Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
404 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Return the 404 Not Found HTTP Status Code in the ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Examples. Please read our previous article on discussing How to Return 403 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
404 HTTP Status Code
The HTTP 404 status code indicates that the server cannot find the requested resource. This error is commonly referred to as “Not Found.” When a client requests a resource that doesn’t exist on the server or is unavailable, the server responds with a 404 status code. It’s one of the most common HTTP status codes and typically means that the URL you entered doesn’t point to any content on the server.
The 404 code is considered a client-side error, suggesting that the error was due to a mistyped URL, an outdated link that the client followed, or a user-requested resource that does not exist on the server. The following are some of the common reasons why you might encounter a 404 error:
- Incorrect URL: The URL might have been typed incorrectly, or the resource may have been moved or deleted.
- Broken Links: Links on your website or other sites might point to a page that no longer exists.
- Server Configuration: The server might be misconfigured, or the routing might be incorrect in your web application.
- Missing Files: The file or resource requested is not present on the server.
How To troubleshoot a 404 error:
- Check the URL: Ensure it’s typed correctly.
- Verify Resource Existence: Confirm that the resource exists on the server and is in the correct location.
- Review Server Logs: Look at the server logs for more details on the error.
- Check Routing Configuration: If you’re working with a web application (e.g., ASP.NET Core), ensure the routing configuration is set up correctly.
How to Return 404 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API?
In ASP.NET Core Web API, returning a 404 HTTP status code can be handled in a few different ways depending on the context of your application.
Using NotFound Helper Method:
The simplest way to return a 404 status code is by using the NotFound() method provided by the ControllerBase class. This method is useful when an item cannot be found in the database or if a particular condition is not met. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to implement this:
- Define Your Controller: Ensure your controller inherits from ControllerBase or a similar base class that provides the necessary action result methods.
- Implement the Action: In the action where you want to return a 404 status, check the condition under which the resource would not be found. If the condition is met, return the NotFound result.
- Use NotFound Method: The NotFound method can be called with no arguments or with an object that provides additional details about the error.
For a better understanding, please modify the EmployeeController as follows. Here, the GetResource action tries to find a resource by its ID and returns a 404 Status Code if the resource cannot be found:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public IActionResult GetResource(int id)
{
var resource = FindResourceById(id);
if (resource == null)
{
// Resource not found, return 404
return NotFound();
}
// Resource found, return it with 200 OK status
return Ok(resource);
}
// Mock method to simulate resource lookup
private object FindResourceById(int id)
{
// Assume this method returns null if the resource is not found
// In a real application, you would query your database or data source here
return null;
}
}
}
Response:
Now, run the application and access the above endpoint, and you should get the following 404 Not Found response:
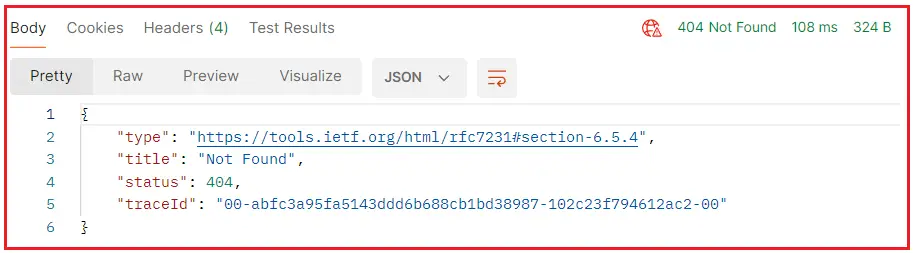
Returning 404 with Custom Error Message:
You can also pass an object to the NotFound Helper method that includes details about why the resource was not found. For a better understanding, please modify the EmployeeController as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public IActionResult GetResource(int id)
{
var resource = FindResourceById(id);
if (resource == null)
{
// Resource not found, return 404
var customResponse = new { message = $"No Employee Found with the Id: {id}" };
return NotFound(customResponse);
}
// Resource found, return it with 200 OK status
return Ok(resource);
}
// Mock method to simulate resource lookup
private object FindResourceById(int id)
{
// Assume this method returns null if the resource is not found
// In a real application, you would query your database or data source here
return null;
}
}
}
Response:
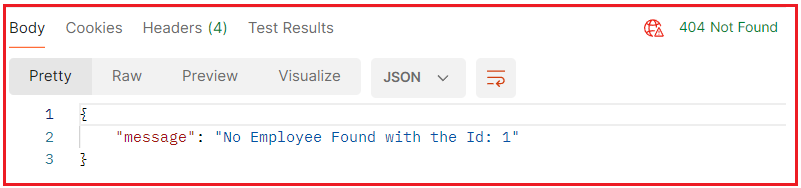
Manually Returning 404 Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API:
We need to use the StatusCode method, and to this method, we need to pass the 404 Status Code and optional object that we want to return. For a better understanding, please modify the EmployeeController as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public IActionResult GetResource(int id)
{
var resource = FindResourceById(id);
if (resource == null)
{
// Resource not found, return 404
var customResponse = new { message = $"No Employee Found with the Id: {id}" };
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status404NotFound, customResponse);
}
// Resource found, return it with 200 OK status
return Ok(resource);
}
// Mock method to simulate resource lookup
private object FindResourceById(int id)
{
// Assume this method returns null if the resource is not found
// In a real application, you would query your database or data source here
return null;
}
}
}
Response:

