Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
Fluent API Conditional Validations in ASP.NET Core Web API
In this article, I will discuss How to Implement Fluent API Conditional Validations in ASP.NET Core Web API Applications with Examples. Please read our previous articles discussing How to Implement Fluent API Custom Validators in ASP.NET Core Web API Applications.
Conditional Validation in Fluent API
Conditional validation with FluentValidation involves applying rules only when certain conditions are met. This approach enables developers to define dynamic business logic, making validation scenarios more flexible and easier to maintain. For example, a field might only need to be validated if another field has a specific value or if a certain condition in the domain logic is true. Conditional validation is particularly useful when:
- Dynamic Business Rules: Validation rules change based on the state of the object or other properties.
- Custom Scenarios: Specific validation is required only under certain conditions.
- Complex Logic: Rules depend on input types or external factors.
How to Use Fluent API for Conditional Validation
In FluentValidation, the When and Unless methods are used to define conditional validation rules. They allow you to specify that a rule should only be applied if a certain condition is met (When) or not met (Unless).
- When: Executes a rule only if a certain condition is met.
- Unless: Executes a rule unless a certain condition is met.
When Method
The When method allows us to apply a validation rule only when a specific condition is met. We need to use it to specify a condition under which the validation rule should be executed. The following is the example syntax.
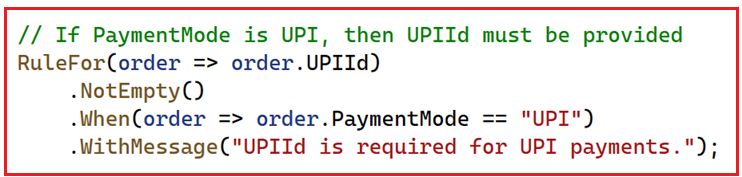
Here,
- RuleFor(): Specifies the property for which we are adding the validation rule.
- NotEmpty(): Defines the actual validation rule.
- When(): Specifies the condition that needs to be true for the validation to be applied.
The above conditional validation states that if the PaymentMode is UPI, please make sure the UPIId property is not NULL or Empty. We need to use the When method when a field is required or needs validation only under a specific condition. The following is another way to use the When method.
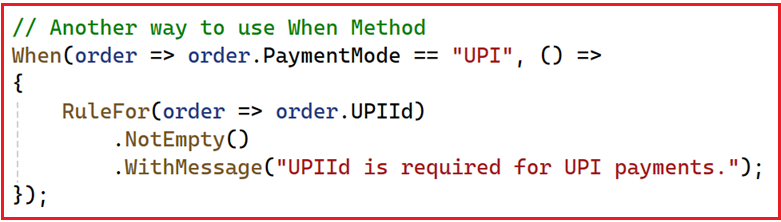
Unless Method
The Unless method is essentially the opposite of When. It applies a validation rule when the specific condition is not met. The following is the syntax:

Here,
- RuleFor(): Specifies the property for which you add the validation rule.
- InclusiveBetween(): Defines the actual validation rule.
- Unless(): Specifies the condition that needs to be false for the validation to be applied.
The above conditional validation states that for non-cash payments, ensure the Discount is within an acceptable range (10% to 30%). If the Payment Mode is Cash, Skip the Validation. So, we need to use the Unless method when a field is required or needs validation except under a specific condition. The following is another way to use the When method.

