Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
How to Install Swagger API in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss how to Install and Use Swagger API in the ASP.NET Core Web API Project. I will show you both the Options: Adding Swagger API while creating the Project and Adding Swagger API after creating the Project. Please read our previous article, where we discussed Default ASP.NET Core Web API Files and Folders, i.e., those created by default when we create a new ASP.NET Core Web API Application.
What is Swagger in ASP.NET Core Web API?
Swagger, often implemented using the Swashbuckle package, is a powerful tool used for documenting RESTful APIs developed with ASP.NET Core Web API. It provides a way to help plan, design, and document RESTful APIs. Swagger in ASP.NET Core Web API helps developers create, document, and consume RESTful APIs.
Swagger, now more commonly referred to as OpenAPI, helps both developers who produce APIs and those who consume them. It provides beautiful, interactive documentation that allows users to try out API calls directly from the browser.
Key Features of Swagger in ASP.NET Core Web API:
- API Documentation: Swagger automatically generates interactive API documentation, known as Swagger UI, based on your ASP.NET Core Web API Project. This documentation includes details about endpoints, parameters, request and response schemas, and even allows users to try out API calls directly from the documentation interface. The documentation can be dynamically updated as changes occur in the API.
- Standardization: Swagger uses the OpenAPI Specification (OAS), which is a widely adopted industry standard for documenting RESTful APIs.
- Testing and Debugging: Through Swagger UI, developers can send requests to the API, view the responses, and effectively test API functionality in a user-friendly web interface without the need for a separate tool or writing additional code. This real-time interaction helps in debugging and improving the API during the development phase.
- API Versioning: Swagger supports easy API versioning, which is important for evolving an API without breaking the existing client integrations. It provides a clear and structured way to communicate changes and deprecations to API consumers.
How to Install the Swagger Package in ASP.NET Core Web API:
Integrating Swagger into the ASP.NET Core Web API project is straightforward using the Swashbuckle.AspNetCore NuGet package. Once we install the package and register the required Swagger services and middleware components, Swagger automatically generates the API documentation, reducing the effort required to maintain separate documentation files.
We can install the Swagger API while creating a new Project or after the project is created. We can install the Swashbuckle.AspNetCore Package using the Nuget Package Manager for Solution or the Package Manager Console. Let us proceed and see both options for installing the Swagger API Package.
Method 1: Enable Swagger API While Creating the ASP.NET Core Web API Project
While creating a new ASP.NET Core Web API Project, we can check the Enable OpenAPI Support checkbox while providing the Additional Information, which will automatically install the Swagger API in our project, as shown in the image below.
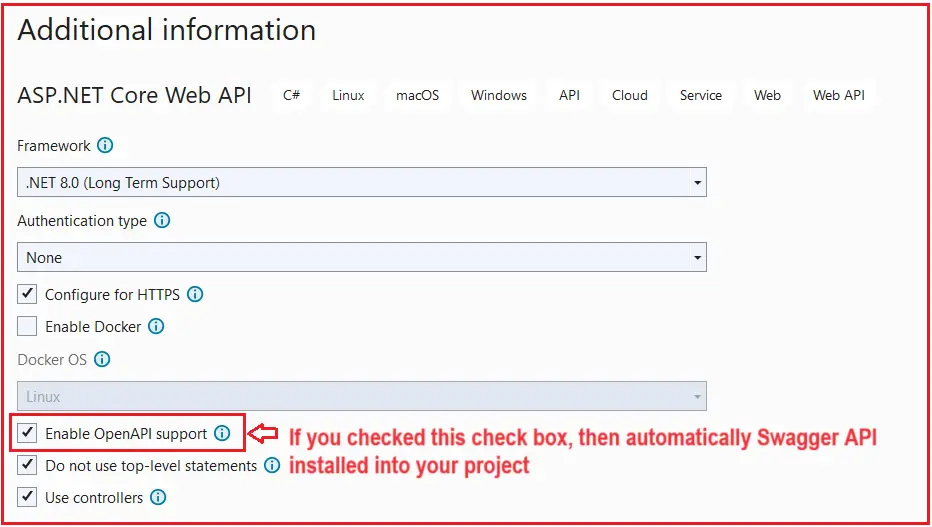
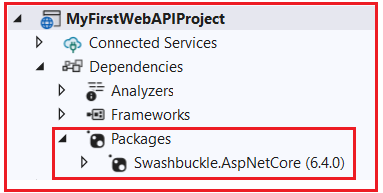
If you remember, in our Creating ASP.NET Core Web API Project in Visual Studio article, we checked this checkbox while creating the project, which is why we can access the Swagger Page in our application. If Swagger is installed, then you will find the corresponding Swashbuckle.AspNetCore package is inside the Packages folder, which comes inside the Dependencies folder, as shown in the image below. Any package that we install in our Project will come inside the Packages folder.
Method 2: Installing Swagger API using NuGet Package Manager
If you have already created the ASP.NET Core Web API project without checking the Enable OpenAPI support checkbox, you can still install the Swagger API using NuGet Package Manager. So, let us create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project with the name SwaggerDemo, and in the Addition Information window, please uncheck the Enable OpenAPI support checkbox as shown in the image below.

