Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
Entity Framework Core Database First Approach
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is Microsoft’s modern, lightweight, and cross-platform Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework. It simplifies database interactions in .NET applications by allowing developers to work with C# objects instead of SQL queries directly. EF Core automatically maps classes (entities) to database tables and handles the generation and execution of SQL statements for CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
EF Core supports two major development approaches:
- Code First – The database schema is generated from C# model classes.
- Database First – The model classes and DbContext are generated from an existing database.
What is EF Core Database First Approach?
The Database First Approach in EF Core is a reverse-engineering process in which the ORM components (entity classes and DbContext) are generated automatically from an existing database schema.
In other words, instead of starting with C# classes to create a database (as in Code First), the database acts as the source of truth, and EF Core generates the corresponding .NET classes that represent the tables, relationships, and constraints.
This approach is especially beneficial when:
- A database already exists and is maintained by database administrators.
- The development process follows a database-centric workflow, where the schema is finalized before application coding begins.
- The development team needs to integrate a legacy or third-party database with a new .NET Core application.
- The organization wants to ensure strict adherence to existing database standards and stored procedures.
Entity Framework Core Database First Approach with an E-commerce Application
Let’s understand how this approach works in a real-world scenario, such as integrating EF Core with an existing E-commerce Database.
Creating the Database Schema
In the Database First approach, everything begins with a well-structured SQL Server database. For example, consider an E-commerce application that manages customers, products, orders, payments, and related data. A database administrator designs the schema with properly normalized tables, primary and foreign keys, relationships, and constraints.
Key Tables in the E-commerce Database
The E-commerce database will manage several key tables essential for an online shopping platform. The key tables and their purposes are:
OrderStatusMaster
This table stores all predefined order status values, such as “Pending”, “Confirmed”, “Shipped”, “Delivered”, and “Cancelled”. These statuses help track the lifecycle of an order. It ensures every order has a valid, standardized status and supports filtering, dashboards, and customer notifications.
PaymentStatusMaster
This master table stores the status of payment attempts, including “Pending”, “Success”, “Failed”, and “Refunded”. It supports tracking real-time payment progress, integration with gateways, and accurate reporting of payment outcomes.
PaymentMethodsMaster
The PaymentMethodsMaster table stores all supported payment methods in the e-commerce system, including UPI, Wallet, Credit Card, Debit Card, Net Banking, and Cash on Delivery (COD). It ensures that every payment is made using a valid and predefined method.
RefundStatusMaster
This table stores the status of refund attempts, including “Initiated”, “Processing”, “Successful”, and “Failed”. It helps track the state of both partial and full refunds and assists customer support and reconciliation teams.
StockTransactionMaster
This table defines all possible types of stock movements, such as “ORDER_PLACED”, “ORDER_CANCELLED”, “MANUAL_ADJUSTMENT”, “SUPPLIER_RESTOCK”, or “ORDER_RETURNED”. It ensures consistent classification of stock changes and improves inventory reporting and analytics.
ShipmentStatusMaster
This master table stores the statuses used in the delivery journey, such as “Pending”, “Shipped”, “In Transit”, “Out for Delivery”, and “Delivered”. It standardizes shipment tracking and helps logistics teams monitor delivery progress.
Customers
This table stores customers’ personal and login information. It contains names, email addresses, phone numbers, passwords, and verification statuses. Customers can have multiple roles, addresses, carts, orders, and reviews associated with them.
Roles
The Roles table stores predefined system roles, such as Administrator, Seller, and Customer. These roles define what actions a user can perform inside the platform and support role-based access control.
CustomerRoles
This table links customers with roles and supports a many-to-many relationship. It allows assigning multiple roles to a single customer and ensures flexible and secure authorization throughout the system.
Addresses
The Addresses table stores all saved addresses for a customer, including home, office, and alternate delivery addresses. Each address includes full location details and can be marked as default for faster checkout.
Brands
This table stores product brand information, such as Apple, Sony, Adidas, etc. Associating products with brands helps customers browse brand-wise and supports brand-based filtering, promotions, and search.
Categories
This table organizes products into hierarchical groups such as Electronics → Mobile Phones → Smartphones. It helps users browse and filter products easily and enables structured catalog management.
Products
The Products table stores complete information about each item sold on the website, including name, price, discount rules, tax handling, and stock quantity. It also maintains real-time price breakup (MRP, discount, tax, payable price) and supports all product-related operations across orders, carts, and inventory.
StockTransactions
This table logs every change made to product stock, increases or decreases, ensuring a complete audit trail. It records the type of movement, reference order or refund IDs, quantity changes, old and new stock values, and timestamps. It is essential for accurate inventory management and debugging stock discrepancies.
ProductCategories
This table connects products to categories using a many-to-many relationship. A product may belong to multiple categories (e.g., “Electronics” and “New Arrivals”), allowing for more flexible browsing and filtering.
ProductImages
This table stores URLs of product images. It supports multiple images per product and indicates which image is the primary one shown to customers. This enhances product presentation and improves conversions.
ProductAttributes
This table stores dynamic product specifications such as color, size, material, capacity, or RAM. It offers flexibility because each product can have different attribute sets without modifying the main Product table.
ShoppingCarts
This table represents a customer’s online shopping cart, where items are temporarily stored before order placement. A user can have one active cart at a time, which is automatically updated as they add or remove items.
CartItems
This table stores each item added to the cart, along with price snapshots (discounted price, tax, final price) at the time of adding. It ensures cart totals remain stable even if product prices change later.
Orders
The Orders table stores the complete order details, including amounts, discount totals, shipping cost, platform fees, addresses, order status, and timestamps. It acts as the parent record for items, payments, shipments, and order history.
OrderItems
This table stores each product purchased within an order along with full pricing snapshots (MRP, discount, tax, shipping charge, final price). It helps calculate totals, supports refunds, and enables detailed invoice generation.
Payments
The Payments table tracks all payment attempts for an order across various methods, including UPI, Wallet, Card, NetBanking, and COD. It stores gateway details, retry attempts, transaction IDs, and payment logs for debugging. It ensures complete payment visibility from initiation to completion.
Refunds
This table stores refund attempts linked to a payment or order. It includes refund amount, reason, gateway IDs, retry count, status, and timestamps. It supports both partial and complete refunds and provides detailed refund tracking.
OrderStatusHistory
This table maintains a timeline of all changes to an order’s status (such as Confirmed → Packed → Shipped → Delivered). It helps with customer support, audits, analytics, and order lifecycle tracking.
Reviews
The Reviews table stores customers’ ratings and feedback for purchased products. It includes rating score, text, and customer reference. Reviews improve product credibility and guide customer decisions.
DeliveryPartners
The table stores the database of logistics partners such as BlueDart, Delhivery, or Ekart. It includes their names and tracking URL patterns used for shipment tracking.
Shipments
The Shipments table stores shipping details for orders, such as tracking number, shipping date, partner used, delivery date, and shipment status. It helps monitor package movement and delivery operations.
FailureLog
This table records system errors, exceptions, and failures, including payment gateway failures, API errors, and order processing issues. It stores the stack trace, payload, severity, and correlation ID to support debugging, monitoring, and production issue analysis.
SQL Scripts for Database Creation
Let’s start by creating the EcommerceDB database and all necessary tables, with proper relationships. So, please execute the following SQL script in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
-- Create and use the Database
CREATE DATABASE EcommerceDB;
GO
USE EcommerceDB;
GO
-- OrderStatusMaster
-- Stores all possible statuses an order can have (Pending, Confirmed, Shipped, Delivered, Cancelled)
-- Used by Orders and OrderStatusHistory to track lifecycle of an order.
CREATE TABLE OrderStatusMaster (
OrderStatusID INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
StatusName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(200),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
UpdatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
UpdatedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- PaymentStatusMaster
-- Stores gateway payment status: Pending, Success, Failed, etc.
