Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
Introduction to Unit Testing in ASP.NET Core
In this article, I will give you a brief introduction to Unit Testing in ASP.NET Core. Unit testing is like the regular health check-up for your code. Just as you visit a doctor to catch health issues early, unit tests help developers catch bugs as soon as new code is written. In modern software development, especially with frameworks like ASP.NET Core, unit testing isn’t just a “nice-to-have”; it’s a core practice that ensures code reliability, reduces long-term costs, and keeps software maintainable as it grows. This post will help you:
- Understand what unit testing is and how it’s different from integration and functional testing.
- Learn the purpose, benefits, and core principles of writing good unit tests.
- See practical, real-world examples using the xUnit framework.
What is Unit Testing?
Unit testing is a software testing approach that isolates and tests the smallest pieces of functionality in a program, commonly referred to as units. Typically, a unit is a method or function in an object-oriented programming language, such as C#. The goal is to verify that this unit performs correctly independently, without any dependency on external systems, such as databases, web services, or file systems.
- Isolation is key. You test a piece of code independently from the rest of the system.
- It ensures the unit behaves as intended for given inputs and produces expected outputs.
- Unit tests run fast and give immediate feedback, helping developers detect and fix issues early.
Examples to Understand the Importance of Unit Testing
Let’s understand the need for Unit Testing with some real-world scenarios.
Example 1: Calculator App: Imagine you have a calculator app with an “Add” button. Unit testing means writing a small test to check if the “Add” function returns the correct sum when you input 2 and 3, no matter what other buttons exist. If the test passes, you know the addition works perfectly, without needing to test the entire app.
Example 2: ATM Withdrawal: Before connecting to the bank’s backend, you test if the withdrawal function deducts the right amount from the user’s balance correctly. You isolate this function so it works as expected, regardless of the bank server’s status.
Example 3: Food Delivery App: Testing if the order calculation logic (price + tax + delivery fee) works correctly without involving the user interface or payment gateway systems.
Goals of Unit Testing
- Isolation: Unit tests should focus purely on the logic of the code being tested without interacting with external systems such as databases or APIs. This ensures that failures are due to problems within the code unit itself, rather than external factors.
- Validation of Logic: The test verifies that a method or function produces the correct output or effect for the given inputs, confirming the logic is accurate and complete.
- Speed: Because unit tests cover small pieces of code and avoid external dependencies, they run quickly. Fast tests provide developers with quick feedback, thereby speeding up the development process and enabling continuous integration.
What are the different Unit Testing Frameworks for ASP.NET Core?
There are several unit testing frameworks available in the .NET ecosystem. The following are the most popular for ASP.NET Core:
- xUnit.net: The most commonly used in ASP.NET Core projects. It offers simple, extensible test patterns and integrates well with .NET Core and Visual Studio. Uses [Fact] and [Theory] attributes for test methods.
- NUnit: A mature, feature-rich testing framework with extensive attributes and assertions. Uses [Test] for test methods. It is used for legacy and cross-platform projects.
- MSTest: Microsoft’s own testing framework, integrated into Visual Studio, is often used for legacy projects or those that prefer Microsoft tooling. Uses [TestMethod] attribute for test methods.
To determine which framework to use, please refer to the following diagram.
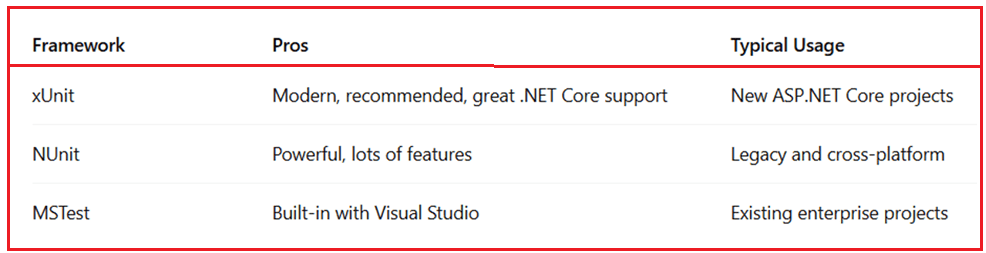
Note: All these frameworks integrate with Visual Studio and CI/CD tools, but xUnit is preferred for new ASP.NET Core projects.
Understanding the Testing Pyramid
The Testing Pyramid is a widely accepted model that illustrates the ideal distribution of automated tests in software development. It emphasizes having a large number of fast and isolated Unit Tests at the base, fewer Integration Tests in the middle that verify component interactions, and a small number of slower and more complex UI or Functional Tests at the top. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following diagram:
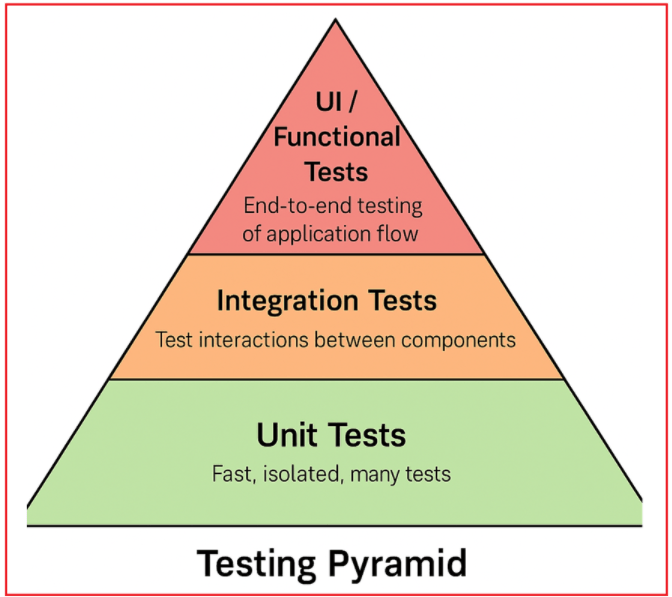
This structure helps maintain fast feedback cycles, cost-effective testing, and stable, maintainable software by focusing on robust unit tests while balancing the need for higher-level testing.
Example to Understand Unit Testing
Create a simple Console App first with the name CalculatorApp, but you can follow the same steps for an ASP.NET Core Web API project. Once you create the project, please add a class file named CalculatorService.cs and then copy and paste the following code. This class will be the target of our unit test. We will write a unit test for each of these methods.
namespace CalculatorApp
{
public class CalculatorService
{
// Adds two integers and returns the sum
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
// Subtract b from a
public int Subtract(int a, int b)
{
//Introducing some error by adding 5 to the result
return a - b + 5;
}
// Multiply two numbers
public int Multiply(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}
// Divide a by b; throws DivideByZeroException if b is zero
public int Divide(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
throw new DivideByZeroException("Division by zero is not allowed.");
return a / b;
}
}
}
Code Explanations:
- Each method is small, one public method = one unit.
- Methods return a value or throw an exception on invalid input (e.g., division by zero).
- No external dependencies (no database, no file I/O). This isolation makes testing straightforward.
What Exactly is a Unit?
In software, a unit is usually the smallest testable piece of code, often a single method or function within a class. For example, the Add method in CalculatorService is a unit. Testing it independently means verifying that it produces the correct result without needing to run the entire application.
Create the Unit Test Project
You should keep your unit tests in a separate project inside the same solution for better organization. So, add a new project to existing solution using the xUnit Test Project template which uses C# as the programming language and give the project name as CalculatorApp.Test. This will create a new project named CalculatorApp.Tests are configured to use xUnit.
Add Project Reference to the Main Project
Your test project must reference the main project to access its classes. So, from your test project, add a reference to your main project.
Arrange-Act-Assert (AAA) Pattern in Unit Testing
Unit tests should be clear, consistent, and readable. A well-structured unit test follows the Arrange-Act-Assert (AAA) pattern:
- Arrange: Set up the necessary objects, data, and prerequisites for the test.
- Act: Invoke the unit (method/function) under test.
- Assert: Verify that the output or behaviour matches the expected result.
For a better understanding, please have a look at the following diagram:

Write Unit Tests for Calculator Service
In xUnit, we decorate test methods with attributes to indicate their purpose:
- [Fact]: Marks a test method with no parameters. It tests a single scenario.
- [Theory]: Marks a parameterized test method. That means it allows parameterized tests that run multiple times with different input data. Input values are supplied using the [InlineData] attribute.
When creating a unit test, we need to provide a clear and descriptive test method name. A good test name typically follows this pattern: MethodName_StateUnderTest_ExpectedBehavior. This naming style helps anyone reading the test code understand exactly what is being tested and the expected outcome without requiring a deep dive into the implementation.
Create a class file named CalculatorServiceTests.cs inside the test project and then copy and paste the following code.
namespace CalculatorApp.Test
{
public class CalculatorServiceTests
{
// Arrange
private readonly CalculatorService _calculator;
// Constructor runs before each test; creates fresh CalculatorService instance
public CalculatorServiceTests()
{
// Arrange
_calculator = new CalculatorService();
}
// Test Add method for adding positive numbers
[Fact]
public void Add_WhenCalledWith2And3_Returns5()
{
// Arrange - done in constructor
// Act
var result = _calculator.Add(2, 3);
// Assert
Assert.Equal(5, result);
}
// Test Subtract method with positive numbers
[Fact]
public void Subtract_WhenCalledWith5And3_Returns2()
{
// Arrange - done in constructor
// Act
var result = _calculator.Subtract(5, 3);
// Assert
Assert.Equal(2, result);
}
// Parameterized test for Multiply method using Theory and InlineData
[Theory]
[InlineData(2, 3, 6)]
[InlineData(-2, 3, -6)]
[InlineData(0, 5, 0)]
public void Multiply_WhenCalled_ReturnsExpectedResult(int a, int b, int expected)
{
// Arrange - done in constructor
// Act
var result = _calculator.Multiply(a, b);
// Assert
Assert.Equal(expected, result);
}
// Test Divide method for normal case
[Fact]
public void Divide_WhenCalledWith6And3_Returns2()
{
// Arrange - done in constructor
// Act
var result = _calculator.Divide(6, 3);
// Assert
Assert.Equal(2, result);
}
// Test Divide method to check division by zero throws exception
[Fact]
public void Divide_WhenDividingByZero_ThrowsDivideByZeroException()
{
// Act and Assert
Assert.Throws<DivideByZeroException>(() => _calculator.Divide(10, 0));
}
}
}
Run All Tests:
To run all test cases, go to the Test menu and select Run All Tests from Visual Studio, as shown in the image below:

This will run all the test cases and display the results as shown in the image below.

Test Results: Passed tests show green check marks; failures show red crosses with detailed error messages.
Testing Individual Test Cases:
If you want to test individual test cases, then you need to choose Test => Test Explorer from the context menu, as shown in the image below:

This will open the following Page. Here, you can right-click on Individual Test Cases and click on the Run option to run the test case as shown in the image below:

Debug Tests:
Right-click a test → Debug to run tests with breakpoints for step-through debugging.
What is the Assert Class?
The Assert class is a core component of any unit testing framework. It provides a set of static methods that allow us to verify whether the code under test behaves as expected. Each assertion compares the actual result produced by the code against an expected value or condition. If the assertion passes, the test continues; if it fails, the test is marked as failed and usually stops execution.
Important Assert Methods:
The following are some of the most commonly used Assert methods:
- Assert.Equal(expected, actual): Verifies that two values are equal.
- Assert.NotEqual(notExpected, actual): Verifies that two values are not equal.
- Assert.True(condition): Verifies that a condition is true. For example, Assert.True(result > 0);
- Assert.False(condition): Verifies that a condition is false. For example, Assert.False(result < 0);
- Assert.Null(object): Verifies that an object is null.
- Assert.NotNull(object): Verifies that an object is not null.
- Assert.Same(expected, actual): Verifies that two object references refer to the same object.
- Assert.NotSame(notExpected, actual): Verifies that two object references do not refer to the same object.
- Assert.Empty(collection): Verifies that a collection is empty.
- Assert.NotEmpty(collection): Verifies that a collection is not empty.
Benefits of Unit Testing in Software Development
The following are the key reasons why unit testing is essential, especially in modern software development like ASP.NET Core:
Early Defect Detection
Unit tests are usually written alongside or just after the code itself, allowing developers to catch bugs immediately. Early bug detection saves time and reduces cost since fixing bugs later in QA or production is far more expensive.
- Example: If a calculation logic in a service method is wrong, a unit test will catch this mistake as soon as the code is written.
Enables Safe Refactoring
As software evolves, developers need to refactor code to improve readability, performance, or maintainability. Unit tests act as a safety net during this process, ensuring that any change does not unintentionally break existing functionality.
- Example: You optimize an order processing service’s logic. With unit tests, you know right away if your optimization breaks anything.
Improves Code Quality
Writing unit tests encourages writing code that is modular, loosely coupled, and single-responsibility oriented. These principles naturally make the code more maintainable and scalable.
- Example: When designing ASP.NET Core Web API controllers and services, building them with testability in mind often leads to better separation of concerns between layers.
Documentation for Developers
Unit tests serve as living documentation. They specify exactly how a piece of code should behave, what inputs it expects, and the expected outputs.
- Example: New developers joining a project can review unit tests to quickly understand system behaviour without sifting through large text documents.
Speeds Up Development (in the Long Run)
Though writing tests adds initial effort, it reduces debugging and troubleshooting time later. Developers can confidently add features or refactor without fear of breaking existing features.
- Example: A project with hundreds of APIs can be updated rapidly because unit tests ensure existing endpoints still work correctly after changes.
Unit testing is not just an optional task. It is an essential practice for building reliable, maintainable, and high-quality ASP.NET Core applications. It leads to faster development cycles, reduced bugs, safer code changes, and better documentation. Mastering unit testing empowers you to write cleaner code and deliver robust software with confidence.
In the next article, I will discuss Implementing Unit Testing in an ASP.NET Core Web API Project using the xUnit Framework. In this article, I provide an introduction to Unit Testing in ASP.NET Core. I hope you enjoy this article on ‘What Is Unit Testing in ASP.NET Core’.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.

Thanks for reading! If you’d like to see unit testing in ASP.NET Core explained with practical, real-time examples, don’t miss my YouTube video on this topic.
👉 Watch the full video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vU4cB03NDO0
Feel free to leave your questions or feedback in the video comments, and consider subscribing for more ASP.NET Core tutorials!