Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Introduction to Concurrency
As a developer, we all want to develop good software or good application. We also know that good software is one that is Testable, Maintainable, Reusable, Flexible, and Efficient. Now, we are going to focus on the efficiency aspect. When we talk about efficiency, we probably think in terms of speed. For example, let us say we have a program A that performs a task in 60 seconds. And another program B performs the same task in two seconds. We can say that Program B is more efficient than Program A.
How we can Achieve Efficiency?
One of the ways to achieve efficiency is to have a faster computer i.e. the computer having more RAM, More CPU, more SSD, etc. Unfortunately, this is going to be expensive and there are also some limitations in terms of RAM, CPU, SSD, etc. Another option is to take the advantage of the power of different cores of our processor.
What is Concurrency?
Concurrency means doing several things at the same time. For example, if we have to do a million tasks, then instead of doing them sequentially one by one, we can do them simultaneously, thus reducing the duration of the program execution.
Let us understand Concurrency with one real-time example. If you have a restaurant with only one cook, then that cook is responsible for cooking everything that each customer asks for. Now, if one cook is cooking everything and handling every customer, then definitely the waiting time to serve the customer is going to be more. That means one cook is doing multiple tasks i.e. preparing food for multiple customers.
Now, we want to reduce the waiting time for customers. Then what do we need to do? We need to hire another cook. In this way, both cooks will simultaneously prepare customers’ food and customers will have to wait less time.
This concept of having a Set of Tasks and dividing them into several parts and those several parts can be performed simultaneously is called Parallelism. Understandably, in our restaurant analogy, we were able to achieve parallelism by adding new a cook. For example, one cook is going to serve veg foods. Another cook is going to serve non-veg foods.
How we can Achieve Parallelism in Programming?
In Programming, we can achieve Parallelism by using threads. A thread is a sequence of instructions that can be executed independently of other code. Since they are independent within a process, so we can have several threads. And if our processor allows, then we can run several threads simultaneously. When we are executing multiple threads simultaneously, then it is called multithreading. So, Parallelism uses multiple threads to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. Therefore, parallelism uses multithreading and multithreading is a form of concurrency.
However, there are other ways to do concurrency. We just talk about efficiency and we associate it with speed. Efficiency also has to do with Resource use. For example, if we have a web server, we want to serve as many web requests as we can concurrently. For that, we need to release threads when they are not in use. We can do this by using Asynchronous Programming.
Asynchronous Programming allows us to use threads efficiently and threads are prevented from being unnecessarily blocked.
Suppose you ordered a pizza using any food delivery app and they tell you it will take 30 minutes to deliver the pizza to your location. What will you do in those 30 minutes? Do you just freeze yourself waiting for the pizza, or will you do some other tasks while the pizza arrives? So, obviously, you want to do a few things while waiting for the pizza.
In our example, pizza preparation is an operation and that operation is not going to be satisfied immediately. And you are just like a thread. Instead of being stuck waiting for the result of the operation, it is better to do some other tasks.
So, using Asynchronous Programming, we can serve more HTTP requests on our web server and each request is handled by a thread and multiple threads can handle multiple HTTP Requests by avoiding thread blocking.
Introduction to Parallel Programming
Parallel Programming helps us to divide a task into different parts and execute those parts simultaneously. For example, if we have a set of images and we want to apply a series of filters to each image, we can do this by taking the advantage of Parallel Programming.
The main benefit of Parallel Programming is saving time. Time is saved by maximizing the use of computer resources. The idea is that if the computer allows the use of multi-threading, we can use multiple threads when we have a task to solve. Instead of underusing our processor i.e. using a single thread, we can use as many threads as we can to speed up the processing of the task.
Parallel Programming is very important for systems that process a huge amount of data. For example, on Facebook, approximately two hundred and fifty thousand photos are uploaded per minute. As you can imagine, it takes a lot of power to process such a high volume of information. So, we can take advantage of parallelism to accomplish more tasks in less time.
In C#, we can implement Parallel Programming in two ways. They are as follows:
- The Task Parallel Library (TPL)
- Parallel LINQ (PLINQ)
The Task Parallel Library is a library that makes life easier for us. When we see parallelism or Parallel Programming in our programs the TPL (Task Parallel Library) abstracts the low-level detail of thread handling i.e. how to create threads and how to execute the tasks using multiple threads is handled by the TPL. This allows us to concentrate on program logic rather than threads.
On the other hand, PLINQ or Parallel LINQ is an implementation of LINQ that allows us to work in parallel. For example, in LINQ, we can filter the elements of an array. Then with Parallel LINQ, we can filter the same array in parallel. This allows us to use the cores of our processor to perform the evaluations of the elements of the array simultaneously.
