Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
HTTP OPTIONS Method in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Implement the HTTP OPTIONS Method in ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Real-Time Examples. Please read our previous article discussing the HTTP HEAD Method in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
HTTP OPTIONS Method
The HTTP OPTIONS method is used to describe the communication options for the target resource. It is part of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web. The OPTIONS method requests permitted communication options for a given URL or server. This can be useful for discovering allowed methods and other options without initiating resource retrieval or other operations.
Key Characteristics of the HTTP OPTIONS Method:
- Purpose: The OPTIONS method allows clients to determine the features supported for a specific resource or server. For example, it can be used to determine which HTTP methods are supported by a server or endpoint.
- CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) Preflight Requests: In the context of CORS, the OPTIONS method is used as a preflight request to determine whether the actual request is safe to send. Before performing a request with an HTTP method other than GET or POST or with custom headers, browsers can use an OPTIONS request to check the rules defined by the server.
- Headers: Responding to an OPTIONS request typically includes headers that specify allowed methods and other options. Common headers such as Allow, which lists the supported HTTP methods (such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), and Access-Control-Allow-Methods for CORS, indicate which methods are allowed when accessing the resource from a different origin.
- No Resource Retrieval: The OPTIONS method does not retrieve the target resource’s content. It only retrieves the communication options available, making it a safe method that does not cause any side effects on the server.
How to Implement HTTP OPTIONS Method in ASP.NET Core Web API
The HTTP OPTIONS method in ASP.NET Core Web API is used to describe the communication options for the target resource. This method allows a client to determine the available HTTP methods and other options supported by the web server without performing any action or initiating a resource retrieval. It plays an important role in RESTful services. It is particularly useful for supporting Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) by informing clients about which HTTP headers are available for use in requests.
In ASP.NET Core Web API, handling the OPTIONS method can be achieved in various ways, depending on the level of customization and control required:
Attribute Routing
You can explicitly handle OPTIONS requests by decorating an action method with the [HttpOptions] attribute. This approach is useful when you need to provide custom logic for an OPTIONS request on a specific endpoint.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace HTTPMethodDemo.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/resource")]
public class ResourceController : ControllerBase
{
// Example of a GET method
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
return Ok("GET Response");
}
// Implementing OPTIONS
[HttpOptions]
public IActionResult Options()
{
Response.Headers.Add("Allow", "GET, POST, OPTIONS");
return Ok();
}
}
}
Now, run the application, test the OPTIONS endpoint using Postman, and check the response header as shown in the below image:
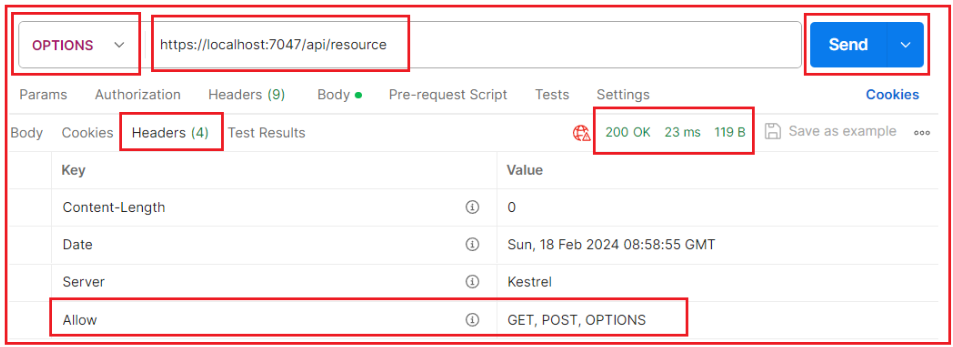
Global OPTIONS Handler
You might implement a global handler for OPTIONS requests for a more centralized approach. This can be done by configuring the request pipeline to check for OPTIONS requests and return a standardized response before reaching MVC middleware. So, add the following code to the Program.cs class file. If an OPTIONS request comes, the following middleware component will execute and return the response.
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
if (context.Request.Method == HttpMethods.Options)
{
context.Response.Headers.Add("Allow", "GET, POST, PUT, OPTIONS");
context.Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.OK;
return;
}
await next.Invoke();
});
Now, run the application, test the OPTIONS endpoint using Postman, and check the response header, as shown in the image below. You can also access it without specifying the URI.
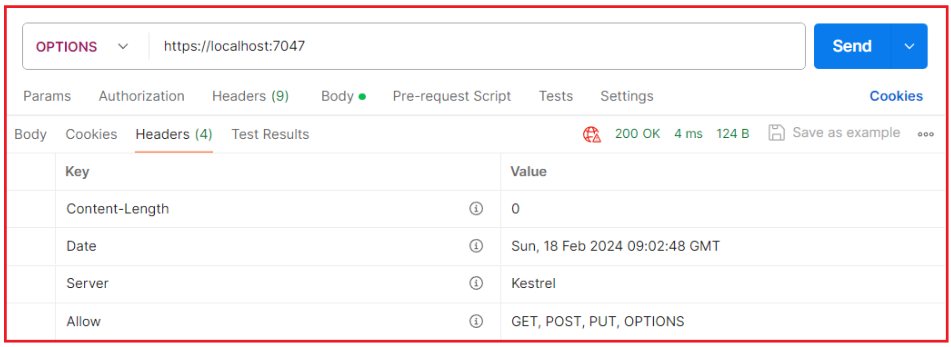
Automatic Handling via CORS Middleware
ASP.NET Core provides built-in middleware to handle CORS requests, including automatic responses to OPTIONS requests. When you configure CORS policies in your Program.cs class file, you can specify which origins, headers, and methods are allowed. The middleware intercepts OPTIONS requests and responds appropriately based on these policies without requiring additional code for each controller or action.
