Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss the Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# with Examples. Please read our previous article where we discussed the Non-Generic Queue Collection Class in C# with Examples. The Non-Generic SortedList class belongs to System.Collections namespace. At the end of this article, you will understand the following pointers with examples.
- What is SortedList in C#?
- Methods, Properties, and Constructor of Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C#
- How to Create a SortedList in C#?
- How to Add Elements into a SortedList in C#?
- How to access a SortedList in C#?
- How to Remove Elements from a SortedList in C#?
- How to check the availability of key/value pairs in a SortedList in C#?
- How to Clone the Non-Generic SortedList in C#?
- What is the use of the CopyTo method of Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C#?
- When to Use Non-Generic SortedList Collection in C#?
What is SortedList in C#?
The Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# represents a collection of key/value pairs that are sorted by the keys and are accessible by key and by index. By default, it sorts the key/value pairs in ascending order.
Properties of Non-Generic SortedList Class in C#:
- The Non-Generic SortedList Class in C# implements the IEnumerable, ICollection, IDictionary, and ICloneable interfaces.
- We can access the element by its key or by its index in SortedList.
- The Non-Generic SortedList object internally maintains two arrays to store the elements of the list, i.e, one array for the keys and another array for the associated values. Here, the key cannot be null, but the value can be null. And one more, it does not allow duplicate keys.
- The capacity of the Non-Generic SortedList object is the number of key/value pairs it holds.
- In the Non-Generic SortedList object in C#, we can store values of the same type and of the different types as it operates on the object data type.
- In the same SortedList, it is not possible to store keys of different data types. If you try then the compiler will throw an exception.
Methods, Properties, and Constructor of Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C#:
If you go to the definition of the Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class, then you will see the following. As you can see the SortedList Collection Class implements the IEnumerable, ICollection, IDictionary, and ICloneable interfaces.

