Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
How to Implement the Authentication Server using ASP.NET Core Web API:
In this article, I will discuss how to implement the Authentication Server Application using ASP.NET Core Web API. Please read our previous article, which discusses the basic concepts of SSO Authentication. This is the First Application of SSO Implementation.
Authentication Server Application using ASP.NET Core Web API
In this project, we will demonstrate how to build an Authentication Server using ASP.NET Core Web API, using powerful technologies such as ASP.NET Core Identity, JSON Web Tokens (JWT), and Entity Framework Core with SQL Server. The server not only handles basic user registration and login but also supports Single Sign-On (SSO), allowing users to authenticate once and access multiple services securely without repeated logins.
Key Technologies and Their Roles
- ASP.NET Core Identity: This framework simplifies user management by providing built-in features like user registration, login, password hashing, role management, and more. It manages user credentials securely in the database.
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): JWTs are compact, URL-safe tokens used to transmit information between parties securely. We use JWT to issue tokens after user authentication, enabling stateless, scalable authorization for API requests.
- Entity Framework Core (EF Core): EF Core is an Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) that enables us to interact with SQL Server databases using .NET objects, simplifying data access and reducing errors.
- SSO (Single Sign-On): SSO enables users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple related systems without needing to log in repeatedly. This server generates unique SSO tokens to facilitate this seamless user experience.
Core Functionalities of the Authentication Server
This Authentication Server will handle essential security operations such as User Registration, Login, SSO Token Generation, and SSO Token Validation, which are fundamental to Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication.
1. User Registration
This is the process by which new users create accounts in the system. It involves collecting user details such as username, email, and password, and then securely storing them in the database.
- ASP.NET Core Identity automatically handles user creation, password hashing, and data storage.
- Proper validation ensures that the data is accurate and secure before an account is created.
2. User Login
Once registered, users can log in by providing their username and password.
- The system verifies the credentials against the stored data.
- On successful authentication, the server generates a JWT token.
- The JWT token serves as proof of authentication and is required for accessing protected API endpoints without requiring repeated logins.
3. SSO Token Generation
After logging in, users can request an SSO token.
- The server generates a unique, time-limited token (typically a GUID) and stores it along with metadata, including expiration time, user details, and usage status.
- This SSO token enables users to authenticate across multiple services without needing to re-enter their credentials.
- It improves the user experience and enhances security by limiting token reuse and setting an expiry time.
4. SSO Token Validation
When a user presents an SSO token to access another service:
- The server checks whether the token:
- Exists in the database,
- Has not already been used,
- Is still within its valid time frame.
- If valid, the token is marked as used, and a new JWT token is issued for access.
- If invalid or expired, access is denied.
Creating a New Project and Adding Necessary NuGet Packages
Open Visual Studio and create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project named AuthenticationServer. Once you create the Project, please add the following NuGet packages, which are required for Entity Framework Core with SQL Server Database, Identity Setup, and JWT Authentication.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer: Enables EF Core to work with SQL Server.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools: Provides command-line tools for EF Core (e.g., migrations).
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore: Integrates ASP.NET Core Identity with Entity Framework Core.
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer: Supports JWT Bearer token authentication.
You can add these packages using NuGet Package Managers for Solution or by executing the following code in Visual Studio Package Manager Console:
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
- Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
- Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer
Creating SSO Token Model:
By default, ASP.NET Core Identity manages users and roles but does not provide a built-in model for SSO token management. Therefore, we need to create a custom model to manage SSO tokens.
First, create a folder named Models in the project root directory. Then, create a class file named SSOToken.cs within the Models folder and copy and paste the following code.
namespace AuthenticationServer.Models
{
public class SSOToken
{
public int Id { get; set; } // Unique ID for the token record
public string UserId { get; set; } = null!; // Links token to a specific user
public string Token { get; set; } = null!; // The SSO token string (usually a GUID)
public DateTime ExpiryDate { get; set; } // When the token expires
public bool IsUsed { get; set; } // Whether the token has been used
public bool IsExpired => DateTime.UtcNow > ExpiryDate; // Computed property to check if the token is expired.