Once you create the project, you will see the Swashbuckle.AspNetCore package is not installed, as shown in the image below. There is no Packages folder under the Dependencies folder, which means no additional packages are installed in our project.

Let’s see how to add the Swagger Packages to our Project. To Add Swagger, open the NuGet Package Manager window and search for Swashbuckle.AspNetCore is in the browse tab, as shown in the image below. Then, choose the Swashbuckle.AspNetCore package, select the project where you want to install this package, and finally, click on the Install button, as shown in the image below.

Once you click on the Install button, the Preview Changes window will open. Click on the OK button, as shown in the image below.

Then, it will open the Accept License window. Click on the I Accept button to accept the license, as shown in the image below.

That’s it. It will install the Swagger API Package. If you verify the Dependencies folder, you will see the following. It should add the Packages folder, and within the Packages folder, it should add the Swashbuckle.AspNetCore package.

Note: You can also install the Swagger API using the Package Manage Console window as: Install-Package Swashbuckle.AspNetCore
Configure Swagger Services:
To configure Swagger API, we need to add the AddEndpointsApiExplorer() and AddSwaggerGen() services to the built-in dependency injection container within the Main method of the Program class, as shown in the code below. Both AddEndpointsApiExplorer and AddSwaggerGen are typically used together when setting up a project that uses Swagger for documenting APIs.
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer(); builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
AddEndpointsApiExplorer() Service:
The AddEndpointsApiExplorer() method configures the API Explorer service, which is responsible for providing metadata about API endpoints in our ASP.NET Core application. This metadata includes details such as:
- Names of Controllers and Actions.
- Supported HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.).
- Route templates and parameters.
- Data types of input and output parameters.
This service is essential when using libraries like Swashbuckle to generate Swagger documentation. It enables the generation of API metadata, which tools like Swagger use to produce human-readable documentation of our API endpoints.
This method should be called before adding Swagger or any API documentation-related services, as it prepares the API endpoints for further exploration and data extraction by these tools.
AddSwaggerGen() Service:
AddSwaggerGen is a method from the Swashbuckle.AspNetCore package that adds Swagger generation services to the project. It generates the Swagger/OpenAPI specification document (swagger.json) based on the API metadata provided by the API Explorer. AddSwaggerGen configures and initializes the generation of the OpenAPI specification, which includes information about all the paths, operations, and information flows of your API.
This method also allows for customization of the Swagger documentation, such as setting the title and version and even adding custom descriptions and schemas. This specification is then used to power the interactive Swagger UI, which provides a rich and interactive documentation interface.
Enable Swagger Middleware Components:
Once we configure the Swagger API services to the built-in dependency injection container, we need to register the Swagger Middleware components in the Application Request Processing Pipeline. To enable Swagger, we need to register the following Middleware Components in the Program class.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
UseSwagger Middleware:
The UseSwagger middleware serves the generated Swagger specification as a JSON endpoint. This JSON file is the output of the AddSwaggerGen service, which creates a Swagger document based on your API’s structure and annotations. By default, the UseSwagger middleware makes this document available at a specified URL path, usually /swagger/v1/swagger.json.
UseSwaggerUI Middleware:
The UseSwaggerUI middleware provides a web-based user interface that reads the Swagger JSON document by UseSwagger and presents a rich, interactive, and user-friendly page. This page allows developers to see the endpoints, parameters, and other important details of the API. They can also try out API calls directly from their browser, which is highly beneficial for testing and demonstrations.
With the above changes, the Program.cs class file code should look as follows. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
namespace SwaggerDemo
{
public class Program
{
// Main method: the entry point of the application.
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new builder for the web application using the command-line arguments provided.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the dependency injection container.
// Here, MVC controllers are being added, which handle web API requests.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Registering Swagger services to help generate API documentation and provide an API explorer.
// Register the necessary services to enable API exploration capabilities
// which Swashbuckle utilizes to generate Swagger documentation
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
// Add Swagger generator services to the services container.
// This will be used to produce the Swagger document (OpenAPI spec) and the Swagger UI
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
// Build the web application using the configurations defined above.
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline, which handles incoming HTTP requests.
// Register Swagger middleware components if in development environment
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
// UseSwagger middleware to serve the generated Swagger as a JSON endpoint.
app.UseSwagger();
// UseSwaggerUI middleware to serve the Swagger UI.
// Swagger UI fetches the Swagger JSON to generate a visual documentation of the API.
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
// Middleware to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS.
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
// Middleware to enforce authorization policies on requests.
app.UseAuthorization();
// Map controller routes. This makes the application aware of the routes defined in the controllers.
app.MapControllers();
// Run the application and start listening for incoming HTTP requests.
app.Run();
}
}
}
How Swagger Works in ASP.NET Core Web API:
Let us understand how Swagger works in ASP.NET Core Web API:
- AddEndpointsApiExplorer(): It generates the Metadata about the API’s endpoints. This includes details like available HTTP methods (GET, POST, etc.), parameters, and route templates. It is used by the AddSwaggerGen() service to understand the API structure and create an accurate OpenAPI specification document.
- AddSwaggerGen(): It generates an OpenAPI specification document. This comprehensive JSON file describes all endpoint URLs, expected parameters, response models, and authentication methods. The UseSwagger() Middleware Component uses it to serve this document at a specific URL.
- UseSwagger(): It serves the OpenAPI specification document over the network. Tools like Swagger UI use it to fetch this document and visualize or interact with the API. It makes the specification available at a URL like /swagger/v1/swagger.json.
- UseSwaggerUI(): It generates a web-based user interface that reads the OpenAPI specification and provides an interactive way to explore the API. This includes executing API calls from the browser. It is used by API developers, testers, and other stakeholders to interact with the API without writing any additional code. You can access this page by using the URL /swagger/index.html
Run the API:
Now, we need to Build and Run the project. Then, access the Swagger UI by navigating to the URL: http://localhost:<port>/swagger, as shown in the below image.

