Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
Setting Up the ASP.NET Core Web API Project
In this article, I will discuss ASP.NET Core Web API Project Setup for Hotel Booking. Please read our previous articles discussing the Database Design of a Hotel Booking Application.
Creating a new ASP.NET Core Web API Project
Once the database design is ready, next, we need to set up our ASP.NET Core Web API Project for the application development. So, create a new ASP.NET Core Web API Project (I am using the latest .NET 8 version while creating this project) named HotelBookingAPI.
Setting Up the Database Connection
We need to find a better way to manage our database connection. You can typically manage your database connection string in the appsettings.json file. So, modify the appsettings.json file as follows:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=HotelDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
Add NuGet Package for ADO.NET Core
To use ADO.NET Core to connect with SQL Server Database, you need to add Microsoft.Data.SqlClient package to your project. You can install this package using NuGet Package Manager or Package Manager Console. You can install Microsoft.Data.SqlClient package by running the following command in the Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Microsoft.Data.SqlClient
Creating Connection Service:
Once the connection string is defined within the appsettings.json file and once we add the required ADO.NET Core Package, we need to create a simple service for creating and opening the database connection.
So, what we are going to do is create a folder called Connection, and inside that Connection folder, we are going to create the Connection class. So, add a folder named Connection to the project root directory, then create a class file named SqlConnectionFactory.cs within the Connection folder, and then copy and paste the following code:
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
namespace HotelBookingAPI.Connection
{
public class SqlConnectionFactory
{
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
public SqlConnectionFactory(IConfiguration configuration)
{
_configuration = configuration;
}
public SqlConnection CreateConnection()
=> new SqlConnection(_configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"));
}
}
Registering the SqlConnectionFactory Service:
Next, we need to register this SqlConnectionFactory service in the Program.cs class file as follows:
builder.Services.AddTransient<SqlConnectionFactory>();
Creating a Custom Response Format:
Next, we need to create a generic class for uniformly returning different types of responses from our application, including both successful and error responses. This approach enhances the integration capabilities with clients and improves the maintainability of the API.
So, create a folder named Models within the Project root directory and inside the Models folder create a class file named APIResponse.cs and copy and paste the following code into it.
using System.Net;
namespace HotelBookingAPI.Models
{
public class APIResponse<T>
{
public bool Success { get; set; }
public HttpStatusCode StatusCode { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
public T Data { get; set; }
public object Error { get; set; } // Flexible enough to include any error details
// Constructor for a Successful Response
public APIResponse(T data, string message = "", HttpStatusCode statusCode = HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
Success = true;
StatusCode = statusCode;
Message = message;
Data = data;
Error = null;
}
// Constructor for an Error Response
public APIResponse(HttpStatusCode statusCode, string message, object error = null)
{
Success = false;
StatusCode = statusCode;
Message = message;
Data = default(T);
Error = error;
}
}
}
Globalization Invariant Mode Set to FALSE.
Globalization Invariant Mode is a feature that is typically used in .NET applications to reduce the deployment size by not including culture-specific data. So, open the Project Properties file and set the InvariantGlobalization to false as follows:
<InvariantGlobalization>false</InvariantGlobalization>
Modifying JSON Serialization Settings:
In ASP.NET Core Web API, the default behavior for JSON serialization involves converting property names to camel cases. This is due to the default JSON options set by the framework to align with JavaScript and JSON standards. However, if you want to keep the property names exactly as they are defined in your models (typically PascalCase), you can customize the JSON serialization settings. So, modify the AddController Service as follows with the Program.cs class file:
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
Integrating Logging Framework:
We are going to use Serilog to logging. Serilog is a popular, high-performance, structured logging library for .NET applications. Please use the following commands to install Serilog using Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Serilog.AspNetCore
Install-Package Serilog.Sinks.File
Install-Package Serilog.Settings.Configuration
Configure Serilog in appsettings.json
In your appsettings.json, define the Serilog configuration. You can specify sinks, filters, minimum log levels, and more. Modify the appsettings.json file as follows, which includes the Serilog configurations and the database connection string.
{
"Serilog": {
"MinimumLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Override": {
"Microsoft": "Error",
"System": "Error"
}
},
"WriteTo": [
{
"Name": "File",
"Args": {
"path": "Logs/MyAppLog-.txt",
"rollingInterval": "Day",
"outputTemplate": "{Timestamp:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff zzz} [{Level:u3}] {Message:lj}{NewLine}{Exception}"
}
}
]
},
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=HotelDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
}
}
Initialize Serilog in Program.cs
In your Program.cs file, you need to load the Serilog configuration from appsettings.json. So, please add the following code to the Program.cs file:
// Initialize Serilog from appsettings.json
builder.Host.UseSerilog((context, services, configuration) => configuration
.ReadFrom.Configuration(context.Configuration)
.ReadFrom.Services(services));
At this point in time, the Program.cs class should look as follows:
using HotelBookingAPI.Connection;
using Serilog;
namespace HotelBookingAPI
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
// Initialize Serilog from appsettings.json
builder.Host.UseSerilog((context, services, configuration) => configuration
.ReadFrom.Configuration(context.Configuration)
.ReadFrom.Services(services));
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
builder.Services.AddTransient<SqlConnectionFactory>();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Note: We will see how to use Serilog once we start creating the Controller and Services.
Note: Please delete the WeatherForecastController.cs and WeatherForecast.cs class files from your project, which are not required.
Creating Folder for Repositories and DTOs:
Next, we need to create the folder structures for Creating Models, DTOs, and Repositories. The models will come inside the Models folder, which we already created. Next, add a folder called Repository to the project root directory. Inside this folder, we will create all our repositories, such as UserRepository, RoomRepository, ReservationRepository, etc.
Next, create another folder named DTOs at the project root directory, and inside this folder, we will create subfolders per each module, such as a subfolder UserDTOs for the user Module, RoomDTOs for Room module, PaymentDTOs for Payment modules, etc. We will see what all modules are as we progress in the development of this application. At this point, the Project structure should look as shown in the below image:
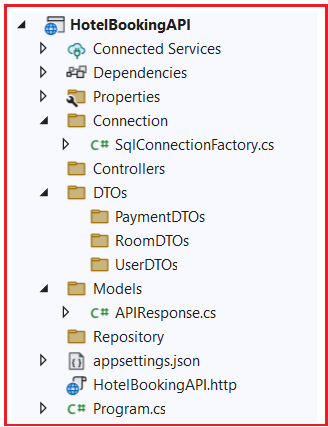
In this article, I explain the ASP.NET Core Web API Project Setup for Hotel Booking. I hope you enjoy this ASP.NET Core Web API Project Setup for Hotel Booking article. Please take a few minutes to give your valuable feedback about this article. Your feedback means a lot to me and motivates me to give better examples and explanations.
What Next? Implementing User Module of our Hotel Booking Application.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