-- Used by Payments table to classify payment attempts.
CREATE TABLE PaymentStatusMaster (
PaymentStatusID INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
StatusName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(200),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
UpdatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
UpdatedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- RefundStatusMaster
-- Stores refund related statuses: Initiated, Processing, Completed, Failed.
-- Used by Refunds table.
CREATE TABLE RefundStatusMaster (
RefundStatusID INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
StatusName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(300),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
-- Audit fields
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Payment Methods Master
-- This table stores ALL available payment methods platform-wide
-- such as UPI, Card, NetBanking, Wallet, COD, etc.
CREATE TABLE PaymentMethodsMaster (
PaymentMethodID INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
MethodCode NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE, -- e.g., UPI, CARD, NETBANKING, WALLET, COD
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, -- e.g., UPI Payment, Credit/Debit Card
Description NVARCHAR(300),
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
UpdatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
UpdatedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- StockTransactionMaster
-- Defines types of stock movements such as ORDER_PLACED, ORDER_CANCELLED,
-- PURCHASE_RESTOCK, RETURN_RECEIVED, MANUAL_ADJUSTMENT, etc.
-- Used by StockTransactions table.
CREATE TABLE StockTransactionMaster (
StockTransactionTypeID INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
TransactionName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE, -- ORDER_PLACED, ORDER_CANCELLED etc.
Description NVARCHAR(200) NULL, -- Readable description
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
UpdatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
UpdatedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- ShipmentStatusMaster
-- Stores shipping lifecycle statuses: Pending, Shipped, In Transit, Delivered, Returned.
-- Used by Shipments table.
CREATE TABLE ShipmentStatusMaster (
ShipmentStatusID INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
StatusName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(200),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
UpdatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
UpdatedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Customers
-- Stores user account details used for authentication, orders, carts, reviews.
-- Related to: Addresses, CustomerRoles, ShoppingCarts, Orders, Reviews.
CREATE TABLE Customers (
CustomerID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
LastName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
Email NVARCHAR(150) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Phone NVARCHAR(20),
PasswordHash NVARCHAR(500) NOT NULL,
IsEmailVerified BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- Audit Fields
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Roles
-- Stores system roles such as Admin, Seller, Customer.
-- Connected through CustomerRoles many-to-many relationship.
CREATE TABLE Roles (
RoleID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
RoleName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(200),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- CustomerRoles
-- Many-to-many relation between Customers and Roles.
-- Used for authorization and permission management.
CREATE TABLE CustomerRoles (
CustomerID BIGINT NOT NULL,
RoleID BIGINT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_CustomerRoles PRIMARY KEY (CustomerID, RoleID),
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (RoleID) REFERENCES Roles(RoleID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Addresses
-- Stores multiple addresses for each customer (Home, Office, etc.).
-- Used during checkout to store shipping and billing addresses.
CREATE TABLE Addresses (
AddressID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID BIGINT NOT NULL,
AddressType NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'Home',
AddressLine1 NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
AddressLine2 NVARCHAR(200),
City NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
State NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
PostalCode NVARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
Country NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
IsDefault BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
CONSTRAINT FK_Addresses_Customer
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Brands
-- Stores product brand names (Nike, Apple, Samsung, etc.)
-- Linked to Products table for filtering and search.
CREATE TABLE Brands (
BrandID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
BrandName NVARCHAR(150) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(300),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Categories
-- Supports multi-level product categorization (Electronics → Mobiles → Smartphones).
-- Many-to-many with Products through ProductCategories.
CREATE TABLE Categories (
CategoryID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CategoryName NVARCHAR(150) NOT NULL,
Description NVARCHAR(500),
ParentCategoryID BIGINT,
DisplayName NVARCHAR(100) NULL,
CONSTRAINT FK_Category_Parent
FOREIGN KEY (ParentCategoryID) REFERENCES Categories(CategoryID),
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Products
-- Stores core product information: name, price, tax, discount, stock.
-- Connected to: ProductCategories, ProductImages, ProductAttributes, CartItems, OrderItems.
-- Products Table
CREATE TABLE Products (
ProductID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
BrandID BIGINT NULL,
ProductName NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
SKU NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Description NVARCHAR(MAX),
-- BUSINESS FLAGS
IsDiscountActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
IsTaxIncluded BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- PRICE INPUTS
MRP DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL,
BasePrice DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL,
DiscountPercent DECIMAL(5,2) NULL DEFAULT 0,
FlatDiscount DECIMAL(18,2) NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- COMPUTED COLUMNS WITH PROPER DECIMAL(18,2)
DiscountAmount AS
CAST(
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0) / 100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0
END
AS DECIMAL(18,2))
PERSISTED,
FinalPrice AS
CAST(
BasePrice -
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0) / 100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0
END
AS DECIMAL(18,2))
PERSISTED,
TaxPercent DECIMAL(5,2) NULL DEFAULT 0,
TaxAmount AS
CAST(
CASE
WHEN IsTaxIncluded = 1 THEN
((BasePrice -
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0)/100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0 END
) * ISNULL(TaxPercent,0)
/ (100 + ISNULL(TaxPercent,0)))
ELSE
((BasePrice -
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0)/100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0 END
) * ISNULL(TaxPercent,0) / 100)
END
AS DECIMAL(18,2))
PERSISTED,
PayablePrice AS
CAST(
CASE
WHEN IsTaxIncluded = 1 THEN
(BasePrice -
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0)/100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0 END
)
ELSE
(BasePrice -
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0)/100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0 END
)
+ ((BasePrice -
CASE WHEN IsDiscountActive = 1
THEN ((BasePrice * ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0)/100) + ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0))
ELSE 0 END
) * ISNULL(TaxPercent,0) / 100)
END
AS DECIMAL(18,2))
PERSISTED,
-- Stock
StockQuantity INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- Foreign Keys
CONSTRAINT FK_Products_Brand FOREIGN KEY (BrandID) REFERENCES Brands(BrandID),
-- CHECKS
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_Stock CHECK (StockQuantity >= 0),
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_MRP CHECK (MRP >= 0),
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_BasePrice CHECK (BasePrice >= 0),
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_DiscountPercent CHECK (ISNULL(DiscountPercent,0) >= 0),
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_FlatDiscount CHECK (ISNULL(FlatDiscount,0) >= 0),
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_Tax CHECK (ISNULL(TaxPercent,0) >= 0),
CONSTRAINT CK_Products_MRP_vs_Base CHECK (MRP >= BasePrice),
-- Audit Fields
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- StockTransactions
-- Complete audit log for stock changes.
-- Related to Products and StockTransactionMaster.
-- Supports stock-in and stock-out through +/- QuantityChange.
CREATE TABLE StockTransactions (
StockTransactionID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
StockTransactionTypeID INT NOT NULL, -- FK to StockTransactionMaster
QuantityChange INT NOT NULL, -- +ve = Stock In, -ve = Stock Out
ReferenceID BIGINT NULL, -- OrderID, RefundID, PurchaseID
ReferenceType NVARCHAR(50) NULL, -- 'Order', 'Refund', 'Purchase', 'Adjustment'
OldStock INT NOT NULL, -- Product stock before change
NewStock INT NOT NULL, -- Product stock after change
Remarks NVARCHAR(500) NULL,
TransactionDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
-- FOREIGN KEYS
CONSTRAINT FK_StockTransactions_Product
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID),
CONSTRAINT FK_StockTransactions_TransactionType
FOREIGN KEY (StockTransactionTypeID) REFERENCES StockTransactionMaster(StockTransactionTypeID),
-- VALIDATION
CONSTRAINT CK_StockTransactions_QuantityChange CHECK (QuantityChange <> 0),
-- AUDIT FIELDS (MATCHING YOUR SCHEMA STYLE)
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- ProductCategories
-- Many-to-many link between Products and Categories.
