Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
405 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Return the 405 Method Not Allowed HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing How to Return the 404 Not Found HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
405 HTTP Status Code
The HTTP 405 status code is called “Method Not Allowed.” This error occurs when the resource does not support the HTTP method used in the request. This means that the server recognizes the request method but does not allow it for the resource identified by the request URI. For example, if a client sends a POST request to a URL that only accepts GET requests, the server will respond with a 405 status code.
This is considered a client error, indicating that the method used was valid but not supported for the resource you are trying to access. When a server returns a 405 response, it should include an “Allow” header that lists the HTTP methods that the resource supports. For example, if a client sends a PUT request to a resource that only supports GET and POST, the server might respond with a 405 Status Code and include the Allow: GET POST header in the response. This helps the client understand what options are available.
Common Causes for 405 HTTP Error:
- Incorrect HTTP Method: The client might be using the wrong HTTP method for the endpoint. For example, you might be trying to POST to an endpoint that only allows GET.
- Unsupported HTTP Method: The server does not support the method used in the request (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) for the specific resource.
- Misconfigured Routes: In web applications, routes might be misconfigured to handle only specific HTTP methods.
- Server Configuration: The server or framework might be configured to disallow certain methods for specific endpoints.
How to Return 405 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API
In ASP.NET Core Web API, we can explicitly return a 405 HTTP status code (“Method Not Allowed”) by using the StatusCode method, using HTTP Method Attributes, or configuring our API to automatically handle using a Custom Middleware and respond with this status when an HTTP method is used that isn’t supported for a specific route. Let us proceed and understand both approaches with examples.
Using HTTP Method Attributes to Return 405 Status Code
In ASP.NET Core, we can decorate the Action methods with HTTP Attributes. For example, we can decorate [HttpGet], [HttpPost], [HttpPut], [HttpDelete], etc. attributes on controller actions to specify the allowed methods. If a request is made using a method not supported by the action, ASP.NET Core automatically returns a 405 Status Code. For a better understanding, please modify the SampleController as follows. Here, you can see the PostAction() method is decorated with the [HttpPost] attribute. That means we can access this endpoint using HTTP Post Request.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class SampleController : ControllerBase
{
// This action only supports POST method
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult PostAction()
{
return Ok("Data processed");
}
}
}
Now, if you access the above endpoint using the HTTP GET, PUT, or DELETE request, you will receive a 405 Method Not Allowed Status Code, as shown in the image below. Here, I am using the Postman and HTTP GET methods to access the above endpoint.
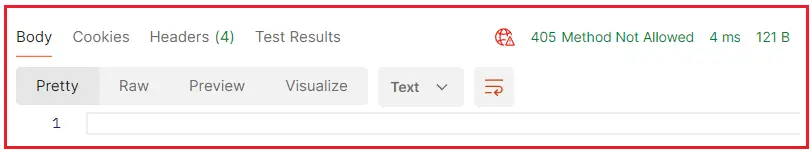
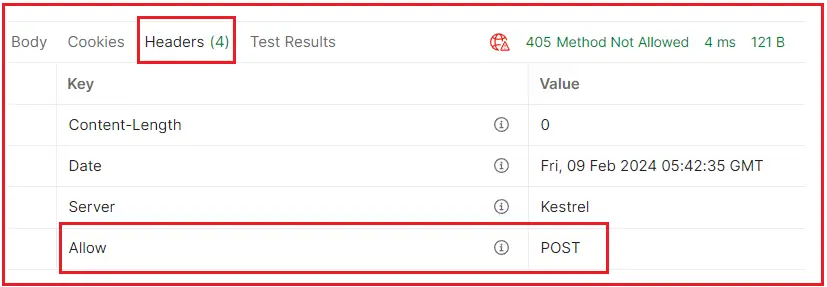
If you verify the Response header, you will see that it includes the Allow HTTP header and set its value to POST, as shown in the image below. This tells the client to please use a POST request to access the above endpoint.
Using StatusCode Method to Return 405 Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API
If an action method in a controller lacks a specific HTTP method attribute (e.g., [HttpGet], [HttpPost]), and a request is made to that action using a method that ASP.NET Core does not assume to support. Then, we can handle this scenario using the StatusCode method within the action method and return a 405 Status Code.