Real-Time Example: Validating Customer Order
Let us understand how to implement conditional validations in an ASP.NET Core Web API application using Fluent API When and Unless methods. We will understand this by taking an e-commerce application. In an e-commerce application:
- A Customer can place multiple Orders.
- Each Order has payment details, and specific validation rules apply based on the PaymentMode (e.g., CreditCard or UPI).
- Discounts are validated based on the Payment mode. If the Payment mode is other than Cash, a discount of 10% to 30 % can be applied.
Let us proceed and implement this example using Fluent API Conditional validations in an ASP.NET Core Web API, Entity Framework Core, and SQL Server Database.
Setting Up the Project
First, create a new ASP.NET Core Web API Project named FluentAPIValidationDemo and install the following required Packages. You can install the packages using the Package Manager Console by executing the following commands:
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
- Install-Package FluentValidation
Create Entities
Create a folder named Models in the Project root directory where we will create all our Entities:
Customer Entity:
Create a class file named Customer.cs within the Models folder and copy and paste the following code. This class represents the customer entity within the e-commerce application that places orders.
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo.Models
{
// Represents a customer in the e-commerce system.
public class Customer
{
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
// Customer's full name
public string Name { get; set; }
// Navigation property for related orders
public ICollection<Order> Orders { get; set; }
}
}
Order Entity:
Create a class file named Order.cs within the Models folder and copy and paste the following code. This class represents the customer’s order entity and contains details about the order and payment.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo.Models
{
// Represents an order placed by a customer.
public class Order
{
public int OrderId { get; set; } // Primary key
// Foreign key linking to the Customer entity
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
// Navigation property for the associated Customer
public Customer Customer { get; set; }
// Payment mode: "CreditCard", "UPI", or "Cash"
public string PaymentMode { get; set; }
// Credit card number if PaymentMode is CreditCard
public string? CreditCardNumber { get; set; }
// UPI ID if PaymentMode is UPI
public string? UPIId { get; set; }
// Total amount for the order
[Column(TypeName = "decimal(8,2)")]
public decimal OrderAmount { get; set; }
// Discount percentage applied to the order
[Column(TypeName = "decimal(8,2)")]
public decimal Discount { get; set; }
// The date when the order is placed
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
// Shipping address for the order
public string ShippingAddress { get; set; }
}
}
Create Application DbContext Class
First, create a folder named Data at the project root directory, and then inside the Data folder, create a class file named ECommerceDbContext.cs and copy and paste the following code. This class implements DbContext to manage data access to the SQL Server database.
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo.Data
{
// Represents the Entity Framework Core DbContext for the e-commerce application.
public class ECommerceDbContext : DbContext
{
public ECommerceDbContext(DbContextOptions<ECommerceDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
// Seed some initial data for customers
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Customer>().HasData(
new Customer { CustomerId = 1, Name = "John Doe"},
new Customer { CustomerId = 2, Name = "Jane Smith" },
new Customer { CustomerId = 3, Name = "Emily Johnson"}
);
}
public DbSet<Customer> Customers { get; set; }
public DbSet<Order> Orders { get; set; }
}
}
Configure the Database Connection String in the appsettings.json file
To connect our DbContext to the SQL Server database, we need to add the connection string in the appsettings.json file. So, please modify the appsettings.json file as follows. This contains the connection string (ECommerceDBConnection) required to connect to the SQL Server database.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"ECommerceDBConnection": "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=ECommerceDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
}
}
DbConext Configuration
Please modify the Program.cs class file as follows. This class configures the application’s services, such as the ECommerceDbContext and controller services.
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.Data;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers()
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
// Keep original property names during serialization/deserialization.
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
// Register the ECommerceDbContext with dependency injection
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ECommerceDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("ECommerceDBConnection")));
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Generate and Apply Database Migration:
Now, open the Package Manager Console and execute the Add-Migration command to create a new Migration file. Then, execute the Update-Database command to apply the migration and update and sync the database with our models, as shown in the image below.

Once you execute the above commands, it should have created the ECommerceDB database with the Required tables as shown in the below image:

Create the OrderDTO for Validation
Next, create a folder named DTOs. Inside the DTOs folder, create a class file named OrderDTO.cs and copy and paste the following code. This class acts as a Data Transfer Object for creating orders, encapsulating the data received from the client.
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo.DTOs
{
// DTO for creating a new order. Encapsulates order data from the client.
public class OrderDTO
{
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
// Payment mode should be "CreditCard", "UPI", or "Cash"
public string PaymentMode { get; set; }
// Required if PaymentMode is "CreditCard"
public string? CreditCardNumber { get; set; }
// Required if PaymentMode is "UPI"
public string? UPIId { get; set; }
// The total order amount; must be greater than zero
public decimal OrderAmount { get; set; }
// Discount percentage; validated conditionally
public decimal Discount { get; set; }
// Shipping address is required for order processing
public string ShippingAddress { get; set; }
}
}
Create a Validator for OrderDTO:
First, create a folder named Validators at the project root directory, and inside this folder, create a class file named OrderDTOValidator.cs and then copy and paste the following code. This class implements the validation logic for OrderDTO using FluentValidation, including conditional validations based on business rules.
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.Data;
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.DTOs;
using FluentValidation;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo.Validators
{
public class OrderDTOValidator : AbstractValidator<OrderDTO>
{
public OrderDTOValidator(ECommerceDbContext context)
{
// ----- General Validations -----
// Validate that CustomerId is provided and exists in the database
RuleFor(order => order.CustomerId)
.NotEmpty().WithMessage("CustomerId is required.")
.MustAsync(async (customerId, cancellationToken) =>
{
return await context.Customers.AnyAsync(c => c.CustomerId == customerId, cancellationToken);
})
.WithMessage("Invalid Customer.");
// Validate PaymentMode is provided and one of the allowed values
RuleFor(order => order.PaymentMode)
.NotEmpty().WithMessage("Payment mode is required.")
.Must(mode => new List<string> { "CreditCard", "UPI", "Cash" }.Contains(mode))
.WithMessage("Invalid payment mode. Allowed values: CreditCard, UPI, Cash.");
// Order amount must be greater than zero
RuleFor(order => order.OrderAmount)
.GreaterThan(0)
.WithMessage("Order amount must be greater than zero.");
// Shipping address is required
RuleFor(order => order.ShippingAddress)
.NotEmpty()
.WithMessage("Shipping address is required.");
// ----- Conditional Validations -----
// If PaymentMode is UPI, then UPIId must be provided
RuleFor(order => order.UPIId)
.NotEmpty()
.When(order => order.PaymentMode == "UPI")
.WithMessage("UPIId is required for UPI payments.");
// Another way to use When Method
When(order => order.PaymentMode == "UPI", () =>
{
RuleFor(order => order.UPIId)
.NotEmpty()
.WithMessage("UPIId is required for UPI payments.");
});
// If PaymentMode is CreditCard, then CreditCardNumber must be provided
When(order => order.PaymentMode == "CreditCard", () =>
{
RuleFor(order => order.CreditCardNumber)
.NotEmpty()
.WithMessage("CreditCardNumber is required for Credit Card payments.");
});
// For non-cash payments, ensure Discount is within an acceptable range (10% to 30%).
// Using 'Unless' to skip this rule if PaymentMode is "Cash"
RuleFor(order => order.Discount)
.InclusiveBetween(10, 30)
.Unless(order => order.PaymentMode == "Cash")
.WithMessage("Discount must be between 10% and 30% for non-cash payments.");
// Another way to use Unless Method
Unless(order => order.PaymentMode == "Cash", () =>
{
RuleFor(order => order.Discount)
.InclusiveBetween(10, 30)
.WithMessage("Discount must be between 10% and 30% for non-cash payments.");
});
}
}
}
Create the Web API Controller:
Create an Empty API controller named OrdersController within the Controllers folder and then copy and paste the following code. This API controller handles order-related HTTP requests, such as creating a new order.
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.Data;
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.DTOs;
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.Models;
using FluentAPIValidationDemo.Validators;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace FluentAPIValidationDemo.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class OrderController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ECommerceDbContext _context;
public OrderController(ECommerceDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// Creates a new order based on the provided OrderDTO.
// Applies conditional validations and returns errors if any.
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> CreateOrder([FromBody] OrderDTO orderDTO)
{
// Initialize the validator with the current DbContext for any database-related checks.
var validator = new OrderDTOValidator(_context);
var validationResult = await validator.ValidateAsync(orderDTO);
// If validation fails, return a 400 Bad Request with the details.
if (!validationResult.IsValid)
{
var errorResponse = validationResult.Errors.Select(e => new
{
Field = e.PropertyName, // Property that failed validation
Error = e.ErrorMessage // Detailed error message
});
return BadRequest(new { Errors = errorResponse });
}
// Map the validated DTO to the Order entity.
var order = new Order
{
CustomerId = orderDTO.CustomerId,
PaymentMode = orderDTO.PaymentMode,
CreditCardNumber = orderDTO.CreditCardNumber,
UPIId = orderDTO.UPIId,
OrderAmount = orderDTO.OrderAmount,
Discount = orderDTO.Discount,
OrderDate = DateTime.Now,
ShippingAddress = orderDTO.ShippingAddress
};
// Save the order to the database asynchronously.
_context.Orders.Add(order);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(new { Message = "Order created successfully.", OrderId = order.OrderId });
}
}
}
Testing the API:
Valid Order Request Body
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"PaymentMode": "CreditCard",
"CreditCardNumber": "1234-5678-9012-3456",
"OrderAmount": 500,
"Discount": 20,
"ShippingAddress": "123 Main Street, City, Country"
}
Response in Swagger:

Invalid Order:
The PaymentMode is “CreditCard,” but the CreditCardNumber is missing, or the discount is out of the allowed range for non-cash payments.
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"PaymentMode": "CreditCard",
"OrderAmount": 500,
"Discount": 50,
"ShippingAddress": "123 Main Street, City, Country"
}
Response in Swagger:

Conditional validation in Fluent API Validation is a powerful feature that allows us to apply complex business rules based on the state of our data. We can create flexible and maintainable validation logic that adapts to different scenarios by using When and Unless.
In the next article, I will discuss How to Validate Nested Complex or Collection Properties using Fluent API in ASP.NET Core Web API Applications with Examples. In this article, I explain How to Implement Fluent API Conditional Validations in ASP.NET Core Web API Applications with Examples. I hope you enjoy this article, How to Implement Fluent API Conditional Validations in ASP.NET Core Web API.
