Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Multiple Inheritance in C# with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss Multiple Inheritance with Interfaces in C# with Examples. In order to gain the full advantage of this article and in order to understand Multiple Inheritance, I will strongly recommend you to read the following three articles before proceeding with this article. Because whatever we discussed in the below articles we are going to use here.
Before understanding Multiple Inheritance with Interfaces, let us have a look at what is an Interface.
What is an Interface in C#?
An Interface in C# is a fully un-implemented class used for declaring only abstract members. So, we can also define an interface as a pure abstract class which allows us to define only abstract members especially abstract methods or abstract properties. An abstract method is a method without a body or implementation.
And interface members (abstract methods) implementation is going to be provided by the child class of the interface. The class which implements the interface must and should provide the implementation of all the methods that are declared inside the interface without fail i.e. mandatory.
Multiple Inheritance in C#:
If you read my Inheritances in C# article, then you will know that we have a set of rules and regulations that we need to follow while working with inheritance. In our Types of Inheritances in C# article, we discussed the different types of inheritance. As per the standard of Object-Oriented Programming, we have five types of inheritances. They are as follows:
- Single Inheritance
- Multi-Level Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
For a better understanding, please have a look at the below diagram which shows the pictorial representation of different types of Inheritance according to object-oriented programming.
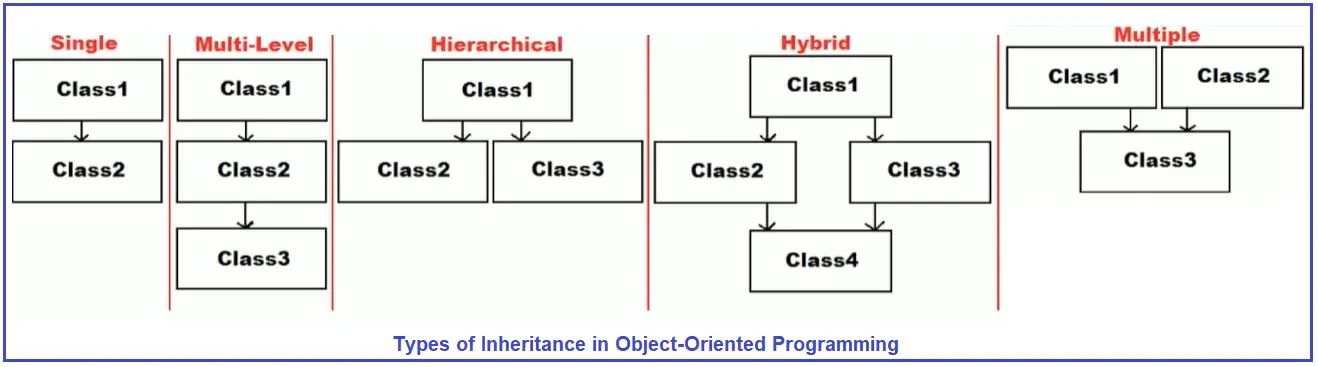
We also discussed in our Types of Inheritances article that in C#, with class, only Single, Multi-Level and Hierarchical inheritances are supported. With class, Hybrid and Multiple Inheritance are not supported. Basically, Multiple Inheritance is not supported by the class. Hybrid Inheritance is the combination of Multiple and (Single, Multi-Level and Hierarchical) inheritances. If Multiple Inheritance is not supported, it means Hybrid Inheritance is also not supported with classes.
And then we categorized the Inheritance into two types based on the Immediate Parent class as follows:
- Single Inheritance: If a class can have only one Immediate Parent class, then we call it Single Inheritance. Examples: Single, Multi-Level, and Hierarchical Inheritances. You can take any class and you will see that that class has only one immediate parent class.
- Multiple Inheritances: If a class has more than one Immediate Parent class, then we call it Multiple Inheritance. Examples: Multiple and Hybrid Inheritances. Here, you can see, that a class can have more than one Immediate Parent class.
Even if Multiple Inheritance is not supported through classes in C#, it is still supported through interfaces. A class can have one and only one immediate parent class, whereas the same class can have any number of interfaces as its parent i.e. Multiple Inheritance is supported in C# through interfaces. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below diagram.