-- Improves product filtering and catalog organization.
CREATE TABLE ProductCategories (
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
CategoryID BIGINT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_ProductCategories PRIMARY KEY (ProductID, CategoryID),
CONSTRAINT FK_ProductCategories_Product
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT FK_ProductCategories_Category
FOREIGN KEY (CategoryID) REFERENCES Categories(CategoryID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- ProductImages
-- Stores all images of a product.
-- Supports multiple images and primary image flag.
CREATE TABLE ProductImages (
ProductImageID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
ImageUrl NVARCHAR(500) NOT NULL,
AltText NVARCHAR(200),
IsPrimary BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
CONSTRAINT FK_ProductImages_Product
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- ProductAttributes
-- Stores dynamic attributes for products (Color, Size, RAM, Material, etc.)
-- Flexible key-value pair design.
CREATE TABLE ProductAttributes (
ProductAttributeID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
AttributeName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
AttributeValue NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT FK_ProductAttributes_Product
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- ShoppingCarts
-- Represents a customer's active cart.
-- A customer may have multiple carts historically but only one IsCurrent.
CREATE TABLE ShoppingCarts (
CartID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID BIGINT NOT NULL,
IsCurrent BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- CartItems
-- Stores products added to cart with complete pricing snapshot.
CREATE TABLE CartItems (
CartItemID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CartID BIGINT NOT NULL,
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
-- PRODUCT SNAPSHOT
ProductName NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
SKU NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
BrandName NVARCHAR(200) NULL,
ProductAttributeJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
ThumbnailImageUrl NVARCHAR(500) NULL,
-- PRICE SNAPSHOT (CLEAR NAMING)
MRP DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Printed product price
SellingPrice DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Base price at time of add-to-cart
DiscountPercent DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, -- % discount
DiscountFlat DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, -- Fixed discount
DiscountTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- % + flat combined
PriceAfterDiscount DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- SellingPrice - DiscountTotal
TaxPercent DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, -- GST %
TaxAmount DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- GST on discounted price
FinalPrice DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- PriceAfterDiscount + TaxAmount
Quantity INT NOT NULL CHECK (Quantity > 0),
-- FOREIGN KEYS
FOREIGN KEY (CartID) REFERENCES ShoppingCarts(CartID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID),
-- AUDIT FIELDS
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Orders
-- Stores overall order details including totals, addresses, and status.
-- Related to: OrderItems, Payments, Shipments, Refunds, OrderStatusHistory.
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID BIGINT NOT NULL,
OrderStatusID INT NOT NULL,
OrderDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
-- ADDRESS SNAPSHOT (Stored because customer may update/delete later)
ShippingAddressJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NOT NULL,
BillingAddressJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NOT NULL,
-- AGGREGATED PRICE BREAKUP FROM ORDER ITEMS
-- Sum of OrderItems.PriceAfterDiscount * Qty
ItemsTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL,
-- Combined discount from all OrderItems
OrderDiscountTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- Sum of OrderItems.TaxAmount * Qty
OrderTaxTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- Sum of OrderItems.ShippingCharge
ShippingTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- Optional: service fee / convenience fee
PlatformFee DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
-- Final amount customer pays
GrandTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL,
-- FOREIGN KEYS
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID),
FOREIGN KEY (OrderStatusID) REFERENCES OrderStatusMaster(OrderStatusID),
-- VALIDATIONS
CONSTRAINT CK_Orders_Totals CHECK (
ItemsTotal >= 0 AND
OrderDiscountTotal >= 0 AND
OrderTaxTotal >= 0 AND
ShippingTotal >= 0 AND
GrandTotal >= 0
),
-- AUDIT FIELDS
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- OrderItems
-- Stores per-item snapshot of products in an order including pricing, tax, and shipping.
-- Used for invoices, refunds, reporting, and analytics.
CREATE TABLE OrderItems (
OrderItemID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
OrderID BIGINT NOT NULL,
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
-- PRODUCT SNAPSHOT
ProductName NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
SKU NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
BrandName NVARCHAR(200) NULL,
ProductAttributesJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
-- PRICE SNAPSHOT
MRP DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Printed price
SellingPrice DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Base price at order time
DiscountPercent DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
DiscountFlat DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
DiscountTotal DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Combined discount
PriceAfterDiscount DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Before tax
TaxPercent DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
TaxAmount DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- GST on discounted price
FinalPrice DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- One unit final price
-- ITEM TOTAL CALCULATION
Quantity INT NOT NULL CHECK (Quantity > 0),
-- Total payable for this item line
LineTotal AS (FinalPrice * Quantity) PERSISTED,
-- FOREIGN KEYS
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID),
-- AUDIT FIELDS
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Payments
-- Stores payment attempts for orders.
-- Works for UPI, COD, Cards, NetBanking, Wallets, etc.
-- Supports multiple attempts and stores gateway logs.
CREATE TABLE Payments (
PaymentID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
OrderID BIGINT NOT NULL,
-- Core Payment Info
Amount DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL,
CurrencyCode NVARCHAR(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'INR',
PaymentStatusID INT NOT NULL, -- Pending / Success / Failed
PaymentMethodID INT NOT NULL, -- UPI, CARD, NETBANKING, WALLET, COD
PaymentGateway NVARCHAR(100) NULL, -- Razorpay, Stripe, Paytm, Cashfree, InternalCOD
AttemptNumber INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1, -- For retry attempts
-- Gateway Identifiers
MerchantTransactionID NVARCHAR(200) NULL, -- Your internal payment ref
GatewayTransactionID NVARCHAR(200) NULL, -- RazorpayPaymentId / StripeChargeId
-- Method Specific Metadata
UpiVpa NVARCHAR(200) NULL,
CardLast4 NVARCHAR(4) NULL,
CardNetwork NVARCHAR(50) NULL,
BankReferenceNo NVARCHAR(100) NULL,
-- Logging
GatewayRequestJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
GatewayResponseJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
-- Timestamps
PaymentInitiatedAt DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
PaymentCompletedAt DATETIME NULL,
-- Foreign Keys
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (PaymentStatusID) REFERENCES PaymentStatusMaster(PaymentStatusID),
FOREIGN KEY (PaymentMethodID) REFERENCES PaymentMethodsMaster(PaymentMethodID),
-- Validation
CONSTRAINT CK_Payments_Amount CHECK (Amount > 0),
-- Audit
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Refunds
-- Supports full or partial refunds for payments.
-- Stores gateway refund IDs, retry attempts, status, and metadata.
CREATE TABLE Refunds (
RefundID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
PaymentID BIGINT NOT NULL,
OrderID BIGINT NOT NULL,
-- Refund Info
RefundAmount DECIMAL(18,2) NOT NULL, -- Amount refunded
CurrencyCode NVARCHAR(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'INR',
RefundStatusID INT NOT NULL, -- From RefundStatusMaster
AttemptNumber INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1, -- Retry for failed refunds
-- Gateway Identifiers
RefundTransactionID NVARCHAR(200) NULL, -- RazorpayRefundID / StripeRefundID
GatewayReferenceID NVARCHAR(200) NULL, -- Bank reference ID for refund
-- Refund Metadata
RefundReason NVARCHAR(300) NULL,
InitiatedBy NVARCHAR(100) NULL, -- User / Admin
IsAutoRefund BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, -- Auto refund on cancellation?
-- Gateway JSON Logs
GatewayRequestJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
GatewayResponseJSON NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
-- Timestamps
RefundInitiatedAt DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
RefundCompletedAt DATETIME NULL,
-- Foreign Keys
FOREIGN KEY (PaymentID) REFERENCES Payments(PaymentID) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (RefundStatusID) REFERENCES RefundStatusMaster(RefundStatusID),
-- Validation
CONSTRAINT CK_Refunds_Amount CHECK (RefundAmount > 0),
-- Audit
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- OrderStatusHistory
-- Stores every change in an order's status.