There are two forms of parallelism. They are as follows
- Data Parallelism
- Task Parallelism
In Data Parallelism, we have a collection of values and we want to use the same operation on each of the elements in the collection. The examples will be to filter the elements of an array in parallel.
Task Parallelism occurs when we have a set of independent tasks that we want to perform in parallel. An example would be if we want to send an email and SMS to a user, we can perform both operations in parallel if they are independent.
Just because we have the concept of parallelism, that doesn’t mean we should use parallelism. We will see later that there are times when it is better to not use parallelism because in certain cases using parallelism is slower than not using it.
Introduction to Asynchronous Programming
Asynchronous Programming allows us to handle the threads of our processes in a more efficient way. The idea is to avoid blocking a thread while waiting for a response, either from an external system such as a Web service or from the computer’s file management system.
For example, if we have a web application, it will be able to serve more HTTP requests at the same time by using Asynchronous Programming. This is because each HTTP request is handled by a thread, and if we avoid blocking threads, then there will be more threads available to process HTTP requests.
To work with asynchronous programming in C# we use async and await keywords. The idea is that we need to use the async keyword to mark a method as asynchronous and with await, we can wait for an asynchronous operation in such a way that the original thread is not blocked.
The method which is marked with the async keyword must return a Task or Task<T>. The idea of a Task is that it represents an asynchronous operation and does not return anything. In the case of Task<T>, it is like a promise that in the future this method will return a value of the data type T.
Asynchronous Programming can be used in any environment like Desktop, Mobile, and Web. Normally we use Asynchronous Programming when we are going to communicate with External Systems. For example, if our application communicates with a web service, then we need to use Asynchronous Programming.
Whenever we are communicating with an external system, this is nothing but an I/O-Bound Operation. I/O-Bound operations are characterized by the fact that their performance depends on communication between systems. This is the reason why Asynchronous Programming does not improve the speed of the processes since there is no way that from our system, we can make the processing speed of an external system faster. At most what we can do is, we can efficiently manage our threads so that the threads will not block.
CPU vs I/O Bound Operations:
We are already discussed what Asynchronous and Parallel Programming are. It is also important to understand what type of operations both are intended to try to improve.
In the case of Asynchronous Programming, we discussed that it has the specialty to handle IO-Bound operations where IO-bound operations are characterized by communication with external systems. Some examples of IO-bound operations are calls to a Web Service, interaction with a Database, interaction with a file system, etc. Therefore, when we need to perform such kinds of operations, we can consider the use of asynchronous programming to increase the level of scalability of our systems.
When we make a call to an external entity, we have to wait for a response and while waiting for the response, it is productive to free the thread that started the operation so that it can proceed to perform other tasks.
On the other hand, CPU-bound operations are those that are performed primarily using processor power. Here, there are usually no dependencies on external systems, everything depends on our system. If we have multiple CPU operations that are independent, we may want to use parallel programming to decrease the time it takes to perform these operations. Some examples of CPU operations are finding the inverse of a matrix, sorting the elements of an array, etc.
It is also important to understand the difference between IO and CPU-Bound operations to see what you can consider using Parallel or Asynchronous Programming.
If your operation requires communication with some external system to your program, then it is IO bound and therefore you can consider asynchronous programming. On the other hand, if the operation is done entirely within your program and its execution time depends on the processor, then it is a CPU-bound operation and therefore you can consider using parallel programming.
Sequential Programming, Concurrency, Multithreading, Parallelism, Multi-Tasking:
In the context of concurrency, certain relevant terms are handled. Some of these terms are very similar and the differences between them are often certain. Even if they are used interchangeably in informal contexts, they are not exactly the same. We will look at the concepts of Sequential Programming, Concurrency, Multithreading, Parallelism, and multitasking. Let’s start with the non-concurrent programming model.
Sequential programming: Sequential programming is the one in which the instructions are done one at a time. That is where there is no concurrency of any kind. One of the advantages of this programming model is that it is relatively easy to understand since it consists of following a series of steps in an orderly manner. The problem with this programming model is that sometimes it can be slow.
Concurrency: Concurrency means doing several things at the same time. This is the opposite of sequential programming. The term concurrency encompasses everything related to in one way or another doing several things at the same time. There are different forms of concurrency. We have seen a fundamental concept of threads. We remember that a thread is a sequence of instructions that can be executed independently of our code.
Multithreading: Multithreading is the ability to use multiple threads. It is important to clarify that multithreaded does not imply parallelism, since we can have a computer with a processor that is not multicore and I still can use multithreading. This is because an operating system can provide several threads and execute them sequentially without using parallelism
Parallelism: It is running several threads simultaneously. This requires a multicore processor. Since parallelism uses multiple threads, parallelism uses multithreading. However, as we said, we can have multithreading without parallelism. In this case, typically what we have is called multitasking.
