Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
Model Binding Using FromForm in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Implement Model Binding Using FromForm in ASP.NET Core Web API Application with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing Model Binding Techniques in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples.
Model Binding Using FromForm Attribute in ASP.NET Core Web API
In ASP.NET Core Web API, the FromForm attribute is used to bind data from incoming HTTP POST requests to action method parameters when the data is submitted as form data (content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded or multipart/form-data). So, the [FromForm] attribute is used to specify that a parameter should be bound from form data in an HTTP request. This attribute is typically used in POST requests where the data is sent in the body of the request as form data.
How Does FromForm Attribute Work in ASP.NET Core Web API?
When an action method in an API controller has parameters decorated with the FromForm attribute, the ASP.NET Core model binding system attempts to bind incoming form fields to the properties of the parameter object based on the names of the form fields. This is common in scenarios where we are uploading files or when the data from an HTML form needs to be processed by the API.
Note: The [FromForm] attribute is not limited to POST methods; it can be used with any HTTP method that supports body content, but it’s most commonly used with POST and PUT requests.
Example to Understand FromForm Attribute in ASP.NET Core Web API
Let us see an example to understand how to use the [FromForm] attribute in an ASP.NET Core Web API project:
Create a Model
First, define a model that corresponds to the data you expect to receive from the form. For instance, if you are expecting to receive user information, you might create a model like this. So, create a class file named UserModel.cs and then copy and paste the following code:
namespace ModelBinding.Models
{
public class UserModel
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
// Add other properties as needed
}
}
Create an API Controller
Next, create a controller that will handle form submissions. In the controller, define an action method that uses the [FromForm] attribute to bind the posted form data to your model. So, create an API controller named UserController and then copy and paste the following code:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using ModelBinding.Models;
namespace ModelBinding.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class UserController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult CreateUser([FromForm] UserModel user)
{
// Handle the user data, e.g., save it to a database
var response = new
{
Success = true,
Message = $"User {user.Name} created successfully!",
Code = StatusCodes.Status200OK
};
return Ok(response);
}
}
}
Testing the API
To test the API, you can use Postman or create a simple HTML form that posts data to your API endpoint. To test using Postman, open Postman, select the method type as POST, provide the endpoint URL in the request body, select form-data, provide the Key name same as your model name, select the type as text and provide the corresponding values, and finally click on the Send button as shown in the below image:
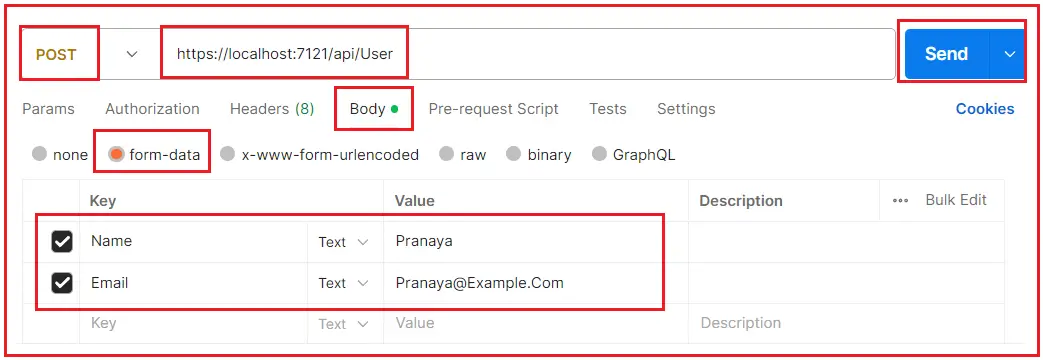
Once you click on the Send button, then you will get the following response:

Test using HTML form:
So, create an HTML file (with a .html or .html extension) and copy and paste the following code. Please change the port number where your application is running.
<form action="https://localhost:7121/api/User" method="post">
<input type="text" name="Name" placeholder="Name" required />
<input type="email" name="Email" placeholder="Email" required />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
Now, once you open the HTML file in a web browser, it will show the following: Please enter your Name and email and then click on the Submit button as shown in the below image:

Make sure your server is running, and then submit the form. Your API should receive the form data, bind it to the UserModel object, and execute the logic defined in the CreateUser method. Once you click on the Submit button, then you will see the following response in the browser:

Handling File Uploads Using FromForm in ASP.NET Core Web API:
The FromForm attribute can also handle file uploads. You can include properties of type IFormFile within your model to bind to uploaded files. Let us understand this with one example. So, modify the UserModel as follows:
namespace ModelBinding.Models
{
public class UserModel
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public IFormFile ProfilePicture { get; set; }
// Add other properties as needed
}
}
Modifying the User Controller:
Next, modify the User Controller as follows. If your form includes file uploads, your model can include one or more IFormFile properties. The [FromForm] attribute ensures that these files are bound correctly to the model. You can then process these files in your action method, for example, by saving them to a server directory.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using ModelBinding.Models;
namespace ModelBinding.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class UserController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> CreateUser([FromForm] UserModel user)
{
if (user.ProfilePicture != null)
{
var uploadsFolderPath = Path.Combine(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(), "Uploads");
if (!Directory.Exists(uploadsFolderPath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(uploadsFolderPath);
}
var filePath = Path.Combine(uploadsFolderPath, user.ProfilePicture.FileName);
using (var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create))
{
await user.ProfilePicture.CopyToAsync(stream);
}
// Handle the user data, e.g., save it to a database
var response = new
{
Success = true,
Message = $"User {user.Name} created successfully!",
ProfilePictureName = user?.ProfilePicture?.FileName,
Code = StatusCodes.Status200OK
};
return Ok(response);
}
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
}
}
Testing the API
To test using Postman, open Postman, select the method type as POST, provide the endpoint URL in the request body, select form-data, provide the Key name same as your model name, select the type as text (Name and Email) and file (Profile Picture) as per the data and provide the corresponding values for Name and Email, select the Profile Picture for the File type and finally click on the Send button as shown in the below image. This will also automatically set the Content-Type header value to multipart/form-data in the request header.