-- Useful for timeline tracking, customer support, and audit logs.
CREATE TABLE OrderStatusHistory (
OrderStatusHistoryID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
OrderID BIGINT NOT NULL,
OldStatusID INT,
NewStatusID INT NOT NULL,
ChangedAt DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
Remarks NVARCHAR(500),
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (OldStatusID) REFERENCES OrderStatusMaster(OrderStatusID),
FOREIGN KEY (NewStatusID) REFERENCES OrderStatusMaster(OrderStatusID),
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Reviews
-- Stores customer ratings and descriptions for purchased products.
-- One review allowed per Product per Customer.
CREATE TABLE Reviews (
ReviewID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
ProductID BIGINT NOT NULL,
CustomerID BIGINT NOT NULL,
Rating INT NOT NULL CHECK (Rating BETWEEN 1 AND 5),
ReviewText NVARCHAR(1000),
FOREIGN KEY (ProductID) REFERENCES Products(ProductID),
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID),
CONSTRAINT UQ_Review UNIQUE(ProductID, CustomerID),
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- DeliveryPartners
-- Stores list of courier services such as BlueDart, Delhivery, etc.
-- Used by Shipments table.
CREATE TABLE DeliveryPartners (
PartnerID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
PartnerName NVARCHAR(150) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
TrackingUrl NVARCHAR(300),
DisplayName NVARCHAR(150) NULL,
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Shipments
-- Stores shipping details for each order including tracking number,
-- shipment dates, partner, and status.
CREATE TABLE Shipments (
ShipmentID BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
OrderID BIGINT NOT NULL,
PartnerID BIGINT NOT NULL,
TrackingNumber NVARCHAR(100),
ShippedDate DATETIME,
DeliveredDate DATETIME,
ShipmentStatusID INT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (PartnerID) REFERENCES DeliveryPartners(PartnerID),
FOREIGN KEY (ShipmentStatusID) REFERENCES ShipmentStatusMaster(ShipmentStatusID),
IsActive BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
CreatedBy NVARCHAR(100),
CreatedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedBy NVARCHAR(100),
ModifiedDate DATETIME
);
GO
-- Shipments
-- Stores shipping details for each order including tracking number,
-- shipment dates, partner, and status.
CREATE TABLE FailureLog (
Id BIGINT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
OrderId BIGINT,
CustomerId BIGINT,
ProductId BIGINT,
PaymentId BIGINT,
MethodName NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
ClassName NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(2000) NOT NULL,
StackTrace NVARCHAR(MAX) NOT NULL,
RequestPayloadJSON NVARCHAR(MAX),
Severity NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'Error',
CorrelationId NVARCHAR(100),
Environment NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'Production',
LoggedAt DATETIME2 NOT NULL DEFAULT SYSUTCDATETIME(),
FOREIGN KEY (OrderId) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerId) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID),
FOREIGN KEY (ProductId) REFERENCES Products(ProductID),
FOREIGN KEY (PaymentId) REFERENCES Payments(PaymentID)
);
GO
Inserting Master Table Data:
Let us proceed and insert the master data for our ecommerce application.
-- OrderStatusMaster
INSERT INTO OrderStatusMaster (StatusName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('PENDING', 'Pending', 'Order placed but awaiting confirmation', 'System'),
('CONFIRMED', 'Confirmed', 'Order confirmed by the system', 'System'),
('PROCESSING', 'Processing', 'Order is being packed', 'System'),
('SHIPPED', 'Shipped', 'Order handed over to courier', 'System'),
('IN_TRANSIT', 'In Transit', 'Order is travelling to destination', 'System'),
('OUT_FOR_DELIVERY', 'Out For Delivery', 'Delivery agent is on the way', 'System'),
('DELIVERED', 'Delivered', 'Order successfully delivered', 'System'),
('CANCELLED', 'Cancelled', 'Order cancelled by user or system', 'System'),
('RETURN_REQUESTED', 'Return Requested', 'Customer initiated return', 'System'),
('RETURNED', 'Returned', 'Returned item received at warehouse', 'System'),
('REFUND_INITIATED', 'Refund Initiated', 'Refund process has started', 'System'),
('REFUND_COMPLETED', 'Refund Completed', 'Refund successfully credited to customer', 'System');
-- PaymentStatusMaster
INSERT INTO PaymentStatusMaster (StatusName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('PENDING', 'Pending', 'Payment initiated but not completed', 'System'),
('SUCCESS', 'Success', 'Payment completed successfully', 'System'),
('FAILED', 'Failed', 'Payment attempt failed', 'System'),
('EXPIRED', 'Expired', 'Payment session timed out', 'System'),
('CANCELLED', 'Cancelled', 'Payment was cancelled by the user', 'System'),
('REFUND_INITIATED', 'Refund Initiated', 'Refund has been initiated for this payment', 'System'),
('REFUND_COMPLETED', 'Refund Completed', 'Refund successfully processed', 'System');
-- PaymentMethodsMaster
INSERT INTO PaymentMethodsMaster (MethodCode, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('UPI', 'UPI Payment', 'Unified Payments Interface digital payment method', 'System'),
('CARD', 'Credit/Debit Card', 'Visa, MasterCard, Rupay card transactions', 'System'),
('NET_BANKING', 'Net Banking', 'Direct transfer via internet banking', 'System'),
('WALLET', 'Wallet Payment', 'Paytm, PhonePe, Amazon Pay, etc.', 'System'),
('COD', 'Cash On Delivery', 'Cash payment at time of delivery', 'System'),
('BANK_TRANSFER', 'Bank Transfer', 'Manual NEFT/RTGS/IMPS bank transfer', 'System'),
('EMI', 'EMI (Credit Card EMI)', 'Monthly installment-based payments', 'System'),
('PAY_LATER', 'Pay Later', 'Simpl, Lazypay and similar pay-later services', 'System');
-- RefundStatusMaster
INSERT INTO RefundStatusMaster (StatusName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('INITIATED', 'Initiated', 'Refund process has started', 'System'),
('PROCESSING', 'Processing', 'Refund is being processed by payment gateway', 'System'),
('FAILED', 'Failed', 'Refund transaction failed', 'System'),
('COMPLETED', 'Completed', 'Refund successfully credited to customer', 'System'),
('PARTIAL', 'Partial Refund', 'A partial refund has been issued', 'System');
-- StockTransactionMaster
INSERT INTO StockTransactionMaster (TransactionName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('ORDER_PLACED', 'Order Placed', 'Stock reduced because an order was placed', 'System'),
('ORDER_CANCELLED', 'Order Cancelled', 'Stock restored due to order cancellation', 'System'),
('RETURN_RECEIVED', 'Return Received', 'Stock increased due to customer return', 'System'),
('PURCHASE_RESTOCK', 'Purchase Restock', 'New stock received from supplier', 'System'),
('MANUAL_ADJUSTMENT', 'Manual Adjustment', 'Admin manually edited stock quantity', 'System'),
('DAMAGED', 'Damaged', 'Stock reduced due to damaged items', 'System'),
('INVENTORY_AUDIT', 'Inventory Audit', 'Stock updated after audit verification', 'System');
-- ShipmentStatusMaster
INSERT INTO ShipmentStatusMaster (StatusName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('PENDING', 'Pending', 'Shipment is not yet processed', 'System'),
('PACKED', 'Packed', 'Shipment is packed and ready to dispatch', 'System'),
('SHIPPED', 'Shipped', 'Shipment handed over to courier', 'System'),
('IN_TRANSIT', 'In Transit', 'Shipment is travelling to destination', 'System'),
