Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
401 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Return a 401 Unauthorized HTTP Status Code from the ASP.NET Core Web API Controller Action method with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing How to Return a 400 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
What is 401 HTTP Status Code?
The HTTP 401 Status Code indicates “Unauthorized.” The web server sends this status code when access to the requested resource requires authentication, and either the authentication has not been provided or has failed. It suggests that the client needs to authenticate themselves in order to get the requested response.
Common Causes of 401 Unauthorized:
- Missing or Incorrect Authentication Credentials: The client has not provided any credentials or has provided incorrect credentials.
- Expired or Invalid Token: In the case of token-based authentication, the token might be expired or invalid.
- Authentication Scheme Mismatch: The server might expect a different type of authentication than what was provided.
How it works:
- Client makes a request: A client sends a request to the server.
- The server needs authentication: If the server requires authentication credentials and the request lacks them, the server responds with a 401 status code.
- The client resends with credentials: Upon receiving the 401 response, the client can resend the request with the appropriate authentication credentials, such as a username and password, an API key, or a token.
Troubleshooting 401 Unauthorized
- Check Authentication Credentials: Verify that the credentials sent with the request are correct and valid.
- Review Token Expiry: Verify if the authentication token (like JWT) has expired and renew it if necessary.
- Permission Levels: Confirm that the authenticated user has the required permissions to access the resource.
- Verify Authentication Scheme: Make sure that the authentication scheme being used matches what the server expects (e.g., Basic, Bearer).
Note: In our upcoming article, we will discuss how to implement authentication and secure our endpoint. In this article, I am just going to give you an overview of the 401 Status Code by returning the same from our action method.
How to Return 401 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API?
Returning a 401 Status Code is typically used when an incoming request lacks valid authentication credentials for the requested resource. Depending on your application’s requirements, returning a 401 HTTP status code in an ASP.NET Core Web API can be achieved in several ways, such as within a controller action, using an attribute, or through middleware.
Returning Directly from a Controller Action
You can directly return a 401 status code from an action method using the Unauthorized() method provided by ControllerBase. This is useful for returning a 401 response in specific scenarios, such as when custom authentication logic determines that the request should be unauthorized. For a better understanding, please modify the EmployeeController as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult SecureResource()
{
// Your authentication logic here
// Assuming this is the result of your auth check
bool isAuthenticated = false;
if (!isAuthenticated)
{
return Unauthorized(); // Returns a 401 Unauthorized response
}
// Proceed with normal action if authenticated
return Ok("Authenticated and Authorized Access.");
}
}
}
In the above example, the SecureResource method checks if a user is authenticated using a hypothetical condition. If isAuthenticated is false, it returns a 401 Unauthorized status code by calling the Unauthorized() method without any parameters. Now, if you access the endpoint using Postman, then you will get the following response:
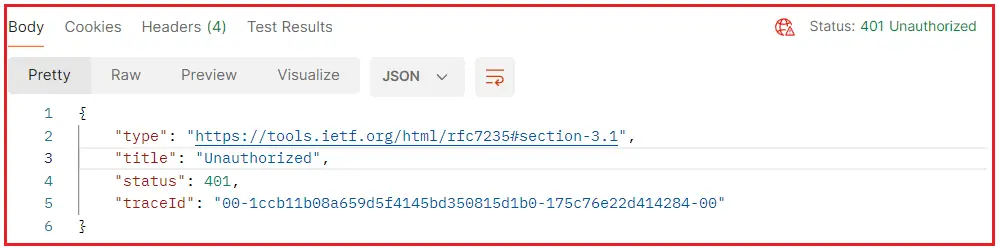
If you need to include additional information with the 401 Response, such as details about why the request is unauthorized or how to authenticate, you can pass an object to the Unauthorized method. For a better understanding, please modify the Controller as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult SecureResource()
{
// Your authentication logic here
// Assuming this is the result of your auth check
bool isAuthenticated = false;
if (!isAuthenticated)
{
// Returns a 401 Unauthorized response
return Unauthorized(new { message = "Access denied. Please provide valid credentials." });
}
// Proceed with normal action if authenticated
return Ok("Authenticated and Authorized Access.");
}
}
}
This would still return a 401 Status Code, but the response body will include the JSON object with the message property, as shown in the image below.
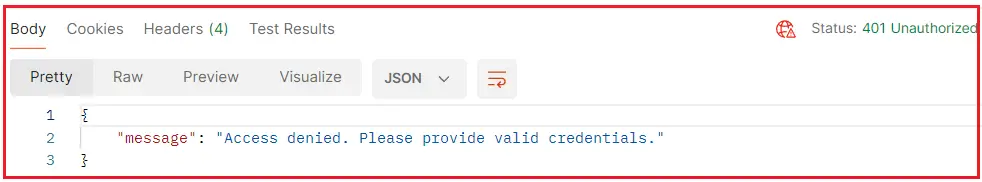
Manually Returning 401 Error Response:
Using the StatusCode method, we can also return the 401 Unauthorized Response along with the custom data. For a better understanding, please modify the controller as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult SecureResource()
{
// Your authentication logic here
// Assuming this is the result of your auth check
bool isAuthenticated = false;
if (!isAuthenticated)
{
// Returns a 401 Unauthorized response
var errorResponse = new
{
StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status401Unauthorized,
Message = "Access denied. Please provide valid credentials."
};
// Use StatusCode method to return 401 Unauthorized status and custom data
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status401Unauthorized, errorResponse);
}
// Proceed with normal action if authenticated
return Ok("Authenticated and Authorized Access.");
}
}
}
Response:

Middleware to Handle 401 Unauthorized Error
If you need to check authentication before reaching the MVC pipeline, you can implement custom middleware to inspect the request and potentially short-circuit the request pipeline by returning a 401 HTTP Status Code to the client. To better understand, please create a class file named CustomAuthenticationMiddleware.cs within the Models folder and copy and paste the following code. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines.
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Models
{
// Define a class for custom authentication middleware
public class CustomAuthenticationMiddleware
{
// Field to store the next middleware in the pipeline
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
// Constructor to initialize the middleware with the next RequestDelegate
public CustomAuthenticationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next; // Assign the next middleware to the private field
}
// Method that gets called for each request to handle authentication
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Custom authorization logic here
bool isAuthorized = CheckAuthorization(context); // Call the method to check authorization
if (!isAuthorized) // If the user is not authorized
{
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status401Unauthorized; // Set the response status code to 401
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json"; // Set the response content type to JSON
// Create a custom response object
var customResponse = new
{
status = 401, // Status code
message = "Unauthorized. Please Provide Valid Credentials" // Custom message
};
// Serialize the custom response object to JSON and write it to the response body
await context.Response.WriteAsync(System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(customResponse));
return; // Short-circuit the pipeline, preventing further middleware execution
}
// If the user is authorized, pass the request to the next middleware in the pipeline
await _next(context);
}
// Private method to check authorization
private bool CheckAuthorization(HttpContext context)
{
// Implement your authorization logic here
// For example, check for a specific header or token
// Simulate unauthorized for this example
return false; // Always return false to simulate an unauthorized request
}
}
}
Registration the Middleware
Once you define the custom middleware, then you need to register it within your application’s request processing pipeline, typically in the Program.cs file, using the UseMiddleware extension method before the MVC middleware. This ensures that your middleware is executed for every incoming HTTP request. So, please add the following statement to the Program.cs class file:
app.UseMiddleware<CustomAuthenticationMiddleware>();
Modifying the Employee Controller:
Next, modify the Employee Controller as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult SecureResource()
{
// Proceed with normal action if authenticated
return Ok("Authenticated and Authorized Access.");
}
}
}
Now, run the application and access the above endpoint, and you should get the following 401 Unauthorized response:

When Should We Use 401 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API?
The 401 HTTP status code should be used in an ASP.NET Core Web API in situations where the client must authenticate itself to get the requested response. The following are some of the specific scenarios where a 401 status code is appropriate:
- Missing Authentication Credentials: When the client makes a request without providing any authentication credentials, the server should respond with a 401 status code to indicate that authentication is required.
- Invalid Authentication Credentials: If the client provides authentication credentials that are invalid or incorrect, the server should respond with a 401 status code, indicating that the provided credentials are not valid.
- Expired Authentication Tokens: When the client’s authentication token (such as a JWT) has expired and is no longer valid, the server should respond with a 401 status code to indicate that the client needs to authenticate again.
- Protected Endpoints Without Authorization: When accessing endpoints that require authentication but the request lacks the necessary credentials, the server should respond with a 401 status code.
In the next article, I will discuss how to Return 403 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. In this article, I try to explain how to Return 401 Unauthorized HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. I hope you enjoy this article on “401 Unauthorized HTTP Status Code in the ASP.NET Core Web API.”
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.

Thank you.