software.
What is a Language?
Generally, languages are used to communicate with others. The languages like Odia / English / Telugu / Hindi are called human/regional languages used to communicate with humans.
A language is nothing but a set of instructions. So generally, if you take English or Hindi, the languages we use to communicate. If we want to communicate with another person, we pass instructions using a particular language. But while using a language, we need to follow some rules or, you can say, a set of instructions. For example, if I want to speak in English, I want to form a sentence to form a sentence. first, we should be grammatically good, or else we cannot.
What is Computer Language?
A computer language is also a set of instructions; in other words, we can say a set of programs that the computer can understand. So, in simple words, we can say that computer language is a formal language used to communicate with a computer.
Why do we need Computer language?
If one person wants to communicate with another, generally, communication means they have to share information, which is nothing but passing instructions. To do so, we use general languages like English, Hindi, Odia, Telegu, etc.
Communicating with the machine is a simple task. If I am asking the question, what are the factorials of five? Everyone can easily answer it as 120. All right, it is a simple calculation. If so, my next question is, what is the factorial of 7? No one can answer because it’s a bit complex operation. This complex operation can be performed very easily by a computer using programs. But the computer only understands the binary language, i.e., 0 and 1. That’s why there is a need for a programming language to communicate with computers.
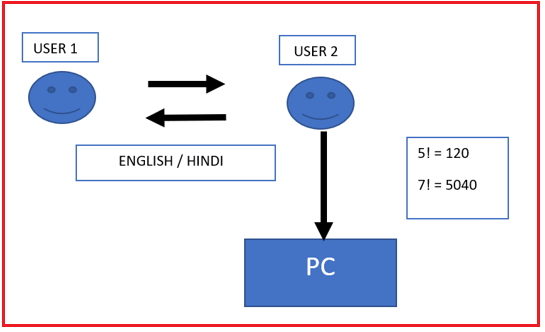
Suppose the person wants to communicate with the computer. In that case, the person needs to pass instructions in the machine code or binary code only, i.e., a computer can understand only machine code or binary code. So that’s why first we have to learn one programming language properly. Many programming languages like C, C++, Java, and C# exist. All these are high-level programming languages.

So, to communicate with Computers, we write programs using any programming language. If you want to communicate with the computer using the C language, first you should learn the C language perfectly. After learning the language, you can write programs. A program means a set of instructions. For example, a equals 10, b equals 20, and c equals a plus b. We are taking two variables, nothing but two values, and adding and printing the result.

Programs get converted by the Compiler and generate machine code. The compiler converts all these instructions into binary language or machine code.

Now, the machine code is ready. So, once the machine code is ready, you can pass it as input to the computer. The computer will produce the output.

This is the process of communication with the computer. Directly, we cannot communicate with the computer. We are communicating with computers to perform complex operations easily.
Imagine the ATM facility is unavailable, and you want to withdraw money from your bank account. How difficult it is, right? So, it is a long process. First, you have to visit the bank, and then you need to do so many processes. And, finally, you will get the money. Suppose if machine availability is there,, i.e. ATM is there, you will get the money within one or two minutes.
So, machines always make our tasks easy, which is the only reason we communicate with machines. Direct communication with the machine/computer is prohibited because we cannot pass instructions in a binary language. First, we have to learn one programming language, and after learning the programming language, we will write programs and then convert the programs into binary instructions using the compiler.
What is an Interface?
It is not always necessary to be a programmer to communicate with machines. An end-user can also communicate with the machine, which is possible using an interface. The interface means without having the background details, we can perform our tasks.
Consider an end user; the end-user wants to perform one ATM transaction, and the end user can communicate using interfaces. For example, if the end-user understands the English language, then the end-user clicks on English. All the instructions will come in English, and operations will be performed.

What is happening in the background is not required for the end user. For example, if you are driving a car and you want to increase the speed of the car, you will accelerate generally. So, the speed will increase whenever we accelerate, but we don’t know what is happening in the background, we don’t know.
We will learn how this interface will communicate with different machines to complete the operations. The End user, whenever entering how much amount he wants to withdraw, is communicating with the server machine, how is communicating with the server machine, by a database machine that the end user does not require.
The end-user leaves the ATM center with the money. For any reason, if the transaction has failed, the end-user directly contacts the bank management, and the bank management contacts the programmer because the programmer provides the interface.
So, as a programmer, we are not communicating with the machines. We are just developing applications, nothing, but we are providing interfaces by which every end-user can easily interact with the machine, and that is our motto.

Types of Computer Languages:
A Programming Language or Computer Language is a language that comprises a set of instructions that is used to communicate with the computer. Programming Language is classified into two types:
- High-Level Programming Language
- Low-level Programming Language
For a better understanding, please have a look at the following image.