}
}
Explanation of Each Property (Regarding SSO):
- Id: Primary key identifying the SSO token record.
- UserId: Associates the token with a user, enabling us to identify which user the token belongs to.
- Token: The actual unique SSO token string generated for authentication (a GUID).
- ExpiryDate: Defines the validity period of the token; tokens become invalid after this time.
- IsUsed: Flags if the token has been consumed to prevent reuse, enhancing security.
- IsExpired: A read-only computed property that returns true if the current UTC time is past expiry.
Define EF Core Db Context
Next, we need to define the Context class for Entity Framework Core. The Context class must be inherited from the IdentityDbContext class instead of the DbContext class. This is required because IdentityDbContext provides all the DbSet properties needed to manage the identity tables in SQL Server.
Also, we need to include the SSOToken model as a DbSet property for which we want to create the SSOTokens table in the database. So, first create a folder named Data and inside the Data folder, create a class file named ApplicationDbContext.cs and copy and paste the following code:
using AuthenticationServer.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace AuthenticationServer.Data
{
// IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser> provides all the necessary tables for authentication, such as AspNetUsers, AspNetRoles, etc.
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser>
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{ }
public DbSet<SSOToken> SSOTokens { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
Here
- IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser>: Includes built-in Identity tables like AspNetUsers, AspNetRoles, etc.
- DbSet<SSOToken>: Tells EF Core to create a table for SSO tokens and manage CRUD operations.
Configuring Connection String and JWT Keys in AppSettings.json file:
Next, we need to define our connection string and JWT settings in the appsettings.json file to centralize configuration. So, please modify the appaettings.json file as follows.
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"AuthenticationServerDBConnection": "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=AuthenticationServerDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"Jwt": {
"Key": "KHPK6Ucf/zjvU4qW8/vkuuGLHeIo0l9ACJiTaAPLKbk=", //Secret Key
"Issuer": "https://localhost:7035" //Authentication Server Domain URL Base Address
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
Configure Services in the Program.cs
Next, we need to register all required services in the dependency injection container, including EF Core, Identity, JWT Authentication, and Swagger for API documentation. The following are the key configurations:
- Adding DbContext with SQL Server connection.
- Adding Identity services with default token providers.
- Setting JWT bearer authentication with token validation parameters.
- Adding controllers and Swagger/OpenAPI services.
So, please modify the Program.cs class file as follows. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
using AuthenticationServer.Data;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
using System.Text;
namespace AuthenticationServer
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Adds support for controllers to the application.
builder.Services.AddControllers()
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
// Disable Camel Case
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
// Configures the ApplicationDbContext to use SQL Server with the connection string from the configuration file.
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("AuthenticationServerDBConnection")));
// Adding ASP.NET Core Identity services.
builder.Services.AddIdentity<IdentityUser, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders(); //Enable support for Password Reset, Email Confirmation, Phone Verification, and 2FA
// Adding and configuring authentication to use JWT Bearer tokens.
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
//Default Authentication Scheme
options.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
})
// Adding the JwtBearer authentication handler to validate incoming JWT tokens.
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
// Configuring the parameters for JWT token validation.
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true, // Ensure the token's issuer matches the expected issuer.
ValidateAudience = false, // Ensure the token's audience matches the expected audience.
ValidateLifetime = true, // Validate that the token has not expired.
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true, // Ensure the token is signed by a trusted signing key.
ValidIssuer = builder.Configuration["Jwt:Issuer"], // The expected issuer, retrieved from configuration (appsettings.json).
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(builder.Configuration["Jwt:Key"] ?? string.Empty)) // The symmetric key used to sign the JWT, also from configuration (appsettings.json).
};
});
// Adds Swagger/OpenAPI documentation.
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configuring the HTTP request pipeline (middleware components).
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
// Enable authentication middleware.
app.UseAuthentication();
// Enable authorization middleware.