('OUT_FOR_DELIVERY', 'Out For Delivery', 'Delivery agent is out for delivery', 'System'),
('DELIVERED', 'Delivered', 'Package successfully delivered to the customer', 'System'),
('RETURN_TO_ORIGIN', 'Return to Origin', 'Shipment returning back to warehouse', 'System'),
('LOST', 'Lost', 'Shipment lost during transit', 'System'),
('RETURNED', 'Returned', 'Customer returned the shipment', 'System');
-- Roles Master
INSERT INTO Roles (RoleName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('ADMIN', 'Admin', 'System administrator with full access', 'System'),
('CUSTOMER', 'Customer', 'Regular platform customer', 'System'),
('SELLER', 'Seller', 'Manages products and order fulfillment', 'System');
-- Brands Master
INSERT INTO Brands (BrandName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('APPLE', 'Apple', 'Premium electronics and smartphones', 'System'),
('SAMSUNG', 'Samsung', 'Electronics, mobiles, and appliances', 'System'),
('NIKE', 'Nike', 'Footwear and sports accessories', 'System'),
('ADIDAS', 'Adidas', 'Sportswear and footwear brand', 'System'),
('SONY', 'Sony', 'Audio and electronics devices', 'System');
-- Insert Script With Category Hierarchy
-- Level 1 Categories
INSERT INTO Categories (CategoryName, DisplayName, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('ELECTRONICS', 'Electronics', 'Electronic products', 'System'),
('FASHION', 'Fashion', 'Clothing and fashion accessories', 'System');
-- Level 2 Categories
INSERT INTO Categories (CategoryName, DisplayName, ParentCategoryID, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('MOBILE', 'Mobile Phones', 1, 'Mobiles and accessories', 'System'),
('MEN', 'Men Fashion', 2, 'Men clothing and accessories', 'System');
-- Level 3 Categories
INSERT INTO Categories (CategoryName, DisplayName, ParentCategoryID, Description, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('SMARTPHONES', 'Smartphones', 3, 'Smart mobile phones', 'System'),
('MOBILE_ACCESSORIES', 'Mobile Accessories', 3, 'Covers, chargers, etc.', 'System'),
('SHOES', 'Men Shoes', 4, 'Footwear for men', 'System'),
('T_SHIRTS', 'Men T-Shirts', 4, 'Cotton and casual T-shirts', 'System');
-- DeliveryPartners
INSERT INTO DeliveryPartners (PartnerName, DisplayName, TrackingUrl, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('DELHIVERY', 'Delhivery', 'https://www.delhivery.com/track/', 'System'),
('BLUEDART', 'Blue Dart', 'https://bluedart.com/tracking', 'System'),
('ECOM_EXPRESS', 'Ecom Express', 'https://www.ecomexpress.in/tracking/', 'System'),
('XPRESSBEES', 'XpressBees', 'https://www.xpressbees.com/track-shipment', 'System'),
('DTDC', 'DTDC', 'https://www.dtdc.in/tracking.asp', 'System'),
('SHADOWFAX', 'Shadowfax', 'https://www.shadowfax.in/track', 'System'),
('INDIA_POST', 'India Post', 'https://www.indiapost.gov.in/TrackConsignment.aspx', 'System'),
('SPEED_POST', 'Speed Post', 'https://www.indiapost.gov.in/TrackConsignment.aspx', 'System');
-- Products Master
INSERT INTO Products
(
ProductName, SKU, BrandID, Description,
IsDiscountActive, IsTaxIncluded,
MRP, BasePrice, DiscountPercent, FlatDiscount, TaxPercent,
StockQuantity, CreatedBy
)
VALUES
-- 1. iPhone 14 (Discount Active, Tax Exclusive, % Discount)
('iPhone 14', 'IP14-BLUE-128', 1,
'Apple iPhone 14 128GB Blue',
1, 0,
79999, 74999, 10, 0, 18,
50, 'System'),
-- 2. Samsung Galaxy S23 (Flat Discount, Tax Exclusive)
('Samsung Galaxy S23', 'S23-BLACK-256', 2,
'Samsung Galaxy S23 256GB Phantom Black',
1, 0,
74999, 69999, 0, 5000, 18,
40, 'System'),
-- 3. Sony WH-1000XM5 (No Discount, Tax Exclusive)
('Sony WH-1000XM5 Wireless Headphones', 'SONY-XM5-BLK', 5,
'Industry-leading noise cancelling wireless headphones',
0, 0,
34990, 32990, 0, 0, 18,
25, 'System'),
-- 4. Apple 20W Charger (No Discount, Tax Included)
('Apple 20W USB-C Charger', 'APP-CHRGR-20W', 1,
'Fast charging Apple 20W USB-C adapter',
0, 1,
1999, 1999, 0, 0, 18,
100, 'System'),
-- 5. Nike Air Zoom Pegasus (Percent + Flat Discount, Tax Exclusive)
('Nike Air Zoom Pegasus', 'NIKE-PGS-42', 3,
'Nike Air Zoom Pegasus running shoes for men',
1, 0,
9999, 8999, 5, 300, 18,
60, 'System'),
-- 6. Adidas Men's T-Shirt (Discount Active, Low Tax Product)
('Adidas Men Cotton T-Shirt', 'ADIDAS-TSHIRT-L', 4,
'Pure cotton casual T-shirt for men',
1, 0,
1999, 1599, 20, 0, 5,
120, 'System');
-- StockTransactions
INSERT INTO StockTransactions
(ProductID, StockTransactionTypeID, QuantityChange, OldStock, NewStock, ReferenceType, Remarks, CreatedBy)
VALUES
(1, 4, 50, 0, 50, 'INITIAL_STOCK', 'Opening Stock', 'System'), -- PURCHASE_RESTOCK
(2, 4, 40, 0, 40, 'INITIAL_STOCK', 'Opening Stock', 'System'),
(3, 4, 25, 0, 25, 'INITIAL_STOCK', 'Opening Stock', 'System'),
(4, 4, 100, 0, 100, 'INITIAL_STOCK', 'Opening Stock', 'System'),
(5, 4, 60, 0, 60, 'INITIAL_STOCK', 'Opening Stock', 'System'),
(6, 4, 120, 0, 120, 'INITIAL_STOCK', 'Opening Stock', 'System');
-- Customers
INSERT INTO Customers
(FirstName, LastName, Email, Phone, PasswordHash, IsEmailVerified, CreatedBy)
VALUES
('Pranaya', 'Rout', 'pranaya.rout@example.com', '9876543210', 'Test@1234', 1, 'System'),
('Suresh', 'Das', 'suresh.das@example.com', '9865321470', 'Test@1234', 1, 'System'),
('Ananya', 'Mohanty', 'ananya.mohanty@example.com', '9856237410', 'Test@1234', 0, 'System');
-- CustomerRoles
INSERT INTO CustomerRoles (CustomerID, RoleID, CreatedBy)
VALUES
(1, 1, 'System'), -- Pranaya -> ADMIN
(2, 3, 'System'), -- Suresh -> SELLER
(3, 2, 'System'); -- Ananya -> CUSTOMER
-- Customer 1 – Pranaya Rout
INSERT INTO Addresses
(CustomerID, AddressType, AddressLine1, AddressLine2, City, State, PostalCode, Country, IsDefault, CreatedBy)
VALUES
(1, 'Home', 'Plot No. 45, Sai Enclave', 'Near InfoCity', 'Bhubaneswar', 'Odisha', '751024', 'India', 1, 'System'),
(1, 'Office', '2nd Floor, DLF Cyber Tower', 'Patia', 'Bhubaneswar', 'Odisha', '751024', 'India', 0, 'System');
-- Customer 2 – Suresh Das
INSERT INTO Addresses
(CustomerID, AddressType, AddressLine1, AddressLine2, City, State, PostalCode, Country, IsDefault, CreatedBy)
VALUES
(2, 'Home', 'Mahatab Road', 'Old Town Area', 'Cuttack', 'Odisha', '753001', 'India', 1, 'System');
--Customer 3 – Ananya Mohanty
INSERT INTO Addresses
(CustomerID, AddressType, AddressLine1, AddressLine2, City, State, PostalCode, Country, IsDefault, CreatedBy)
VALUES
(3, 'Home', 'Lane 7, Sahid Nagar', 'Near BMC Mall', 'Bhubaneswar', 'Odisha', '751007', 'India', 1, 'System');
INSERT INTO ProductAttributes (ProductID, AttributeName, AttributeValue, CreatedBy)
VALUES
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------
PRODUCT 1 — iPhone 14
ProductID = 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
(1, 'COLOR', 'Blue', 'System'),
(1, 'STORAGE', '128 GB', 'System'),
(1, 'RAM', '6 GB', 'System'),
(1, 'DISPLAY', '6.1-inch Super Retina XDR', 'System'),
(1, 'PROCESSOR', 'A15 Bionic Chip', 'System'),
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------
PRODUCT 2 — Samsung Galaxy S23
ProductID = 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
(2, 'COLOR', 'Phantom Black', 'System'),
(2, 'STORAGE', '256 GB', 'System'),
(2, 'RAM', '8 GB', 'System'),
(2, 'CAMERA', '50 MP Triple Camera', 'System'),
(2, 'DISPLAY', '6.1-inch AMOLED 120Hz', 'System'),
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------
PRODUCT 3 — Sony WH-1000XM5 Headphones
ProductID = 3
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
(3, 'COLOR', 'Black', 'System'),
(3, 'CONNECTIVITY', 'Bluetooth 5.2', 'System'),