As you can see in the above image, a class can have one and only one immediate parent class. At the same time, the same class can have n number of interfaces as its parent. So, the point that you need to remember is in C#, Multiple Inheritance is supported through interfaces in C#, not supported through classes. Now, let us proceed and try to understand why Multiple Inheritance is not supported through classes in C#.
Why Multiple Inheritance Not Supported Through Classes in C#?
You might have one question in your mind about why Multiple Inheritance is not Supported through classes and how it is supported through interfaces in C#. Let us understand this.
Multiple Inheritance is not Supported through classes because we came across the ambiguity problem. What is the ambiguity problem? Is the following class code Valid? No. Why because in a class we cannot define two methods with the same name and same parameters i.e. with the same signature.

If the compiler allows two method signatures to be the same in a class, then what problem we will face? We will face the ambiguity problem. Please observe the following code. Now, when we create an instance of the class and when we invoke the Test method, the compiler gets confused to call which version of the Test method.

So, you can see it is saying The call is ambiguous between the following methods or properties: ‘Class3.Test()’ and ‘Class3.Test()’ and hence compiler restricts us to define two methods with the same name and parameters in a class. This is nothing but an ambiguity problem.
And we will also face the same ambiguity problem if our class is inheriting from two or more classes. Let us try to understand the ambiguity problem with multiple inheritances with classes. please have a look at the below diagram.

As you can see in the above image, the class Class3 is inherited from two classes i.e. Class1 and Class2. In both the classes (Class1 and Class2) we have a method called Test(). That means the same Test() method getting inherited to class Class3. That means Class3 contains 2 Test methods now with the same name and same signature. But we know that no class can contain multiple methods with the same name and signature. If present ambiguity problem arises. In this case, the two classes provide the method to the child class for consumption and hence we are facing the ambiguity problem. So, to avoid this ambiguity problem, while you are inheriting one class from more than one class, then the compiler will give you an error saying that you cannot have multiple base classes as shown in the below image.

But with interfaces, we don’t have this ambiguity problem. Suppose, one class is inherited from two interfaces, and if both the interfaces contain the same method, then also we will not face the ambiguity problem. The reason is, in this case, the interface provides the method to the child class for implementation, but not for consumption. Consumption creates ambiguity problems, not implementation. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below diagram.

So, here both the interfaces request the child class to implement the method, not to consume the method, and hence no ambiguity problem.
Example to Understand Multiple Inheritance with Interfaces in C#:
Let us understand Multiple Inheritance with Interfaces in C# with an example. First, create two interfaces as follows. Here, both interfaces contain the same Test method.
public interface Interface1
{
void Test();
}
public interface Interface2
{
void Test();
}
Now, create one class as follows by inheriting from the interfaces. At this moment we are not implementing the interfaces method.
public class MultipleInheritanceTest : Interface1, Interface2
{
}
Now, when you try to run or compile the above code, you will get two compile-time errors as shown in the below image.

And this makes sense. Because the class MultipleInheritanceTest does not implement the Test method of both Interface1 and Interface2 and hence we are getting two errors. So, here it is showing Interface1.Test() and Interface2.Test() method not implemented by MultipleInheritanceTest class. Now, implement the Test method in the Child class as follows.
public class MultipleInheritanceTest : Interface1, Interface2
{
public void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test Method is Implemented in Child Class");
}
}
Here, you will observe that once we implement the Test method in the MultipleInheritanceTest class, then both the compile-time errors are gone. Now, you will see the code is compiled successfully. How is this possible? Previously we have two errors. We have implemented it only once and both the errors are removed.
This is possible because, the interface asks the child class to implement the method, not to consume the method. And class implement the method. Now, you have one doubt, the Test method implementation in MultipleInheritanceTest class will be for the Interface1 Test method or the Interface2 Test method? The answer is both. Why because Interface1 doesn’t know anything i.e. any method name or anything present in Interface2 and Interface2 doesn’t know anything i.e. any method name or anything present in Interface1.
So, in this case, Interface1 will look into the class for Test method implementation and sees that the Test method is implemented and so, Interface1 is happy now and will not give any error. Similarly, Interface2 will look into the class for Test method implementation and sees that the Test method is implemented, hence Interface2 is also happy and will not give any error.
Simply speaking we are cheating both interfaces by implementing the method only once. So, we are telling both the interfaces that this Test method is yours and we are implementing this in our class. And both Interfaces are not aware of each other, because they are not aware of each other, both interfaces are thinking that my method is implemented in the Child class. And this is the reason why we are not getting any ambiguity errors.
Example to Understand Multiple Inheritances with Interfaces in C#:
Whatever we have discussed so far, the complete example code is given below.
using System;
namespace MultipleInheritance
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MultipleInheritanceTest obj = new MultipleInheritanceTest();
obj.Test();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public interface Interface1
{
void Test();
}
public interface Interface2
{
void Test();
}
public class MultipleInheritanceTest : Interface1, Interface2
{
public void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test Method is Implemented in Child Class");
}
}
}
Output: Test Method is Implemented in Child Class
How to Implement Each Interfaces Method Separately in C#?
In our previous article, we have already discussed the concept of Explicit Interfaces Implementation in C#. With Explicit Interfaces Implementation in C#, we can implement each interface method separately in the child classes.
When each interface method is implemented separately under the child class by providing the method name along with the interface name explicitly then it is called Explicit Interface Implementation. In this case, while calling the method we should compulsorily use the interface reference that is created using the object of a class or type cast the object to the appropriate interface type.
In the below example, we are implementing the Show method explicitly twice in the child class by specifying the Interface name.
using System;
namespace MultipleInheritance
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MultipleInheritanceTest obj = new MultipleInheritanceTest();
obj.Test();
//You cannot call the Show method using obj
//obj.Show();
//Using Interface Reference call the Show method
Interface1 i1 = obj;
i1.Show();
//Typecase the object to interface type and call the show method
((Interface2)obj).Show();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public interface Interface1
{
void Test();
void Show();
}
public interface Interface2
{
void Test();
void Show();
}
public class MultipleInheritanceTest : Interface1, Interface2
{
//Normal Implementation
public void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test Method is Implemented in Child Class");
}
//Explicit Interface Implementation
void Interface1.Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("Interface1 Show Method is Implemented in Child Class");
}
//Explicit Interface Implementation
void Interface2.Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("Interface2 Show Method is Implemented in Child Class");
}
}
}
Output:

Frequently Asked Interview Questions
When do you choose interface over an abstract class or vice versa in C#?
If we want some implementation that will be the same for all the derived classes, then it is better to go for an abstract class instead of an interface. With the interface, we can move our implementation to any class that implements the interface. With the abstract class, we can share the implementation for all the derived classes in one central place, and thus avoid code duplication in the derived classes.
Can an interface inherit from another interface in C#?
Yes, an interface can inherit from another interface in C#. It is possible for a class to inherit an interface multiple times, through base classes or interfaces it inherits. In this case, the class can only implement the interface one time, if it is declared as part of the new class. If the inherited interface is not declared as part of the new class, its implementation is provided by the base class that declared it. It is possible for a base class to implement interface members using virtual members; in that case, the class inheriting the interface can change the interface behavior by overriding the virtual members.
Can you create an instance of an interface in C#?
No, you cannot create an instance of an interface in C#. But you can create a reference variable of an interface.
If a class inherits an interface, what are the 2 options available for that class?
Option 1: Provide Implementation for all the members inherited from the interface. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following example.

Option 2: If the class does not wish to provide Implementation for all the members inherited from the interface, then the class has to be marked as abstract and also needs to declare the unimplemented interface methods as abstract. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following example.

A class inherits from 2 interfaces and both interfaces have the same method name as shown below. How should the class implement the drive method for both Car and Bus interfaces?
namespace MultipleInheritance
{
interface Car
{
void Drive();
}
interface Bus
{
void Drive();
}
class Demo : Car, Bus
{
//How to implement the Drive() Method inherited from Bus and Car
}
}
By using explicitly Interface Implementation. To implement the Drive() method use the fully qualified name as shown in the example below. To call the respective interface drive method typecast the demo object to the respective interface and then call the drive method.
using System;
namespace MultipleInheritance
{
interface Car
{
void Drive();
}
interface Bus
{
void Drive();
}
class Demo : Car, Bus
{
//How to implement the Drive() Method inherited from Bus and Car
void Car.Drive()
{
Console.WriteLine("Drive Car");
}
void Bus.Drive()
{
Console.WriteLine("Drive Bus");
}
static void Main()
{
Demo DemoObject = new Demo();
((Car)DemoObject).Drive();
((Bus)DemoObject).Drive();
Console.Read();
}
}
}
Output:
![]()
In the next article, I am going to discuss Multiple Inheritance Real-Time Examples in C#. Here, in this article, I try to explain Multiple Inheritance in C# with Examples. I hope you enjoy this Multiple Inheritance in C# with Examples article. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this Multiple Inheritance using Interface article.

very clear in explaining concepts. Keep writing. Thank you.
Thanks for sharing this article
Nice explanation