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Creating Data Transfer Objects (DTOs):
DTOs define the shape of data exchanged between clients and server endpoints, focusing only on required fields to enhance security and maintain clean interfaces. First, create a folder named DTOs in the project root directory, and then add the following DTOs.
RegisterDTO
Create a class file named RegisterDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, then copy and paste the following code. This DTO is used for user registration by encapsulating the necessary information (username, email, and password).
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace AuthenticationServer.DTOs
{
public class RegisterDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Username is Required")]
public string Username { get; set; } = null!;
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Please provide a valid Email")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Email is Required")]
public string Email { get; set; } = null!;
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is Required")]
public string Password { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
LoginDTO
Create a class file named LoginDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, then copy and paste the following code. This DTO provides a straightforward way to pass the username and password when logging in.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace AuthenticationServer.DTOs
{
public class LoginDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Username is Required")]
public string Username { get; set; } = null!;
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is Required")]
public string Password { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
LoginResponseDTO
Create a class file named LoginResponseDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, then copy and paste the following code. This DTO returns the authentication result (e.g., a JWT token) after a successful login.
namespace AuthenticationServer.DTOs
{
public class LoginResponseDTO
{
public string Token { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
SSOTokenResponseDTO
Create a class file named SSOTokenResponseDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, then copy and paste the following code. This DTO is used to return the generated SSO token.
namespace AuthenticationServer.DTOs
{
public class SSOTokenResponseDTO
{
public string SSOToken { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
ValidateSSOTokenRequestDTO
Create a class file named ValidateSSOTokenRequestDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, then copy and paste the following code. This DTO encapsulates the SSO token that the server needs to validate.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace AuthenticationServer.DTOs
{
public class ValidateSSOTokenRequesDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "SSOToken is Required")]
public string SSOToken { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
ValidateSSOTokenResponseDTO
Create a class file named ValidateSSOTokenResponseDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, then copy and paste the following code. This DTO provides both a new JWT token and user details after successful SSO token validation. This DTO ensures that the client receives all the necessary information in a single response. Returning the User Details is optional.
namespace AuthenticationServer.DTOs
{
public class ValidateSSOTokenResponseDTO
{
public string Token { get; set; } = null!;
public UserDetails? UserDetails { get; set; }
}
public class UserDetails
{
public string UserId { get; set; } = null!;
public string? Username { get; set; }
public string? Email { get; set; }
}
}
Creating Authentication Controller: API Endpoint
This controller provides endpoints to handle all authentication-related operations:
- Register: Accepts registration data, creates a new user with ASP.NET Core Identity, and returns success or error messages.
- Login: Validates credentials and issues a JWT token on success.
- GenerateSSOToken: Creates a unique SSO token for authenticated users with a 10-minute expiry.
- ValidateSSOToken: Validates SSO token’s existence, usage, and expiry; marks it as used; and returns a new JWT with user details.