Endpoint Does Not Exist Example in ASP.NET Core Web API
In ASP.NET Core Web API, when you attempt to access an endpoint that does not exist, it means that the route you are trying to reach is not defined in the application. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as a typo error in the URL, forgetting to define the route in your controller, or the route being removed but still being referenced elsewhere. By default, ASP.NET Core will respond with a 404 Status Code (Not Found) for such requests. Middleware can be used to catch and respond to these scenarios and provide a custom response when an endpoint does not exist.
Create a Custom Middleware Class
First, you need to create a middleware class that checks if the HTTP response is a 404 and, if so, modifies the response accordingly. So, create a class file named NotFoundCustomMiddleware.cs and then copy and paste the following code. The following class creates a custom middleware in ASP.NET Core to handle 404 (Not Found) HTTP responses by providing a standardized JSON output. The code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
using System.Text.Json;
namespace ReturnTypeAndStatusCodes.Models
{
// Middleware class to handle custom responses for 404 status codes
public class NotFoundCustomMiddleware
{
// Field to hold the next middleware component in the pipeline
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
// Constructor to initialize the middleware with the next component
public NotFoundCustomMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next; // Assign the next middleware component
}
// Method to handle the HTTP context
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
// Call the next middleware component
await _next(context);
// Check if the response status code is 404 and if the response has not already started
if (context.Response.StatusCode == 404 && !context.Response.HasStarted)
{
// Set the response content type to JSON
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
// Create a custom response object with code and message
var customResponse = new
{
Code = 404,
Message = "Endpoint does not exist"
};
// Serialize the custom response object to JSON
var responseJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(customResponse);
// Write the JSON response to the HTTP response
await context.Response.WriteAsync(responseJson);
}
}
}
}
Register the Middleware
After creating the middleware, you need to register it in the Program class. It’s important to add it at the right point in the middleware pipeline to ensure that it correctly catches 404 responses.
app.UseMiddleware<NotFoundCustomMiddleware>();
This middleware checks the status code after all other middleware has executed (assuming none have produced a response). If the status code is 404, it modifies the response to include a custom JSON message indicating that the endpoint does not exist.
Testing:
Now, try to access an endpoint that does not exist, and you should get the following response:

When Should We Return 404 HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API?
In ASP.NET Core Web API, the 404 HTTP status code is used to indicate that the server could not find the requested resource. This status code is particularly useful in RESTful APIs to communicate to the client that the endpoint they are trying to access does not exist or that a specific resource identified by the client (for example, through a URI) cannot be found. The following are the scenarios in which returning a 404 Status Code is appropriate:
- Resource Not Found: The most common scenario to return a 404 response is when a requested resource does not exist. For example, if your API has an endpoint to get a user by ID (GET /api/users/{id}), and there is no user with the provided ID, the API should return a 404 Status Code.
- Endpoint Does Not Exist: If a client sends a request to an endpoint that does not exist, the API should return a 404 Status Code. This helps the client understand that the server does not recognize the URI they requested.
In the next article, I will discuss how to Return the 405 Method Not Allowed HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. In this article, I try to explain how to Return a 404 Not Found HTTP Status Code in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples, and I hope you enjoy this article on “404 Not Found HTTP Status Code in the ASP.NET Core Web API”.

Thank you