Explore the API:
- Swagger UI will display a user-friendly interface with a list of available API endpoints.
- Click on an endpoint to expand it and view details like request parameters, response schemas, and example requests/responses.
- You can use the provided interface to send requests and receive responses directly from Swagger UI.
The swagger will display the details of all the web APIs available for your project. The image below shows one API, /WeatherForecast, with the type GET. Now click on the /WeatherForecast API to see the details shown in the image below.

Once you click on the /WeatherForecast API, the API details will appear, as shown in the image below.

Testing the API:
Now, let us see how to test the /WeatherForecast API using Swagger. To do so, click the try it out button, as shown in the image below.

Once you click on the Try it Out button, it will open below the screen. Here, you need to click on the Execute button, as shown in the image below.

Once you click on the Execute button, it will send a request to the server, and then whatever response it receives from the server will display, as shown in the image below. Here, you can find the request URL, the response body, the response status code, and the response headers.

Customizing Swagger in ASP.NET Core Web API
Customizing Swagger in an ASP.NET Core Web API project can be essential in various scenarios to enhance documentation, usability, and security and meet the specific requirements of your API consumers. This can also include custom information, such as API descriptions and contact information, licenses, versions, etc.
You can customize the Swagger metadata by configuring the SwaggerGen options in Program.cs. So, modify the AddSwaggerGen service as follows. As you can see here, we have provided more information about our APIs, such as the Title, Version, Description, Terms of Service, Contact, and License.
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("V10", new OpenApiInfo
{
Title = "My Custom API",
Version = "V10",
Description = "A Brief Description of My APIs",
TermsOfService = new Uri("https://dotnettutorials.net/privacy-policy/"),
Contact = new OpenApiContact
{
Name = "Support",
Email = "support@dotnettutorials.net",
Url = new Uri("https://dotnettutorials.net/contact/")
},
License = new OpenApiLicense
{
Name = "Use Under XYZ",
Url = new Uri("https://dotnettutorials.net/about-us/")
}
});
});
By default, Swagger API looks for version V1, but we have changed the version to version V10 here. So, we also need to configure the same into the Swagger Middleware component. So, next, modify the UseSwaggerUI as follows:
app.UseSwaggerUI(c =>
{
c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/V10/swagger.json", "My API V10");
});
With the above changes in place, run the application and navigate to the Swagger Page, and you should see the following:

That’s a brief overview of exploring an ASP.NET Core Web API project and integrating Swagger API documentation. In the next article, I will discuss Controllers in ASP.NET Core Web API Application. In this article, I try to explain the Swagger API in ASP.NET Core Web API. I hope you enjoy this Swagger API in the ASP.NET Core Web API article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