A helper method, GenerateJwtToken, is used internally to create signed JWT tokens with relevant claims. Create a new API Empty Controller named AuthenticationController within the Controllers folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
using AuthenticationServer.Data;
using AuthenticationServer.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
using System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Text;
using AuthenticationServer.DTOs;
namespace AuthenticationServer.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class AuthenticationController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly UserManager<IdentityUser> _userManager;
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _context;
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
// Constructor to inject the required services:
// UserManager, ApplicationDbContext, IConfiguration
public AuthenticationController(
UserManager<IdentityUser> userManager,
ApplicationDbContext context,
IConfiguration configuration)
{
_userManager = userManager;
_context = context;
_configuration = configuration;
}
// POST: api/Authentication/Register
[HttpPost("Register")]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<IActionResult> Register([FromBody] RegisterDTO dto)
{
// Create a new IdentityUser based on the incoming model data
var user = new IdentityUser
{
UserName = dto.Username,
Email = dto.Email
};
// Create the user in the identity system
var result = await _userManager.CreateAsync(user, dto.Password);
// If creation succeeded, return a success message
if (result.Succeeded)
{
return Ok(new { Result = "User Registered Successfully" });
}
// If creation failed, return the validation errors
return BadRequest(result.Errors);
}
// POST: api/Authentication/login
[HttpPost("Login")]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<ActionResult<LoginResponseDTO>> Login([FromBody] LoginDTO dto)
{
// Find the user based on the username
var user = await _userManager.FindByNameAsync(dto.Username);
// Validate the user's credentials
if (user != null && await _userManager.CheckPasswordAsync(user, dto.Password))
{
// Generate the JWT token and return it
var token = GenerateJwtToken(user);
LoginResponseDTO loginResponseDTO = new LoginResponseDTO()
{
Token = token,
};
return Ok(loginResponseDTO);
}
// If authentication fails, return an unauthorized response
return Unauthorized("Invalid username or password");
}
// POST: api/Authentication/GenerateSSOToken
[HttpPost("GenerateSSOToken")]
[Authorize] // Ensures that the user is authenticated
public async Task<ActionResult<SSOTokenResponseDTO>> GenerateSSOToken()
{
try
{
// Get the UserId from the JWT Token Claims
var UserId = User.FindFirstValue("User_Id");
if (UserId == null)
{
return NotFound("Invalid token");
}
// Fetch the user from the database using the UserId
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(UserId);
// Check if the user exists
if (user == null)
{
return NotFound("User not found");
}
// Create a new SSO token and add it to the database
var ssoToken = new SSOToken
{
UserId = user.Id,
Token = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), // Generate a unique SSO token
ExpiryDate = DateTime.UtcNow.AddMinutes(10), // Set an expiration time for the token
IsUsed = false
};
// Add the token to the database
_context.SSOTokens.Add(ssoToken);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
//Prepare the Response
SSOTokenResponseDTO ssoTokenResponseDTO = new SSOTokenResponseDTO()
{
SSOToken = ssoToken.Token
};
// Return the newly created SSO token
return Ok(ssoTokenResponseDTO);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle any exceptions that occur and return a server error response
return StatusCode(500, $"Internal server error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// POST: api/Authentication/ValidateSSOToken
[HttpPost("ValidateSSOToken")]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<ActionResult<ValidateSSOTokenResponseDTO>> ValidateSSOToken([FromBody] ValidateSSOTokenRequesDTO request)
{
try
{
// Fetch the SSO token from the database
var ssoToken = await _context.SSOTokens.FirstOrDefaultAsync(t => t.Token == request.SSOToken);
// Check if the token is valid (exists, not used, not expired)
if (ssoToken == null || ssoToken.IsUsed || ssoToken.IsExpired)
{
return BadRequest("Invalid or expired SSO token");
}
// Mark the token as used
ssoToken.IsUsed = true;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Find the user associated with the SSO token
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(ssoToken.UserId);
if (user == null)
{
return BadRequest("Invalid User");
}
// Generate a new JWT
var newJwtToken = GenerateJwtToken(user);
// Return the new JWT token along with user details (e.g., username and email)
ValidateSSOTokenResponseDTO validateSSOTokenResponseDTO = new ValidateSSOTokenResponseDTO()
{
Token = newJwtToken,
UserDetails = new UserDetails()
{
UserId = user.Id,
Email = user.Email,
Username = user.UserName
}
};
return Ok(validateSSOTokenResponseDTO);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle exceptions and return a server error response
return StatusCode(500, $"Internal server error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Helper method to generate a JWT token for the authenticated user
private string GenerateJwtToken(IdentityUser user)
{
// Defines a set of claims to be included in the token.
var claims = new List<Claim>
{
// Custom claim using the user's ID.
new Claim("User_Id", user.Id.ToString()),
// Standard claim for user identifier, using username.
new Claim(ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier, user.UserName ?? string.Empty),
// Standard claim for user's email.
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Email, user.Email ?? string.Empty),
// Standard JWT claim for subject, using user ID.