builder.Services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("AllowSpecificOrigins",
builder =>
{
builder.AllowAnyOrigin()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.WithMethods("GET", "POST", "OPTIONS");
});
});
Understanding the Origins, Header, and WithMethods Methods:
WithOrigins or AllowAnyOrigin
The WithOrigins method specifies which origins are allowed to request your Web API. An origin is defined by the scheme (http or https), host (domain or IP), and port of a URL. By specifying origins, you tell your API which domains are permitted to access your resources.
For example, if your API is hosted at https://api.example.com and you want to allow a web application hosted at https://www.client.com to access it, you would configure your CORS policy using WithOrigins like this: builder.WithOrigins(“https://www.client.com”);
You can specify multiple origins by adding more parameters to the WithOrigins method: builder.WithOrigins(“https://www.client.com”, “https://www.anotherclient.com”);
To allow all origins, you can use the AllowAnyOrigin method instead: builder.AllowAnyOrigin();
WithHeaders or AllowAnyHeader
HTTP requests can include various headers, which are used to pass information between the client and the server. The AllowAnyHeader method allows you to specify that your API should accept requests with any headers.
This is useful when your API needs to read custom headers sent by the client or when you want to simplify CORS configuration by not restricting headers: builder.AllowAnyHeader();
You can also specify which headers are accepted by the server using the WithHeaders method as: builder.WithHeaders(“header1”, “header2”); // Custom headers
WithMethods or AllowAnyMethod
The WithMethods method is used to specify which HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) can be used when accessing your API from the allowed origins. This allows you to restrict access to certain types of operations based on the request method. For example, if you want to allow only GET and POST requests from the specified origins, you would configure your CORS policy like this: builder.WithMethods(“GET”, “POST”);
To allow all standard HTTP methods, you can use the AllowAnyMethod method instead: builder.AllowAnyMethod();
Register the CORS Middleware:
Next, you need to ensure the CORS policy is applied to your HTTP requests. This is done in the Program.cs file using the UseCors middleware. Please add the following statement to the Program.cs class file. Here, UseCors is called with the name of the CORS policy you defined earlier (“AllowSpecificOrigins“). This applies the CORS policy to every request processed by the application.
app.UseCors(“AllowSpecificOrigins”);
Note: We will discuss CORS in detail in our upcoming articles. You will not check the CORS issue using client tools like Postman, Swagger, or Fiddler. We need to browse from a different domain to check the CORS issue, which we will discuss in our upcoming article.
Best Practices:
- CORS Policies: When using CORS middleware, ensure your policies are correctly configured to prevent unintended cross-origin requests.
- Custom Logic: If your OPTIONS response requires custom logic (e.g., varying allowed methods based on the request or resource state), consider handling OPTIONS requests explicitly in your controllers.
- Security: Always validate and sanitize inputs in your OPTIONS handlers to prevent security vulnerabilities.
When Should We Use HTTP OPTIONS Method in ASP.NET Core Web API?
The HTTP OPTIONS method is used in ASP.NET Core Web API (as well as in other web frameworks) to describe the communication options for the target resource. Its primary role is to allow the client to determine the options and/or requirements associated with a resource or the capabilities of a server without implying a resource action. Here are several scenarios where the OPTIONS method is particularly useful in ASP.NET Core Web API:
- CORS Preflight Requests: One of the most common uses of the OPTIONS method is handling Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) preflight requests. Browsers send an HTTP OPTIONS request to a server before making a request that could affect user data (e.g., POST, PUT, DELETE) to another domain that the browser has not interacted with before. This is done to ensure that the server accepts requests from the origin. In ASP.NET Core, CORS policies can be configured to handle these preflight requests automatically.
- Discovering Allowed HTTP Methods: The OPTIONS method can be used by clients to discover which HTTP methods are supported by a server at a given endpoint. This is particularly useful for RESTful APIs where different resources may support different sets of methods. For example, a client can send an OPTIONS request to a resource URI to determine if it supports methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. This helps in building dynamic clients that can adapt to the capabilities of the server.
- API Exploration and Documentation: While not its primary use, the OPTIONS method can be leveraged to provide metadata about the API, such as links to documentation or other related resources. This can allow developers to explore the API and understand its structure and capabilities without resorting to external documentation.
- Application-specific Uses: Developers can also use the OPTIONS method for application-specific purposes, such as implementing custom handshakes or negotiation mechanisms between the client and server. This could include negotiating data formats, language preferences, authentication mechanisms, etc., before making actual resource requests.
In the next article, I will discuss ASP.NET Core Web API using ADO.NET Core with Examples. In this article, I explain How to Implement the HTTP OPTIONS Method in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. I hope you enjoy this article, ” HTTP OPTIONS Method in ASP.NET Core Web API.”

