Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
How to Configure the Allowed HTTP Methods Globally in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Configure the Allowed HTTP Methods Globally in ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing How to Return 405 Not Found HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
How to Configure the Allowed HTTP Methods Globally in ASP.NET Core Web API
Configuring the allowed HTTP methods globally in an ASP.NET Core Web API project is essential for defining which HTTP request methods (such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) your application will accept. This configuration can help improve the security and manageability of your API by ensuring that only intended methods are handled by your application. There are several approaches to achieve this configuration.
Using Custom Middleware to Configure Allowed HTTP Methods Globally
You can create custom middleware that checks the HTTP method of each request and decides whether to pass it to the next component in the pipeline or block it. So, create a class file named HttpMethodMiddleware.cs and copy and paste the following code. The following HttpMethodMiddleware class is a custom middleware component. It is used to filter incoming HTTP requests based on the HTTP method (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and only to allow requests that use specified methods. Requests that use disallowed methods are rejected with a “405 Method Not Allowed” status code. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
using System.Text.Json;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Models
{
// Declaring the HttpMethodMiddleware class
public class HttpMethodMiddleware
{
// Declaring a private field to store the next middleware delegate
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
// Declaring a private field to store the allowed HTTP methods
private readonly string[] _allowedMethods;
// Constructor to initialize the middleware with the next delegate and allowed methods.
public HttpMethodMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, string[] allowedMethods)
{
_next = next; // Storing the next delegate in the pipeline.
_allowedMethods = allowedMethods; // Storing the allowed HTTP methods.
}
// Asynchronous method that processes each HTTP request.
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Checks if the current HTTP method is not in the list of allowed methods.
if (!_allowedMethods.Contains(context.Request.Method))
{
// Setting status code to 405.
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status405MethodNotAllowed;
// Setting the response content type to JSON.
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
// Creating an anonymous object to hold the error details.
var customResponse = new
{
Code = 405, // HTTP status code for "Method Not Allowed".
Message = "HTTP Method not allowed" // Custom error message.
};
// Serializing the custom response object to JSON.
var responseJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(customResponse);
// Writing the serialized JSON to the HTTP response.
await context.Response.WriteAsync(responseJson);
return; // Short-circuiting the pipeline to prevent further processing.
}
// If the method is allowed, pass the context to the next middleware in the pipeline.
await _next(context);
}
}
}
This middleware checks if the HTTP method of incoming requests is allowed. If it’s not allowed, it returns a 405 Method Not Allowed status code with a JSON response indicating that the method is not supported. If the method is allowed, the request continues down the pipeline to the next middleware.
Register the Middleware
After creating the middleware, you need to register it in the Program class. It’s important to add it at the right location in the middleware pipeline to ensure it executes before executing any action method. Here, we need to specify which HTTP methods are allowed globally.
var allowedMethods = new[] { "GET", "POST", "DELETE" };
// Use a lambda to manually instantiate the middleware
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
var middleware = new HttpMethodMiddleware(next, allowedMethods);
await middleware.InvokeAsync(context);
});
Creating Controller:
Create the following controller. We have created the following controller using five different HTTP methods.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class SampleController : ControllerBase
{
// This action only supports GET method
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetAction()
{
return Ok("GetAction Data processed");
}
// This action only supports POST method
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult PostAction()
{
return Ok("PostAction Data Processed");
}
// This action only supports PUT method
[HttpPut]
public IActionResult PutAction()
{
return Ok("PutAction Data processed");
}
// This action only supports PUT method
[HttpPatch]
public IActionResult PatchAction()
{
return Ok("PatchAction Data processed");
}
// This action only supports DELETE method
[HttpDelete]
public IActionResult DeleteAction()
{
return Ok("DeleteAction Data processed");
}
}
}
Now, run the application and access the above endpoints. You will see that GET, POST, and DELETE requests are accepted, as shown in the below image:
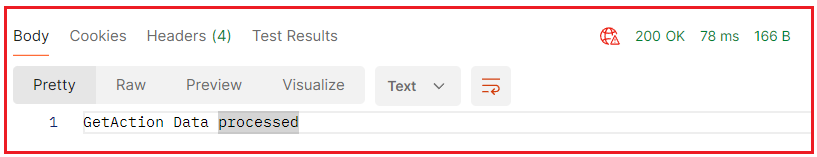
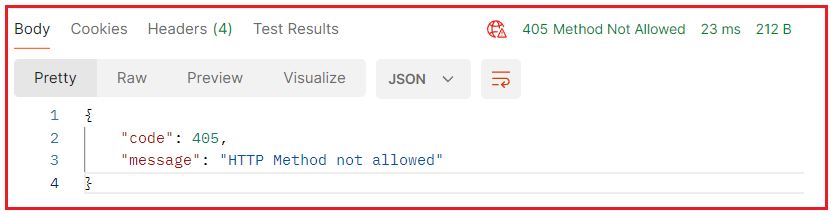
On the other hand, PUT and PATCH requests are going to return 405 Method Not Allowed responses, as shown in the image below.
Global Action Filter to Handle 405 Status Code
You can create a global action filter that checks the HTTP method of incoming requests and decides whether to allow or reject them. This filter can then be added to the MVC options in the Program.cs class file. So, create a class file named HttpMethodFilter.cs and copy and paste the following code. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Filters;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Models
{
// Declares a class that implements the IActionFilter interface to intercept actions in MVC.
public class HttpMethodFilter : IActionFilter
{
// Private field to hold allowed HTTP methods.
private readonly string[] _allowedMethods;
// Constructor to initialize the filter with a list of allowed methods.
public HttpMethodFilter(string[] allowedMethods)
{
// Stores the allowed HTTP methods passed during instantiation.
_allowedMethods = allowedMethods;
}
// Method called before an action method executes.
public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
// Check if the current request's HTTP method is not in the allowed list.
if (!_allowedMethods.Contains(context.HttpContext.Request.Method))
{
// Creates an anonymous object to represent the custom error response.
var customResponse = new
{
Code = 405, // HTTP status code for "Method Not Allowed".
Message = "HTTP Method not allowed" // Custom error message.
};
// Setting the action result to an ObjectResult with the custom response and status code.
context.Result = new ObjectResult(customResponse)
{
StatusCode = 405 // Explicitly setting the HTTP status code to 405.
};
}
}
// Method called after an action method executes.
public void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext context)
{
// This method is part of the IActionFilter interface but is not used here.
// You can implement post-processing logic here if needed.
// This method is intentionally left empty as no post-action processing is required
}
}
}
Here,
- HttpMethodFilter is an action filter specifically designed to restrict access based on the HTTP method used in the request.
- OnActionExecuting is implemented to intercept requests before they reach the controller action. It checks if the method is allowed, and if not, it sets the result of the context to a 405 Method Not Allowed status with a custom JSON response.
- OnActionExecuted is not used in this scenario but is required as part of the IActionFilter interface implementation. It could be used for any cleanup or additional processing after the action method is completed.
Registering the Filter Globally:
Please add the following code to the Program.cs class file. By adding the filter, we are specifying which HTTP methods are allowed for our application.
builder.Services.AddControllers(options =>
{
options.Filters.Add(new HttpMethodFilter(new[] { "GET", "POST", "DELETE" }));
});
With the above changes in place, run the application and test each endpoint. It should work as expected in the previous example.
In the next article, I will discuss how to Return the 500 Internal Server Error HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. In this article, I try to explain how to Configure the Allowed HTTP Methods Globally in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. I hope you enjoy this article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.


I got clear idea on this.thank u.