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Sub, user.Id.ToString())
};
// Get the symmetric key from the configuration and create signing credentials
var key = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(_configuration["Jwt:Key"] ?? string.Empty));
var creds = new SigningCredentials(key, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
// Create the JWT token
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: _configuration["Jwt:Issuer"]
claims: claims,
expires: DateTime.UtcNow.AddMinutes(30),
signingCredentials: creds);
// Serialize the token and return it as a string
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token);
}
}
}
Database Migration
Once the models and DbContext are ready, run Add-Migration IdentityMigration1 in the Package Manager Console. This command generates the migration scripts based on your models. Then, run Update-Database to apply migrations and create or update database tables, as shown in the image below.
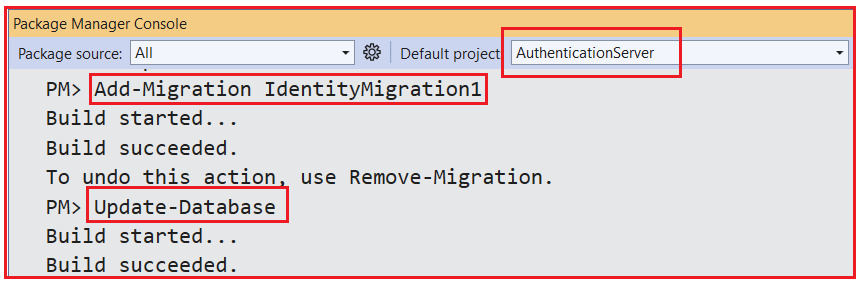
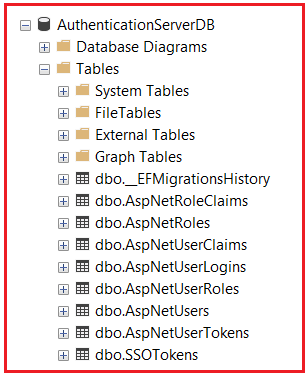
This process creates all ASP.NET Core Identity tables, as well as your custom SSOTokens table, as shown in the image below.
Testing the Registration Endpoint
Endpoint: /api/Authentication/ Register
Method: POST
Request Body:
{
"Username": "Pranaya",
"Email": "Pranaya@Example.com",
"Password": "Test@1234"
}
Expected Response: If successful, you will receive a 200 OK response with the message:
Testing the Login Endpoint
Endpoint: /api/Authentication/Login
Method: POST
Request Body:
{
"Username": "Pranaya",
"Password": "Test@1234"
}
Expected Response: On success, you should receive a 200 OK response with a JWT token:
Testing the Generate SSO Token Endpoint
Endpoint: /api/Authentication/GenerateSSOToken
Method: POST
Request Header:
Authorization: Bearer <JWT Token>
Expected Response: On success, you should receive a 200 OK response with the generated SSO token:

Testing the Validate SSO Token Endpoint
Endpoint: /api/Authentication/ValidateSSOToken
Method: POST
Request Body Example:
{
"SSOToken": "9d813b1f-569c-4e86-8e3c-554c0198b2cd"
}
Expected Response: On success, you should receive a 200 OK response with a new JWT token:

That’s it. We are done with our Authentication Server Implementation using ASP.NET Core Web API, ASP.NET Core Identity, Entity Framework Core with SQL Server Database.
By implementing this Authentication Server, you create a solid foundation for managing user identities and securing API access in modern web applications. The use of ASP.NET Core Identity combined with JWT tokens ensures scalable and stateless authentication, while the SSO mechanism enhances user convenience across multiple systems. This approach offers a flexible and secure solution that can be extended with additional features like email confirmation, password recovery, and multi-factor authentication as needed.
That’s it. We have completed the implementation of our Authentication Server using ASP.NET Core Web API, ASP.NET Core Identity, and Entity Framework Core with an SQL Server Database. In the next article, I will discuss how to implement the Resource Server using ASP.NET Core Web API. I hope you enjoy this article on implementing an authentication server using ASP.NET Core Web API.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
