Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
How to Implement HTTP Post Method in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Implement the HTTP POST Method in ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Real-Time Examples. Please read our previous article discussing the HTTP GET Method in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
HTTP Post Method
The HTTP POST method sends data to a server to create a new resource. The data sent to the server with POST is stored in the body of the HTTP request. POST is one of the most common HTTP methods and is often used to submit form data or upload a file.
Characteristics of the POST Method:
- Data Encapsulation: The POST requests encapsulate data in the body of the request, making it a more secure way of transferring data. This is particularly useful for sensitive information, such as passwords, PINs, credit card details, etc.
- No Data Size Limit: POST does not limit the size of the request body, making it suitable for large data transfers like file uploads.
- Non-Idempotent: POST requests are non-idempotent, meaning multiple identical POST requests may have different effects, such as creating multiple records.
- Use Cases: Common use cases for POST requests include submitting form data, uploading files, and performing operations that change the state or update data on the server.
- Response Codes: Successful POST requests generally return HTTP status codes like 200 (OK) for successful updates, 201 (Created) if a new resource has been created, and 204 (No Content) if the action was successful but there is no additional content to send in the response.
- Headers: POST requests often include headers like Content-Type (to specify the type of the data being sent, such as application/json or application/xml) and Content-Length (to indicate the size of the request body).
How to Implement HTTP Post Method in ASP.NET Core Web API
The HTTP POST Method in ASP.NET Core Web API is designed to submit data to be processed (e.g., creating a resource). In ASP.NET Core Web API, Implementing POST requests involves defining an action method that uses the [HttpPost] attribute to process POST requests. This method usually accepts data sent in the request body, processes it, and returns a response.
Suppose we have an e-commerce application where we want to add a new product. Here’s how to implement a POST method in an ASP.NET Core Web API to create a new product. Let us understand this with an example.
Defining a Model
Define a C# class representing the data structure you wish to accept via POST requests. So, create a class file named Product.cs and then copy and paste the following code:
namespace HTTPMethodDemo.Models
{
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
}
}
Create a Service
Create a class file named ProductRepository.cs and copy and paste the following code. We are not interacting with the database here, but for simplicity, we are working with in-memory data. This is the repository where we will perform all database operations related to the product model.
namespace HTTPMethodDemo.Models
{
public class ProductRepository
{
public List<Product> Products = new List<Product>()
{
new Product() { Id = 1, Name= "Laptop", Price = 1000, Quantity = 10 },
new Product() { Id = 2, Name= "Desktop", Price = 2000, Quantity = 20 }
};
// Add a New Product and return the newly Created Product Id
public int AddProduct(Product product)
{
//Set the Product Id
product.Id = 3;
Products.Add(product);
return product.Id;
}
// Get a Product by ID
public Product GetById(int Id)
{
var product = Products.FirstOrDefault(u => u.Id == Id);
return product;
}
}
}
Here,
- AddProduct Method: This method is used to add a new product to the Products collection.
- GetById Method: This method is used to find a Product by its ID.
Register Service:
Please add the following statement to the Program.cs class file. This will add the service to the dependency injection container.
builder.Services.AddScoped<ProductRepository>();
Creating the Controller
Create a controller named ProductsController within the Controllers directory and copy and paste the following code. This controller will contain the action method that handles POST requests.
using HTTPMethodDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace HTTPMethodDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ProductRepository _productRepository;
public ProductController(ProductRepository productRepository)
{
_productRepository = productRepository;
}
// Post method for adding a new product
// POST api/product
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Post([FromBody] Product product)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
// Add the product to your data store.
int ProductId = _productRepository.AddProduct(product);
product.Id = ProductId;
// Return a 201 Created response with the created resource
return CreatedAtAction("GetProduct", new { Id = product.Id }, product);
}
// GET method for retrieving a product by ID
// GET api/product/1
[HttpGet("{Id}")]
public ActionResult<Product> GetProduct(int Id)
{
// Retrieve and return the product from your data store
var product = _productRepository.GetById(Id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(product);
}
}
}
Here,
- [HttpPost]: This attribute marks a method as a handler for HTTP POST requests.
- [FromBody]: This attribute tells ASP.NET Core Framework to get the value of the product parameter from the body of the incoming HTTP request. ASP.NET Core automatically deserializes the JSON in the request body to the Product type.