How to Create a SortedList Collection in C#?
The Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# is provided with six constructors that we can use to create an instance of SortedList. They are as follows:
- SortedList(): It initializes a new instance of the System.Collections.SortedList class that is empty, has the default initial capacity and is sorted according to the IComparable interface implemented by each key added to the System.Collections.SortedList object.
- SortedList(IComparer comparer): It initializes a new instance of the System.Collections.SortedList class that is empty, has the default initial capacity and is sorted according to the specified IComparer interface. The Parameter comparer specifies the System.Collections.IComparer implementation to use when comparing keys. -or- null to use the System.IComparable implementation of each key.
- SortedList(IDictionary d): IT initializes a new instance of the System.Collections.SortedList class contains elements copied from the specified dictionary, has the same initial capacity as the number of elements copied, and is sorted according to the System.IComparable interface implemented by each key. The Parameter d specifies the System.Collections.IDictionary implementation to copy to a new System.Collections.SortedList object.
- SortedList(int initialCapacity): It initializes a new instance of the System.Collections.SortedList class that is empty, has the specified initial capacity, and is sorted according to the System.IComparable interface implemented by each key added to the System.Collections.SortedList object. The Parameter initialCapacity specifies the initial number of elements that the System.Collections.SortedList object can contain.
- SortedList(IComparer comparer, int capacity): It initializes a new instance of the System.Collections.SortedList class that is empty, has the specified initial capacity, and is sorted according to the specified System.Collections.IComparer interface. The Parameter comparer specifies the System.Collections.IComparer implementation to use when comparing keys. -or- null to use the System.IComparable implementation of each key. The Parameter capacity specifies the initial number of elements that the System.Collections.SortedList object can contain.
- SortedList(IDictionary d, IComparer comparer): It initializes a new instance of the System.Collections.SortedList class contains elements copied from the specified dictionary, has the same initial capacity as the number of elements copied, and is sorted according to the specified System.Collections.IComparer interface. The Parameter d specifies the System.Collections.IDictionary implementation to copy to a new System.Collections.SortedList object. The Parameter comparer specifies the System.Collections.IComparer implementation to use when comparing keys. -or- null to use the System.IComparable implementation of each key.
Let’s see how to create a SortedList using the SortedList constructor in C#:
Step1:
As the SortedList class belongs to System.Collections namespace, so first, we need to import the System.Collections namespace into our program as follows:
using System.Collections;
Step2:
Next, we need to create an instance of the SortedList class using the SortedList () constructor as follows:
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList();
How to Add Elements into a SortedList in C#?
If you want to add a key/value pair to a SortedList, then you need to use the Add() method of the SortedList class.
- Add(object key, object value): The Add(object key, object value) method is used to add an element with the specified key and value to a SortedList. Here, the parameter key specifies the key of the element to add and the parameter value specifies the element to add. The value can be null.
For Example,
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList();
sortedList.Add(1, “One”);
sortedList.Add(3, “Three”);
You can also store a key/value pair in the SortedList using Collection Initializer as follows.
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList
{
{ 1, “One” },
{ 3, “Three” }
};
How to Access a SortedList Collection in C#?
We can access the key/value pairs of the SortedList collection in C# using four different ways. They are as follows:
Using Keys to Access SortedList Elements in C#:
You can access the individual value of the SortedList in C# by using the keys. In this case, we need to pass the key as a parameter to find the respective value. The syntax is given below.
Console.WriteLine($”Key: 1, Value: {sortedList[1]}”);
Console.WriteLine($”Key: 2, Value: {sortedList[2]}”);
Console.WriteLine($”Key: 3, Value: {sortedList[3]}”);
Using Index to Access SortedList Elements in C#:
You can access the individual value of the SortedList in C# by using the Index position. In this case, we need to pass the Integer Index Position as a parameter to find the respective value. The syntax is given below.
Console.WriteLine($”Key: 1, Index: 0, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(0)}”);
Console.WriteLine($”Key: 2, Index: 1, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(1)}”);
Console.WriteLine($”Key: 3, Index: 2, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(2)}”);
Using for loop to Access SortedList Elements in C#:
You can use for loop to access the key/value pairs of the SortedList Collection as shown below.
for (int x = 0; x < sortedList.Count; x++)
{
Console.WriteLine($”Key: {sortedList.GetKey(x)}, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(x)}”);
}
Using foreach loop to access SortedList Elements in C#:
We can also use a for-each loop to access the key/value pairs of the SortedList in C# as follows.
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($”Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}”);
}
Example to Understand How to Create a SortedList and Add Elements and Access Elements in C#:
For a better understanding of how to create a SortedList, how to add elements to a SortedList, and how to access the elements of a SortedList Collection in C# using different ways, please have a look at the below example.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace NonGenericCollections
{
public class SortedListDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Creating sortedList Collection
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList();
//Adding Elements to SortedList using Add Method
//Key type going to be same
sortedList.Add(1, "One");
sortedList.Add(5, "Five");
sortedList.Add(4, "Four");
sortedList.Add(2, "Two");
sortedList.Add(3, "Three");
//Duplicate Key not allowed
//System.ArgumentException: 'Item has already been added. Key in dictionary: '4' Key being added: '4''
//sortedList.Add(4, "Four");
//Null value is allwed
//sortedList.Add(6, null);
//Duplicate Value is allowed
//sortedList.Add(7, "Five");
//In this case string key is not valid, throw Exception
//sortedList.Add("Ten", "Ten");
//Accessing SortedList using For loop
Console.WriteLine("Accessing SortedList using For loop");
for (int x = 0; x < sortedList.Count; x++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {sortedList.GetKey(x)}, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(x)}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nAccessing SortedList using For Each loop");
//Accessing SortedList using For Each loop
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nAccessing SortedList using Keys");
Console.WriteLine($"Key: 1, Value: {sortedList[1]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Key: 2, Value: {sortedList[2]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Key: 3, Value: {sortedList[3]}");
Console.WriteLine("\nAccessing SortedList using Index");
Console.WriteLine($"Key: 1, Index: 0, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(0)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Key: 2, Index: 1, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(1)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Key: 3, Index: 2, Value: {sortedList.GetByIndex(2)}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:
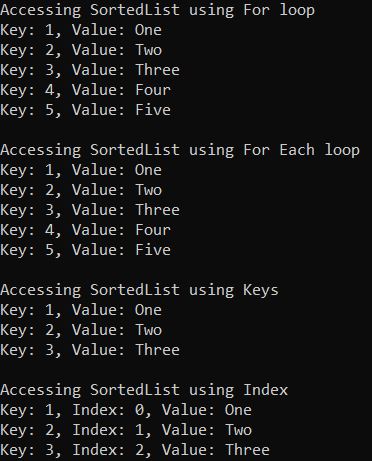
Please note here we are getting the output based on the ascending order of the keys.
Adding Elements to SortedList using Collection Initializer in C#:
In the below example, we are using Collection Initializer syntax instead of the Add method to add key-value pairs into the sorted list in C#.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace NonGenericCollections
{
public class SortedListDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Creating sortedList using Object Initializer
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList
{
{ "Ind", "India" },
{ "USA", "United State of America" },
{ "SA", "South Africa" },
{ "PAK", "Pakistan" }
};
Console.WriteLine("SortedList Elements");
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:

How to Remove Elements from a SortedList Collection in C#?
The Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# provides the following methods to remove elements from SortedList.
- Remove(object key): This method is used to remove the element with the specified key from a System.Collections.SortedList object. The parameter key specifies the element to remove.
- RemoveAt(int index): This method is used to remove the element at the specified index of a System.Collections.SortedList object. The parameter index specifies the element to remove. It is 0 based Index.
- Clear(): This method is used to remove all elements from a System.Collections.SortedList object.
Let us see an example to understand the above methods of SortedList Collection Class in C#. Please have a look at the below example.’
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace NonGenericCollections
{
public class SortedListDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Creating sortedList object
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList();
//Adding Elements to SortedList using Add
sortedList.Add("Ind", "India");
sortedList.Add("USA", "United State of America");
sortedList.Add("SA", "South Africa");
sortedList.Add("PAK", "Pakistan");
Console.WriteLine("SortedList Elements");
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
// Remove value having key PAK Using Remove() method
sortedList.Remove("PAK");
// After Remove() method
Console.WriteLine("\nSortedList Elements After Remove Method");
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
// Remove element at index 1 Using RemoveAt() method
sortedList.RemoveAt(1);
Console.WriteLine("\nSortedList Elements After RemoveAT Method");
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
// Remove all key/value pairs Using Clear method
sortedList.Clear();
Console.WriteLine($"After Clear Method Total Key-Value Pair Present is : {sortedList.Count} ");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:

How to check the availability of key/value pairs in a SortedList in C#?
If you want to check whether the key/value pair exists or not in the SortedList, then you can use the following methods of the SortedList class.
- Contains(object key): This method is used to determine whether the SortedList object contains a specific key. The parameter key to locate in the SortedList object. It returns true if the SortedList object contains an element with the specified key; otherwise, false. If the key is null, then it will throw System.ArgumentNullException.
- ContainsKey(object key): This method is used to determine whether a SortedList object contains a specific key. The parameter key to locate in the SortedList object. It returns true if the SortedList object contains an element with the specified key; otherwise, false. If the key is null, then it will throw System.ArgumentNullException.
- ContainsValue(object value): This method is used to determine whether a System.Collections.SortedList object contains a specific value. The parameter value to locate in the SortedList object. The value can be null. It returns true if the SortedList object contains an element with the specified value; otherwise, false.
Let us understand this with an example. The following example shows how to use the Contains, ContainsKey, and ContainsValue method of the non-generic SortedList collection class in C#.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace NonGenericCollections
{
public class SortedListDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Creating sortedList using Object Initializer
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList
{
{ "Ind", "India" },
{ "USA", "United State of America" },
{ "SA", "South Africa" },
{ "PAK", "Pakistan" }
};
//Checking the key using the Contains methid
Console.WriteLine("Is Ind Key Exists : " + sortedList.Contains("Ind"));
Console.WriteLine("Is NZ Key Exists : " + sortedList.Contains("NZ"));
//Checking the key using the ContainsKey methid
Console.WriteLine("Is Ind Key Exists : " + sortedList.ContainsKey("Ind"));
Console.WriteLine("Is NZ Key Exists : " + sortedList.ContainsKey("NZ"));
//Checking the value using the ContainsValue method
Console.WriteLine("Is India value Exists : " + sortedList.ContainsValue("India"));
Console.WriteLine("Is Bangladesh value Exists : " + sortedList.ContainsValue("Bangladesh"));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:

How to Clone the Non-Generic SortedList in C#?
If you want to clone or copy the Non-Generic SortedList in C#, then you need to use the following Clone() method provided by the SortedList Collection Class.
- Clone(): This method is used to create and return a shallow copy of a SortedList object.
For a better understanding, please have a look at the below example.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace NonGenericCollections
{
public class SortedListDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Creating sortedList using Object Initializer
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList
{
{ "Ind", "India" },
{ "USA", "United State of America" },
{ "SA", "South Africa" },
{ "PAK", "Pakistan" }
};
Console.WriteLine("Sorted List Elements:");
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nCloned Sorted List Elements:");
//Creating a clone sortedList using Clone method
SortedList cloneSortedList = (SortedList)sortedList.Clone();
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in cloneSortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key}, Value: {item.Value}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:

What is the use of the CopyTo method of the Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C#?
CopyTo(Array array, int arrayIndex): The CopyTo method of the Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# is used to copy SortedList elements to a one-dimensional Array object, starting at the specified index in the array. Here, the parameter array specifies the one-dimensional Array object that is the destination of the DictionaryEntry objects copied from SortedList. The Array must have zero-based indexing. The arrayIndex parameter specifies the zero-based index in the array at which copying begins. If the parameter array is null, then it will throw ArgumentNullException. If the parameter arrayIndex is less than zero, then it will throw ArgumentOutOfRangeException.
The key/value pairs are copied to the Array object in the same order in which the enumerator iterates through the SortedList object. This method is an O(n) operation, where n is Count.
- To copy only the keys in the SortedList, use SortedList.Keys.CopyTo.
- To copy only the values in the SortedList, use SortedList.Values.CopyTo.
For a better understanding, please have a look at the below example.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace NonGenericCollections
{
public class SortedListDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Creating sortedList using Object Initializer
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList
{
{ "Ind", "India" },
{ "USA", "United State of America" },
{ "SA", "South Africa" },
{ "PAK", "Pakistan" }
};
Console.WriteLine("Sorted List Elements:");
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in sortedList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Key: {item.Key} : Value: {item.Value}");
}
DictionaryEntry[] myTargetArray = new DictionaryEntry[5];
sortedList.CopyTo(myTargetArray, 1);
Console.WriteLine("\nCopyTo Method to Copy Keys and values:");
for (int i = 0; i < myTargetArray.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{myTargetArray[i].Key} : {myTargetArray[i].Value}");
}
Object[] myObjArrayKey = new Object[5];
Object[] myObjArrayValue = new Object[5];
Console.WriteLine("\nCopyTo Method to Copy Keys:");
sortedList.Keys.CopyTo(myObjArrayKey, 0);
foreach (var key in myObjArrayKey)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{key} ");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nCopyTo Method to Copy Values:");
sortedList.Values.CopyTo(myObjArrayValue, 1);
foreach (var key in myObjArrayValue)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{key} ");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:

Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class Properties in C#
- Keys: Gets the keys in a System.Collections.SortedList object. It returns a System.Collections.ICollection object containing the keys in the System.Collections.SortedList object.
- IsSynchronized: Gets a value indicating whether access to a SortedList object is synchronized (thread-safe). It returns true if access to the SortedList object is synchronized (thread-safe); otherwise, false. The default is false.
- IsReadOnly: Gets a value indicating whether the SortedList object is read-only. It returns true if the System.Collections.SortedList object is read-only; otherwise, false. The default is false.
- IsFixedSize: It returns true if the SortedList object has a fixed size; otherwise, false. The default is false.
- Count: It returns the number of elements contained in the System.Collections.SortedList object.
- Capacity: It returns the number of elements that the System.Collections.SortedList object can contain.
- SyncRoot: It returns an object that can be used to synchronize access to the System.Collections.SortedList object.
- Values: Gets the values in a SortedList object. It returns a System.Collections.ICollection object containing the values in the System.Collections.SortedList object.
When to Use Non-Generic SortedList Collection in C#?
The Non-Generic SortedList Collection is a powerful tool for performing quick manipulation of key-value data in an orderly manner. But there are certain scenarios where this class may not be suitable. For example, by its nature, a SortedList must always be sorted. Therefore, whenever we add a new key-value pair to the list or remove a key-value pair from the SortedList, then it must sort itself to ensure that all elements are in the right order. This becomes more expensive as we increase the number of elements in our SortedList.
We should only use SortedList when we want to handle smaller collections that need to be sorted at all times. When dealing with larger collections, it is more efficient to use a dictionary, HashSet, or even a regular list which we can sort when we need it.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Advantages and Disadvantages of Non-Generic Collection Classes in C# with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# with Examples. I hope this Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C# with Examples article will help you with your needs. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.

Guys, Collection Class concept. If you have any better examples, you can also put them in the comment section. If you have any key points related to the Non-Generic SortedList Collection Class in C#, you can also share the same.
Please give your valuable feedback. And also, give your suggestions about the Non-Generic SortedList