Let us understand this with an example. Please modify the SampleController as follows. As you can see below, we have not decorated the action method with any HTTP Verb Attribute. However, within the action method, we have handled the 405 Method Not Allowed Scenario explicitly. If the request method type is POST or PUT, the server will handle the request. Other than POST and PUT, we are explicitly returning the 405 Method Not Allowed status code. Here, we are using the StatusCode method to return the 405 Status Code.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class SampleController : ControllerBase
{
public IActionResult UnifiedMethod()
{
if (HttpContext.Request.Method == HttpMethod.Post.Method)
{
return Ok("Handled POST request");
}
else if (HttpContext.Request.Method == HttpMethod.Put.Method)
{
return Ok("Handled PUT request");
}
else
{
var customResponse = new
{
Code = 405,
Message = "Support Method are POST and PUT"
};
// Explicitly return 405 for Unsupported Methods
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status405MethodNotAllowed, customResponse);
}
}
}
}
Now, run the application and try to access the action method with a GET request, and you should see the following response body:

Custom Middleware for Handling 405 Method Not Allowed in ASP.NET Core Web API
If you need to handle more complex scenarios or global handling, you can create custom middleware to handle requests and return a 405 status code when necessary. So, basically, we need to create a custom middleware that will intercept the requests and return a 405 status code based on our criteria. Let us understand this with an example. So, create a class file named MethodNotAllowedMiddleware.cs within the Models folder and then copy and paste the following code. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
using System.Net;
using System.Text.Json;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Models
{
// Define a middleware class to handle Method Not Allowed (405) status codes
public class MethodNotAllowedMiddleware
{
// Field to store the next middleware in the pipeline
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
// Constructor to initialize the next middleware
public MethodNotAllowedMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next; // Assign the next middleware
}
// Method to handle the HTTP context
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
// Invoke the next middleware in the pipeline
await _next(context);
// Check if the response status code is 405 Method Not Allowed
if (context.Response.StatusCode == (int)HttpStatusCode.MethodNotAllowed)
{
// Set the response content type to application/json
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
// Create a custom response object with code and message
var customResponse = new
{
// Custom code field indicating the status code
Code = 405,
// Custom message field
Message = "HTTP Method not allowed"
};
// Serialize the custom response object to JSON
var responseJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(customResponse);
// Write the JSON response to the HTTP response body
await context.Response.WriteAsync(responseJson);
}
}
}
}
This middleware enhances the API’s response for situations where an HTTP method is not supported by a particular resource. By injecting this middleware into the application request processing pipeline, any 405 error generated by the API will return a more descriptive JSON object instead of a simple status code. This is useful for APIs consumed by client applications that require structured error data.
Register the Custom Middleware to the Request Processing Pipeline:
After creating the middleware, we need to register it in the Program class. It’s important to add it at the right location in the middleware pipeline to ensure that it catches 405 responses correctly.
app.UseMiddleware<MethodNotAllowedMiddleware>();
This middleware checks the status code after all other middleware has been executed. If the status code is 405, it modifies the response to include a custom JSON message indicating that the HTTP Method is Not Allowed.
Modifying the Sample Controller as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class SampleController : ControllerBase
{
// This action only supports POST method
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult PostAction()
{
return Ok("Data processed");
}
}
}
Now, run the application and access the api/sample endpoint using other than the Post method, and you should get the following response:

How to Troubleshoot 405 Error:
- Check HTTP Method: Ensure that you are using the correct HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) for the resource you are trying to access.
- Review API Documentation: Verify the allowed methods for the endpoint in the API documentation or source code.
- Inspect Routing Configuration: Check your application’s routing configuration to ensure that it supports the method you’re using.
In the next article, I will discuss How to Configure the Allowed HTTP Methods Globally in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. In this article, I try to explain How to Return 405 Method Not Allowed HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples, and I hope you enjoy this article on “405 Method Not Allowed HTTP Status Code in the ASP.NET Core Web API”.