What is a Low-level Programming Language?
Low-Level Programming Languages are languages that the system can easily understand. These are system-dependent languages. In these two languages are there i.e.
- Machine Language
- Assembly Language
What is Machine-level language
Machine Language is the system’s fundamental language and can be directly understandable without any translation. These are machine-oriented languages that use the collection of the binary of 1’s and 0’s.
The machine-level language is a language that consists of a set of instructions that are in the binary form 0’s or 1’s. As we know, computers can only understand machine instructions, which are in binary digits, i.e., 0 and 1, so the instructions given to the computer can be only in binary codes.
Creating a program in a machine-level language is very difficult as it is not easy for programmers to write the program in machine instructions. It is error-prone as it is not easy to understand, and its maintenance is also very high.
A machine-level language is not portable as each computer has its machine instructions, so writing a program on one computer will no longer be valid on another computer. That means the machine instruction of Windows OS is not going to be the same for Linux OS and even not going to be the same for Mac OS.
Assembly Language
The Assembly Language can be called Symbolic Language. Different types of symbols will be used in this language to design the program. However, this assembly code is not directly understandable to the system, so we require translators.
The assembly language contains human-readable commands such as mov, add, mul, div, sub, etc. The problems we were facing in machine-level language are reduced to some extent by using an extended form of machine-level language known as assembly language. Since assembly language instructions are written in English, words like mov, add, mul, sub, etc. So, it is a little easier to write and understand than machine language.
As we know, computers can only understand machine-level instructions, so we require a translator that converts the assembly code into machine code. The translator used for translating the code is known as an assembler. The assembly language code is not portable because the data is stored in computer registers, and the computer has to know the different sets of registers.
The assembly code is not faster than machine code because the assembly language comes above the machine language in the hierarchy, meaning that assembly language has some abstraction from the hardware while machine language has zero abstraction.
What is a high-level programming language?
The High-Level Programming Languages are syntactically similar to English and easy to understand. High-Level Programming Languages are user-dependent languages. A High-Level Programming Language combines alphabets, digits, and symbols. By using a high-level programming language, we are developing user interface applications. Examples: C, C++, VC++, JAVA, C#, Swift, Objective C, D-Language.
Difference between High-Level and Low-Level languages:
The similarities between High-level language and low-level language are that both belong to the category of programming languages. The main difference between high-level and low-level language is that the Programmers can easily understand, interpret, or compile the high-level language compared to low-level language. On the other hand, Machines can easily understand low-level language compared to humans.

As a programmer, if we know the programming language, it is impossible to interact with computers because the computer can only understand binary code. In the above case, recommended to use a translator. As a programmer, if the instruction comes in the programming language, the Translator will convert the programming language code into binary format. According to binary instructions, we will get an application or software.
What is Software?
Software is a collection of programs that uses the resources of the Hardware components. A Program is a set of instructions designed for a particular task. The set of programs is called software.
Let us understand this with an example, i.e., Calculator. For each button, there is some program written inside it. That means a calculator is a collection of programs. And we can also say that a Calculator is a software. That means the software is a collection of programs.

As per IT Standards, the software is a digitalized and automated process. Let us understand this with an example, i.e., AC. If you set the timer to turn off the AC after 1 hour, then after 1 hour, the AC will be off. And again, using digits, you can set the temperature of the AC. And these things are managed by software inside the AC.

Types of Software:
Software is classified into two types, i.e., System Software and Application Software. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below image.

System Software:
System Software is software designed for a general purpose with no limitations. It is designed to provide a platform for other software Systems. So, the Software does the functionality for the hardware devices like printers, mobile, processors, etc. System Software is classified into three types:
- Operating System: DOS, WINDOWS, LINUX, UNIX
- System Support: Compiler, Interpreter, Assembler
- System Development: Linker, Loader, Editor
Application Software:
Application Software is a program or group of programs designed for end-users, i.e., designed for a specific task. Application Software does the functionality for business-oriented applications. Application Software is classified into two types:
- Application-Specific: MS OFFICE, Oracle
- General Purpose Software: Tally
In the next article, I will discuss How Computer Programs Work in detail. Here, in this article, I try to give a brief Introduction to Programming Languages, and I hope you enjoy this Introduction to Programming Languages article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.

It is very good and informative article. Thank you so much for doing this work. But I found one mistake in an Image. Image based on Programing languages have on mistake. In this Image there should be swap the words (High Level languages & Low Level languages), because the hierarchy of image have mistaken in this place.
Beautiful and easy to digest article
Hello Everyone!
In the sentence:
“If I want to speak in English, I want to form a sentence to form a sentence.”
There is a mistake. The sentence has unnecessary repetition. The correct version should be:
“If I want to speak in English, I want to form a sentence.”
By removing the extra part, the sentence becomes clear and grammatically correct.
Learnt something new!