Once you click on the Send button, then you will get the following response:

Now, if you verify the project directory, then it should create the Uploads folder, and within that folder, it should store the uploaded image as shown in the below image:

Test using HTML form:
So, test using HTML and then copy and paste the following code. Please change the port number where your application is running.
<form action="https://localhost:7121/api/User" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="text" name="Name" placeholder="Name" required /> </br>
<input type="email" name="Email" placeholder="Email" required /></br>
<input type="file" name="ProfilePicture" id="ProfilePicture"></br>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
Now, once you open the HTML file in a web browser, it will show the following: Please enter your Name and Email, select the file, and then click on the Submit button as shown in the below image:

Make sure your server is running, and then submit the form. Your API should receive the form data, bind it to the UserModel object, and execute the logic defined in the CreateUser method. Once you click on the Submit button, then you will see the following response in the browser:

What are application/x-www-form-urlencoded and multipart/form-data Content Types?
The application/x-www-form-urlencoded and multipart/form-data are two common content types used in HTML forms and HTTP requests, particularly relevant in web development for handling form submissions:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
This content type is the default for HTML forms. When data is sent in this format, it is encoded as key-value pairs, similar to query strings in URLs. Each key-value pair is joined by an = sign, and pairs are separated by &. For example, if a form with fields for name and age is submitted with the values John and 30, the encoded form data would look like this: name=John&age=30
Key Characteristics:
- Characters that are not standard alpha-numerics (like spaces) are replaced with percent-encoded equivalents (e.g., space becomes %20).
- It’s not suitable for sending large amounts of data or binary data (like files) because everything is converted into a character-based format, which can make the data larger.
multipart/form-data
This content type is used when a form includes any file uploads or when you need to send a significant amount of data. It allows for each form field (or file) to be sent as a separate “part” of a single message, with each part being independently encoded and separated by boundaries. A unique boundary string separates each part of the form data in the HTTP request. For example, if a form submission includes text fields and a file, the HTTP request body might look something like this:
--boundary123 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name" John --boundary123 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="age" 30 --boundary123 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="resume"; filename="resume.pdf" Content-Type: application/pdf %PDF-1.4 --boundary123--
Key characteristics:
- Suitable for sending large and binary data.
Usage Considerations
- When to use application/x-www-form-urlencoded: This format is efficient for small or simple form submissions where files are not uploaded.
- When to use multipart/form-data: This is necessary for forms that include file uploads. It’s also preferable when sending large amounts of data.
Which Model Binder is used with FromForm Attribute in ASP.NET Core Web API?
In ASP.NET Core Web API, the FromForm attribute uses the FormFileModelBinder for binding files and the ComplexTypeModelBinder for binding complex types from form data.
FormFileModelBinder:
This binder is specifically used for handling file uploads in ASP.NET Core. When the action method expects an IFormFile or IFormFileCollection as a parameter, and we are using the FromForm attribute, the FormFileModelBinder is used. It handles the reading file data from the incoming HTTP request where the content type is either multipart/form-data or application/x-www-form-urlencoded.
This binder extracts file information from the request. It constructs an IFormFile or IFormFileCollection object representing the uploaded file(s), making them available to action methods.
ComplexTypeModelBinder:
For other types of form data that are not files, such as text fields in a form that map to properties of a complex object, the ComplexTypeModelBinder is used. This binder is capable of processing the form data and mapping it to properties of complex types.
It operates by iterating over the properties of the model object you’re trying to bind to and applying appropriate binders for each property based on attributes or defaults. It uses value providers to read form data and convert it to the appropriate property types of the model.
When to Use FromForm Model Binding in ASP.NET Core Web API
In ASP.NET Core Web API, the FromForm Attribute is useful in scenarios where the client sends data as application/x-www-form-urlencoded, a common content type for form submissions. Here’s when to use FromForm in your ASP.NET Core Web API:
- Handling HTML Form Submissions: When your API endpoint needs to process data submitted from an HTML form, especially in situations where the client is a web browser submitting form data directly to the server without JavaScript.
- File Uploads: FromForm is especially useful when you need to handle file uploads along with other form data. In this scenario, the form is typically encoded as multipart/form-data, and the FromForm attribute can bind the text fields as well as the file inputs from the form.
In the next article, I will discuss Model Binding Using FromQuery in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples. In this article, I try to explain Model Binding Using FromForm in ASP.NET Core Web API with Examples, and I hope you enjoy this article “Model Binding Using FromForm in ASP.NET Core Web API”.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