(3, 'NOISE_CANCELLATION', 'Active Noise Cancelling', 'System'),
(3, 'BATTERY_LIFE', '30 Hours', 'System'),
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------
PRODUCT 4 — Apple 20W Charger
ProductID = 4
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
(4, 'POWER', '20W', 'System'),
(4, 'PORT_TYPE', 'USB-C', 'System'),
(4, 'COMPATIBILITY', 'iPhone/iPad', 'System'),
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------
PRODUCT 5 — Nike Air Zoom Pegasus Shoes
ProductID = 5
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
(5, 'SIZE', '42', 'System'),
(5, 'COLOR', 'Black/White', 'System'),
(5, 'MATERIAL', 'Mesh', 'System'),
(5, 'SPORT_TYPE', 'Running', 'System'),
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------
PRODUCT 6 — Adidas Men’s Cotton T-Shirt
ProductID = 6
-------------------------------------------------------------------- */
(6, 'SIZE', 'Large', 'System'),
(6, 'COLOR', 'Navy Blue', 'System'),
(6, 'MATERIAL', '100% Cotton', 'System'),
(6, 'FIT', 'Regular Fit', 'System');
Creating a New ASP.NET Core Web API Application:
The Database First Approach in EF Core can be integrated into any .NET Core-based project type.
Entity Framework Core is framework-independent, meaning it can be used with:
- ASP.NET Core Web API – to build RESTful services that interact with a database.
- ASP.NET Core MVC – for web applications with views and controllers.
- Console Applications – for background jobs, utilities, or testing data access layers.
In this example, we use an ASP.NET Core Web API project to demonstrate how EF Core works with an existing EcommerceDB database. So, first create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project and name it EcommerceApplication.
Installing EF Core Packages
Since the Database First Approach relies on EF Core to communicate with SQL Server, we need to install three essential NuGet packages via the Package Manager Console (PMC). Execute the following commands sequentially:
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Explanation of Each Package
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore → The core library that provides ORM capabilities such as change tracking, querying, and saving data.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer → The database provider that allows EF Core to connect and interact with Microsoft SQL Server databases.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools → Provides command-line tools (like Scaffold-DbContext, Migrations, etc.) for generating models and managing database schema changes.
After installing these packages, the project is now ready to connect to the database and generate the DbContext and entity classes automatically using the Database First (Scaffold) process.
Storing Connection String in AppSettings.json file:
We have added Pricing Rules and a connection string to the appsettings.json file.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"PricingRules": {
"ShippingThreshold": 1000,
"ShippingCharge": 50,
"PlatformFeeThreshold": 1000,
"PlatformFee": 5
},
"ConnectionStrings": {
"EcommerceDBConnection": "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EcommerceDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
}
}
Implementing EF Core Database First Approach
Now that the Web API project, EF Core packages, and the database connection string are ready, the next step is to generate the DbContext and entity classes from the existing EcommerceDB database.
Understanding EF Core Reverse Engineering (Scaffolding)
In classic Entity Framework 6.x, developers could use a visual EDMX designer to import a database and automatically generate entities and context classes using a GUI wizard. However, in EF Core, Microsoft removed the visual designer to make the framework lighter, faster, and cross-platform. Instead, EF Core uses a command-line reverse-engineering process known as Scaffolding.
What is Scaffolding?
Scaffolding is the process where EF Core automatically:
- Reads the structure of the existing database (tables, columns, foreign keys, relationships).
- Generates the corresponding C# Entity Classes that represent each table.
- Generates a DbContext Class that manages the connection and interaction with the database.
This process is done via the Scaffold-DbContext command, using the EF Core Tools package.
Scaffolding in EF Core involves reverse-engineering the database schema into code. It allows developers to generate automatically:
- Model classes (Entities) → representing database tables.
- DbContext class → acting as a gateway to interact with the database.
This process eliminates the need to create entity classes manually and ensures the code model exactly mirrors the database structure.
Syntax of Scaffold-DbContext Command
The Scaffold-DbContext command creates entities and a context class based on the schema of the existing database, and we need to do this using the Package Manager Console (PMC) tools. Let us first understand the syntax.
Syntax: Scaffold-DbContext “Connection String” Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -o Models -f
Explanation of Parameters:
- Connection String: Specifies how EF Core connects to the database. It includes server name, database name, authentication mode, and security parameters.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer: identifies the database provider (SQL Server in this case). You can replace it with another provider, such as MySQL or PostgreSQL, if needed.
- -o Models: Defines the output directory where EF Core will place the generated DbContext and entity classes. Here, a folder named Models will be created in the project.
- -f: (Optional) Force overwrite mode. If model files already exist, this flag ensures they are re-generated and replaced.
Example: Connecting to SQL Server EcommerceDB Database
Now that the syntax is clear, let’s apply it practically to our EcommerceDB.
Scaffold-DbContext “Name=ConnectionStrings:EcommerceDBConnection” Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models -f
Syntax Explanation
- “Name=ConnectionStrings:EcommerceDBConnection” → Tells EF Core to read the connection string named EcommerceDBConnection from the appsettings.json configuration file.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer → Specifies the SQL Server provider used by EF Core for database communication.
- -OutputDir Models → Defines the folder named Models where the DbContext and entity classes will be generated.
- -f → Forces regeneration by overwriting any existing model and context files.
So, open the Package Manager Console and execute the following command to create the entities and context class based on our EcommerceDB database:
What Happens When You Run This Command?
Once you execute the Scaffold-DbContext command in the Package Manager Console, EF Core performs the following actions:
- Connects to the Database using the connection string.
- Reads all database metadata (tables, relationships, foreign keys, constraints).
- Generates entity classes for each table (e.g., Customer, Product, Order, Payment, etc.).
- Creates the DbContext class (e.g., EcommerceDbContext) containing DbSet<TEntity> properties for each entity.
- Places the generated files inside the Models folder in your project.
Generated Output
After scaffolding completes successfully, you will see a new Models folder in your project structure containing:
- EcommerceDbContext.cs → The main context class for managing database access.