Multitasking: With multitasking, we can have several tasks running in such a way that we execute their different threads sequentially, typically with some type of Task Execution System. This is handled at the operating system level. For example, if we have a program A with threads one and two and a program B with threads three and four, and we try to execute both programs at the same time, it could be that the system executes the threads in the order one three two, and four.
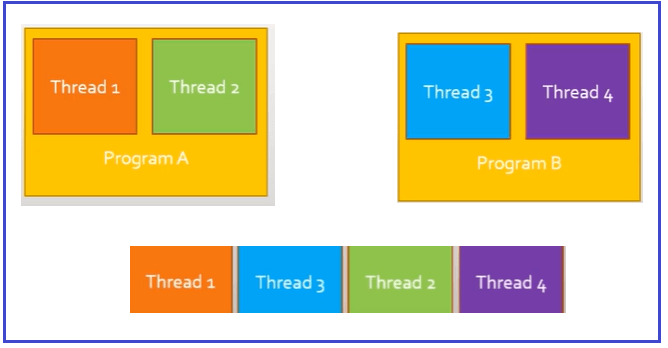
So, it looks like there was parallelism, but there really wasn’t as the threads did not run simultaneously, but in sequence. The computer is so fast that the human eyes could not see that the task was executed in sequence.
Determinism vs Non-Determinism
There are methods where we can predict its result from its input values. If we have a method that takes two integers as input values and returns the sum of the two numbers, then it is clear that we can predict the output value from the input values. If we send 2 and 5, the result will be 7. i.e. 2 plus 5 is seven. This characteristic of being able to predict the result of a method based on its input values we call determinism.
What happens in the opposite case? That is when we have a method where we cannot predict the result. Well, we say then that we are facing a non-deterministic method. A simple example of non-determinism will be the Random class. With this class, we can generate pseudo-random numbers.
Therefore, the output value of the Random method cannot be determined from the input values supplied to its methods. Therefore, the output value of the Random class methods cannot be determined from the input values supplied to these methods.
However, not only with the random class, we have nondeterminism, Parallelism can also cause some sort of non-determinism. Suppose you have a method that processes credit cards and as it processes them writes a message to the console window. If we use sequential programming, we can always predict the order of the messages on the console window. With parallel programming, this is virtually impossible to predict. We know that all operations are going to be executed, but we have no way of knowing the order of execution of the threads that will be in charge of processing the different credit cards. Even if we know that all credit cards will be processed, we cannot predict the order of processing.
Therefore, we must be kept in mind that when we use code in parallel, we will not be able to predict the order of operations until we perform. If you need to have a specific order in the tasks that you have to do, then maybe parallelism is not a good option in your case.
Summary:
- We saw that concurrency refers to, in one way or another, doing several things at the same time. The concept of concurrency encompasses parallel programming and asynchronous programming.
- Parallel programming refers to the use of multiple threads simultaneously to solve a set of tasks. For this, we need processors with adequate abilities to perform several tasks at the same time. In general, we use parallel programming to gain speed.
- Asynchronous programming refers to the efficient use of threads where we do not block a thread unnecessarily. But while we wait for the result of an operation, the thread gets to perform other tasks in the meantime. This increases vertical scalability and allows us to prevent the user interface from freezing during long tasks.
- CPU-bound operations are those that depend entirely on the speed of our processors.
- IO-bound operations are those that depend on communication with entities external to our application.
- Deterministic refers to the fact that we can’t predict the result of something based on the initial conditions. For example, we can predict the result of a method from its input values. With parallel programming, we will not always be able to predict 100 percent the result of something, especially when we refer to the order of operations of a set of tasks, since we do not control the order of execution of the different threads of the application.
In the next article, I am going to discuss how to implement Asynchronous Programming using Async and Await Operators in C# with Examples. Here, in this article, I am trying to explain the basic concepts of Parallel and Asynchronous Programming.


Guys,
Please give your valuable feedback. And also, give your suggestions about this Parallel and Asynchronous Programming concept. If you have any better examples, you can also put them in the comment section. If you have any key points related to Parallel and Asynchronous Programming, you can also share the same.
good
Good Day in your summary you said Deterministic refers to the fact that we can’t predict the result of something based on the initial conditions which contradicts what you explained in the article………It’s a nice article dotnet tutorial is the best place to learn
Probably a mistake there
Thanks for sharing your knowledge
Really appreciated for sharing this knowledge
Why should I use TPL when I have Threads?
I am a Korean developer and I am so grateful that you share your knowledge for free. This is a great tutorial. Every time I read it, I am amazed by your knowledge. Also, how you teach so easily makes the concepts easy to understand. I hope you always have a lot of good things.
Such a great content , very easy to understand , tbh i actually prefer going through content from dotnet tutorials instead referring to online videos