- CreatedAtAction: This method creates a CreatedAtActionResult object that produces a 201 Created response. It also adds a Location header to the response that specifies the URI of the newly created resource. In the CreatedAtAction method, you should pass the action name that can retrieve the resource (GetProduct in this case), the route values (including the id of the newly added product), and the object that was added.
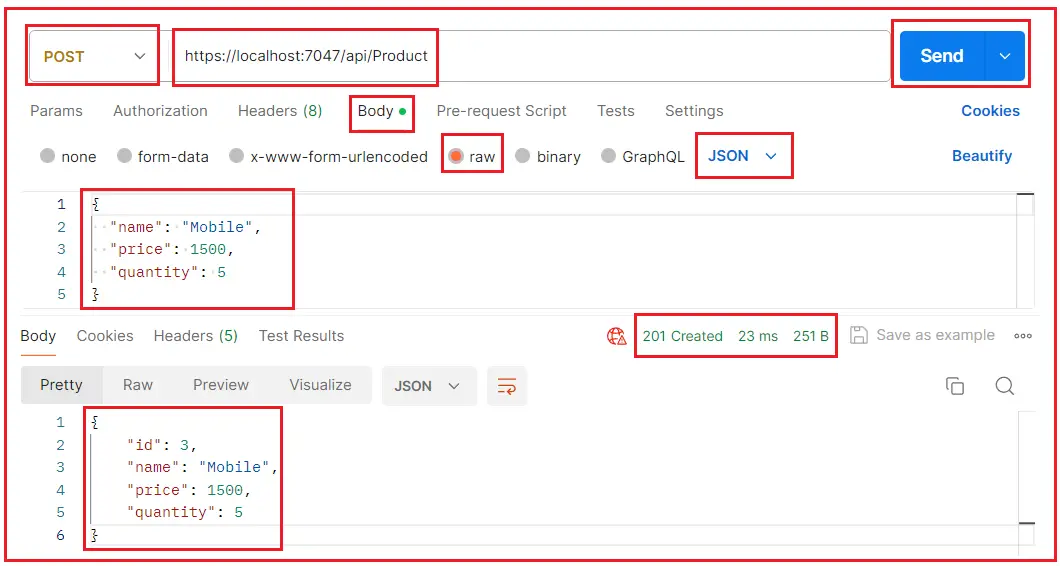
Testing the End Point:
Now, run the application and test the API endpoint, and it should work as expected:
API: Add a New Product
URL: https://localhost:7047/api/Product
Method: POST
Request Body:
{
"name": "Mobile",
"price": 1500,
"quantity": 5
}
Using Postman:
Implementing Asynchronous HTTP POST Method in ASP.NET Core Web API:
In most of the real-time applications, we need to make the action methods or services async if it is performing I/O operations. That means we should make it asynchronous to improve the application performance if it is doing database operations or invoking other services. Let us see how we can implement this.
Modifying the ProductRepository:
First, modify the ProductRepository.cs class file as follows. Here, we are making both methods async. We are delaying the execution of the action method by 1 second using the await keyword. Let’s assume this is the time period that the server will take to communicate with the database and perform the operation. Also, we changed the method name by appending the word Async.
namespace HTTPMethodDemo.Models
{
public class ProductRepository
{
public List<Product> Products = new List<Product>()
{
new Product() { Id = 1, Name= "Laptop", Price = 1000, Quantity = 10 },
new Product() { Id = 2, Name= "Desktop", Price = 2000, Quantity = 20 }
};
// Add a New Product and return the newly Product Id
public async Task<int> AddProductAsync(Product product)
{
//Set the Product Id
product.Id = 3;
Products.Add(product);
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
return product.Id;
}
// Get a Product by ID
public async Task<Product> GetByIdAsync(int Id)
{
var product = Products.FirstOrDefault(u => u.Id == Id);
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
return product;
}
}
}
Modifying the Product Controller:
Next, modify the ProductController as follows to make the action method Asynchronous. While calling the ProductRepository services, we also use the await keyword so that the Main Thread will not be blocked.
using HTTPMethodDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace HTTPMethodDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ProductRepository _productRepository;
public ProductController(ProductRepository productRepository)
{
_productRepository = productRepository;
}
// Add a New product
// POST api/product
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post([FromBody] Product product)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
// Add the product to your data store.
int ProductId = await _productRepository.AddProductAsync(product);
product.Id = ProductId;
// Return a 201 Created response with the created resource
return CreatedAtAction("GetProduct", new { Id = product.Id }, product);
}
// GET method for retrieving a product by ID
// GET api/product/1
[HttpGet("{Id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Product>> GetProduct(int Id)
{
// Retrieve and return the product from your data store
var product = await _productRepository.GetByIdAsync(Id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(product);
}
}
}
With the above changes in place, run the application and test the endpoint by issuing an HTTP Post Request. It should work as expected.
When Should We Use HTTP Post Method in ASP.NET Core Web API?
The HTTP POST method is commonly used in ASP.NET Core Web API for creating resources or submitting data to the server. Here are specific scenarios when you should use the HTTP POST method:
- Creating New Resources: When you need to create a new entity or resource on the server. For example, adding a new user to a database. POST requests are used to send data to the server to create a new resource. The data is included in the body of the request.
- Submitting Form Data: When a client submits form data to the server for processing, this could be anything from a user registration form to posting a message on a forum or any scenario where new data is being submitted to the server.
- Uploading Files: In Web APIs, POST requests are often used to upload files to the server. The file data is included in the request body, typically using multipart/form-data encoding.
- Complex Operations that Result in Creation: Sometimes, creating a new resource may involve complex operations or calculations on the server side based on the input data provided in the POST request.
- Bulk Operations: When you need to send a batch of data to the server to create multiple resources in one go, a POST request can efficiently package and send this data.
HTTP GET vs POST Method in ASP.NET Core Web API
In ASP.NET Core Web API, HTTP GET and POST methods are two fundamental ways to send requests to a server. Each method serves different purposes and is chosen based on the requirements of the API and the nature of the data being handled.
HTTP GET Method
- Purpose: GET requests are used primarily to retrieve data from a server. They should only retrieve data and have no other effect, such as fetching user information or retrieving a list of items.
- Data Transmission: Parameters are appended to the URL and sent in the query string. This makes the requested data visible in the URL, which is suitable for non-sensitive information.
- Idempotency: It is idempotent, meaning multiple identical GET requests should have the same effect as a single request and should not change the state of the server.
- Cacheable: GET responses can be cached by the browser or web servers to improve performance on subsequent requests.
- Security: It is not suitable for sensitive data transmission as data is exposed in the URL.
- Limitations: There is a limit on the length of the URL, which can restrict the amount of data that can be sent in a GET request. This limit varies by browser and server.
- Use Cases: It’s used for retrieving data, such as fetching a specific item or a list of items. Examples include searching, filtering, and navigating to a specific page.
- The [HttpGet] attribute is used to define a method that responds to an HTTP GET request.
HTTP POST Method
- Purpose: It is used to send data to a server to create/update a resource. POST requests are often used to submit form data or upload files.
- Data Transmission: Data is sent in the request body. It is more secure for sensitive information since data is not displayed in the URL.
- Idempotency: It is not idempotent. Multiple identical POST requests typically result in multiple resources being created or updated on the server.
- Cacheable: Responses to POST requests typically are not cached.
- Security: More secure for transmitting sensitive data as it is included in the request body and not exposed in the URL.
- Limitations: Generally, the amount of data that can be sent is unlimited. However, the server configuration might impose limits on the size of POST requests for performance and security reasons.
- Use Cases: It’s used for actions that involve creating or updating resources, such as submitting a form, uploading a file, or making a transaction.
- The [HttpPost] attribute defines a method that responds to an HTTP POST request, with data usually provided in the request body.
Choosing Between GET and POST
- Use GET when you’re requesting data from a server without causing any side effects (e.g., searching, retrieving).
- Use POST when you’re sending data to the server to create or update resources or when the amount of data exceeds what can be sent in a query string.
In the next article, I will discuss How to Implement the HTTP PUT Method in ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Examples. In this article, I explain How to Implement the HTTP POST Method in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. I hope you enjoy this article, “How to Implement HTTP POST Method in ASP.NET Core Web API and Its Best Practices.”
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.