- Customer.cs, Product.cs, Order.cs, etc. → Entity classes representing your database tables.
The Scaffold-DbContext command in EF Core is the cornerstone of the Database First Approach.
It automates model generation, saves development time, and ensures your application stays perfectly synchronized with the existing SQL Server database.
Register the DbContext in the DI Container
Open your Program.cs file and register your DbContext using the connection string from appsettings.json.
using EcommerceApplication.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EcommerceApplication
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers()
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
// Keep JSON property names exactly as defined in the C# models
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
// Register DbContext with dependency injection
builder.Services.AddDbContext<EcommerceDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("EcommerceDBConnection")));
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Create DTOs for Order Placement
We will use Data Annotations for validation and keep the API input clean and secure. So, create a class file named OrderCreateDTO.cs within the DTOs folder, and copy-paste the following code.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EcommerceApplication.DTOs
{
public class OrderCreateDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "CustomerId is required.")]
public long CustomerId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "ShippingAddressId is required.")]
public long ShippingAddressId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "BillingAddressId is required.")]
public long BillingAddressId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "OrderItems are required.")]
public List<OrderItemCreateDTO> OrderItems { get; set; } = new();
}
public class OrderItemCreateDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "ProductId is required.")]
public long ProductId { get; set; }
[Range(1, int.MaxValue, ErrorMessage = "Quantity must be at least 1.")]
public int Quantity { get; set; }
}
}
Create OrdersController with Order Placement Logic
Create an API Empty Controller named Orders Controller within the Controllers folder, then copy and paste the following code.
using EcommerceApplication.DTOs;
using EcommerceApplication.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Infrastructure;
using System.Text.Json;
namespace EcommerceApplication.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly EcommerceDbContext _context;
private readonly IConfiguration _config;
public OrdersController(EcommerceDbContext context, IConfiguration config)
{
_context = context;
_config = config;
}
[HttpPost("Place")]
public async Task<IActionResult> PlaceOrder([FromBody] OrderCreateDTO dto)
{
// Validate basic DTO structure before processing
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(new
{
Success = false,
Message = "Validation failed.",
Errors = ModelState.Values.SelectMany(v => v.Errors).Select(e => e.ErrorMessage)
});
}
// Check whether the customer exists
if (!await _context.Customers.AnyAsync(c => c.CustomerId == dto.CustomerId))
{
return BadRequest(new { Success = false, Message = "Invalid CustomerId." });
}
// Validate that shipping and billing addresses belong to the same customer
var addresses = await _context.Addresses
.AsNoTracking()
.Where(a => a.CustomerId == dto.CustomerId &&
(a.AddressId == dto.ShippingAddressId || a.AddressId == dto.BillingAddressId))
.ToListAsync();
if (addresses.Count != 2)
{
return BadRequest(new
{
Success = false,
Message = "Shipping or billing address does not belong to the specified customer."
});
}
var shippingAddress = addresses.First(a => a.AddressId == dto.ShippingAddressId);
var billingAddress = addresses.First(a => a.AddressId == dto.BillingAddressId);
// Convert address snapshots to JSON to store inside the order record
string shippingAddressJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(shippingAddress);
string billingAddressJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(billingAddress);
// Ensure order contains at least one item
if (dto.OrderItems == null || dto.OrderItems.Count == 0)
{
return BadRequest(new { Success = false, Message = "Order must contain at least one item." });
}
// Fetch product records for validation and pricing snapshot creation
var productIds = dto.OrderItems.Select(i => i.ProductId).ToList();
var products = await _context.Products
.Include(p => p.Brand)
.Include(p => p.ProductAttributes)
.Where(p => productIds.Contains(p.ProductId))
.ToListAsync();
if (products.Count != dto.OrderItems.Count)
{
return BadRequest(new { Success = false, Message = "One or more product IDs are invalid." });
}
// Read pricing rules from appsettings.json
var pricingConfig = _context.GetService<IConfiguration>().GetSection("PricingRules");
decimal shippingThreshold = pricingConfig.GetValue<decimal>("ShippingThreshold");
decimal shippingChargeRule = pricingConfig.GetValue<decimal>("ShippingCharge");
decimal platformFeeThreshold = pricingConfig.GetValue<decimal>("PlatformFeeThreshold");
decimal platformFeeRule = pricingConfig.GetValue<decimal>("PlatformFee");
// Variables to hold order-level calculations
decimal itemsTotal = 0;
decimal discountTotal = 0;
decimal taxTotal = 0;
List<OrderItem> orderItems = new();
// Loop through each ordered product and calculate the snapshot pricing
foreach (var item in dto.OrderItems)
{
var product = products.First(p => p.ProductId == item.ProductId);
// Ensure the requested quantity is available
if (product.StockQuantity < item.Quantity)
{
return BadRequest(new
{
Success = false,
Message = $"Insufficient stock for {product.ProductName}."
});
}
// Calculate the base selling price
decimal sellingPrice = product.BasePrice;
// Calculate discount for this product based on discount rules
decimal discount = product.IsDiscountActive
? ((product.BasePrice * (product.DiscountPercent ?? 0) / 100) +
(product.FlatDiscount ?? 0))
: 0;
// Price after applying discount
decimal priceAfterDiscount = sellingPrice - discount;
// Calculate tax, considering whether the base price already includes tax
decimal tax = product.IsTaxIncluded
? (priceAfterDiscount * (product.TaxPercent ?? 0) /
(100 + (product.TaxPercent ?? 0)))
: (priceAfterDiscount * (product.TaxPercent ?? 0) / 100);
// Calculate final price the customer pays for one unit
decimal finalPrice = product.IsTaxIncluded
? priceAfterDiscount
: priceAfterDiscount + tax;
// Round all values to avoid floating-point precision issues
sellingPrice = Math.Round(sellingPrice, 2, MidpointRounding.AwayFromZero);
discount = Math.Round(discount, 2);
priceAfterDiscount = Math.Round(priceAfterDiscount, 2);
tax = Math.Round(tax, 2);
finalPrice = Math.Round(finalPrice, 2);
// Add totals for order-level summary
itemsTotal += priceAfterDiscount * item.Quantity;
discountTotal += discount * item.Quantity;
taxTotal += tax * item.Quantity;
// Create a complete order item snapshot for auditing, invoice, or refunds
orderItems.Add(new OrderItem
{
ProductId = product.ProductId,
ProductName = product.ProductName,
Sku = product.Sku,
BrandName = product.Brand?.BrandName,
ProductAttributesJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(
product.ProductAttributes.Select(a => new { a.AttributeName, a.AttributeValue })
),
Mrp = product.Mrp,
SellingPrice = sellingPrice,
DiscountPercent = product.DiscountPercent ?? 0,
DiscountFlat = product.FlatDiscount ?? 0,
DiscountTotal = discount,
PriceAfterDiscount = priceAfterDiscount,
TaxPercent = product.TaxPercent ?? 0,
TaxAmount = tax,
FinalPrice = finalPrice,
Quantity = item.Quantity,
IsActive = true,
CreatedBy = "API",
CreatedDate = DateTime.Now
});
}
// Round order-level totals
itemsTotal = Math.Round(itemsTotal, 2);
discountTotal = Math.Round(discountTotal, 2);
taxTotal = Math.Round(taxTotal, 2);
// Determine whether shipping charge applies
decimal shippingTotal = itemsTotal < shippingThreshold
? Math.Round(shippingChargeRule, 2)
: 0;
// Determine whether platform fee applies
decimal platformFee = itemsTotal < platformFeeThreshold
? Math.Round(platformFeeRule, 2)
: 0;
// Calculate the final amount the customer must pay
decimal grandTotal = Math.Round(
itemsTotal - discountTotal + taxTotal + shippingTotal + platformFee,
2,
MidpointRounding.AwayFromZero
);
// Start a database transaction so the entire order is committed atomically
using var transaction = await _context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync();
try
{
// Insert the main order record
var order = new Order
{
CustomerId = dto.CustomerId,
OrderStatusId = 1,
OrderDate = DateTime.Now,
ShippingAddressJson = shippingAddressJson,
BillingAddressJson = billingAddressJson,
ItemsTotal = itemsTotal,
OrderDiscountTotal = discountTotal,
OrderTaxTotal = taxTotal,
ShippingTotal = shippingTotal,
PlatformFee = platformFee,
GrandTotal = grandTotal,
IsActive = true,
CreatedBy = "API",
CreatedDate = DateTime.Now
};
_context.Orders.Add(order);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Insert each order item linked to the newly created order
foreach (var oi in orderItems)
{
oi.OrderId = order.OrderId;
_context.OrderItems.Add(oi);
}
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Update product stock and insert stock transaction logs
foreach (var item in dto.OrderItems)
{
var product = products.First(x => x.ProductId == item.ProductId);
int oldStock = product.StockQuantity;
int newStock = oldStock - item.Quantity;
product.StockQuantity = newStock;
_context.StockTransactions.Add(new StockTransaction
{
ProductId = product.ProductId,
StockTransactionTypeId = 1,
QuantityChange = -item.Quantity,
OldStock = oldStock,
NewStock = newStock,
ReferenceType = "ORDER",
ReferenceId = order.OrderId,
Remarks = "Stock deducted due to order placement.",
IsActive = true,
CreatedBy = "API",
CreatedDate = DateTime.Now
});
}
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Insert order status history entry for tracking
_context.OrderStatusHistories.Add(new OrderStatusHistory
{
OrderId = order.OrderId,
OldStatusId = null,
NewStatusId = order.OrderStatusId,
ChangedAt = DateTime.Now,
Remarks = "Order placed successfully.",
IsActive = true,
CreatedBy = "API",
CreatedDate = DateTime.Now
});
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Commit all changes in a single atomic operation
await transaction.CommitAsync();
return Ok(new
{
Success = true,
Message = "Order placed successfully.",
OrderId = order.OrderId,
GrandTotal = grandTotal
});
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
await transaction.RollbackAsync();
return StatusCode(500, new
{
Success = false,
Message = "Order placement failed.",
Error = ex.Message
});
}
}
}
}
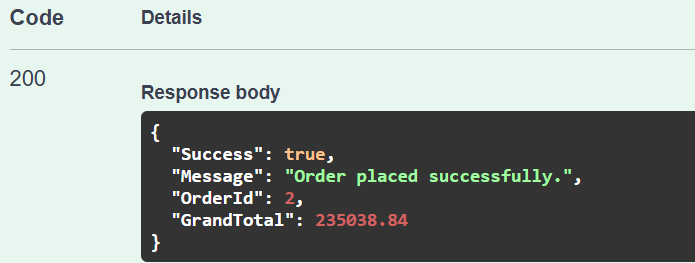
Testing the Endpoint:
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"ShippingAddressId": 1,
"BillingAddressId": 2,
"OrderItems": [
{
"ProductId": 1,
"Quantity": 1
},
{
"ProductId": 2,
"Quantity": 1
},
{
"ProductId": 3,
"Quantity": 2
},
{
"ProductId": 4,
"Quantity": 1
},
{
"ProductId": 5,
"Quantity": 1
},
{
"ProductId": 6,
"Quantity": 2
}
]
}
Response in Swagger:
Advantages of the EF Core Database First Approach
- Quick integration with existing databases: Developers can start building applications on them immediately without altering the schema.
- DBA-driven schema management: In organizations where dedicated database teams manage database structure and relationships, this approach ensures application models remain synchronized with the database.
- Reduced manual effort: EF Core auto-generates entity classes, primary keys, relationships, and navigation properties, eliminating the need to define them manually.
- Strong alignment with enterprise systems: Many enterprise-level applications rely on large, complex databases. The Database First approach ensures model accuracy by directly deriving entities from those schemas.
- Ideal for reverse engineering legacy systems: When migrating or modernizing older applications, this approach provides a smooth way to adopt EF Core without rewriting the database layer.
Do we need to run Scaffold-DbContext every time the database schema changes?
Not always, but here’s the reasoning:
- Scaffold-DbContext is a reverse-engineering command; it reads your database schema and auto-generates (or updates) the C# entity classes and DbContext.
- EF Core does not automatically track database changes once the models are generated.
- Therefore, whenever you change the database schema (e.g., add a table, modify a column, rename constraints), you must manually refresh your EF models, usually by running.
- Scaffold-DbContext “Name=ConnectionStrings:EcommerceDBConnection” Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models -f
- Using the -f (force) flag overwrites any generated files with the latest schema.
In short: If your database schema changes → you must scaffold again to regenerate your models. If your database stays the same → no need to rerun it.
What if I want to add new entities or modify entity properties? Can this be handled using EF Core Code First?
Yes, this can be handled using Code First Migrations. Even though your application uses Database First, you can still extend it by introducing Code First migrations for future changes. However, you must understand the bigger difference:
Difference Between Database First and Code First for Schema Changes
Database First
- DB schema is modified manually (SQL scripts, SSMS).
- EF classes are generated from the DB (Scaffold).
- DB → C# (reverse engineering).
Code First
- DB schema is generated from your C# classes.
- You write the entity classes; EF generates SQL migration files.
- C# → DB (forward engineering)
Can you mix Code First with Database First?
Entity Framework Core allows both Database First and Code First workflows. However, mixing them inside the same project requires careful planning because each workflow has a different philosophy:
- Database First → The database schema is the source of truth.
- Code First → The C# entity classes are the source of truth.
Because both workflows try to “own” the database schema, mixing them blindly can create conflicts. Let us try to understand this concept with real-world scenarios.
Scenario 1: You want to add new tables only via EF Core
Example: Adding Logs, AuditTrail, OTP, and BackgroundJobs tables
- Create a new C# entity class
- Add DbSet to DbContext
- Run migration:
-
- Add-Migration AddLogsTable
- Update-Database
-
This works perfectly because these tables are new and do not interfere with the DB First tables.
Scenario 2: You want to modify existing Database First tables
This scenario is where problems arise. Why is modifying Database First tables using Code First risky? Because:
In Database First:
- The database schema is designed manually.
- The entity classes are generated from the DB using Scaffold-DbContext.
- EF Core expects the schema to remain consistent with the database.
In Code First:
- The schema is generated from your C# model.
- EF Core will create migrations that ALTER existing tables.
- EF assumes it has complete control over the schema.
This creates conflicts when both workflows try to “own” the same table.
Best Practice for Real Projects
Most enterprise applications follow a hybrid rule:
Rule 1 → The core business tables (Orders, Products, Customers) remain DB-First.
Because:
- DBAs control them
- They are shared across multiple systems
- Strict SQL scripts/testing is required
Code First should not modify these tables.
Rule 2 → Application-only tables (Logs, Tokens, Preferences, Caches) can be Code-First.
These are internal to your application and safe to manage with migrations.
So, in short:
- We can mix both approaches in the same project.
- Use Code First only for new tables that EF Core can fully control.
- Do NOT use Code First to modify existing tables from Database First.
- Never mix both workflows on the same database table.
Conclusion:
The Entity Framework Core Database First approach bridges the gap between existing database structures and modern .NET applications. It’s particularly effective in enterprise or legacy environments where the database is the backbone of the system.
In an E-commerce scenario, this approach allows developers to rapidly build APIs or web applications using EF Core without redesigning the database, ensuring scalability, maintainability, and alignment with existing data models.
By combining EF Core’s ORM capabilities with a robust, pre-existing SQL Server schema, the Database First approach provides a clean, efficient, and production-ready data access solution.
