Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
Creating Resource Server and Client Applications with JWT Authentication
In this article, I will discuss Creating Resource Servers and Client Applications with JWT Authentication. Please read our previous article discussing Token-Based Authentication using JWT in ASP.NET Core Web API. This is a continuation of our previous article. Here, I will show you how to create the Resource Server with Secured Endpoints using JWT Token, and then we will create a .NET Console as the client application consuming the services using JWT Token:
- Resource Server Application: This will be an ASP.NET Core Web API Project, exposing secured endpoints to be consumed by clients.
- Client Application: This will be a .NET Core Console Application. This application will first generate the access token using the endpoint provided by the Authentication Server application. Then, using the access token, it will access the secure endpoints from the Resource Server Application.
Creating Resource Server Application:
Now, we will create the Resource Server application to expose secure endpoints to be consumed by clients with JWT Token-Based Authentication. So, create a new ASP.NET Core Web API Project named ResourceServer. Once you create the project, please install the following NuGet package by executing the following command in the Visual Studio Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer
Modify the appsettings.json:
Then, please modify the appsettings.json file as follows. Here, you need to provide the correct URL for the Issuer and JWKS property where your authentication server is running.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"Jwt": {
"Issuer": "https://localhost:7022",
"JWKS": "https://localhost:7022/.well-known/jwks.json"
}
}
Configure JWT Authentication:
Modify the Program.cs file to set up JWT Bearer authentication, pointing to the Authentication Server’s JWKS endpoint for token validation. So, please modify the Program.cs file as follows:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
namespace ResourceServer
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers()
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
// This will use the property names as defined in the C# model
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidIssuer = builder.Configuration["Jwt:Issuer"],
ValidateAudience = false,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
IssuerSigningKeyResolver = (token, securityToken, kid, validationParameters) =>
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
var jwks = httpClient.GetStringAsync(builder.Configuration["Jwt:JWKS"]).Result;
var keys = new JsonWebKeySet(jwks).Keys;
return keys;
}
};
});
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Create the Product Model
First, create a folder named Models in the project root directory. Then, create a class file named Product.cs within the Models folder and copy and paste the following code:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ResourceServer.Models
{
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(100)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[StringLength(500)]
public string Description { get; set; }
[Range(0, double.MaxValue)]
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
}
Creating API Controller:
Let’s create the ProductsController with CRUD operations, using an in-memory list to store products. We will secure all endpoints using JWT authentication. So, create an Empty API Controller named ProductsController within the Controllers folder and copy and paste the following code. The [Authorize] Attribute is applied at the controller level to secure all endpoints. Only authenticated users can access them.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using ResourceServer.Models;
namespace ResourceServer.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
[Authorize] // Secures all endpoints in this controller
public class ProductsController : ControllerBase
{
// In-memory list to store products
private static readonly List<Product> Products = new List<Product>
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Product A", Price = 10.0M, Description = "Test Product A" },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Product B", Price = 20.0M, Description = "Test Product B" },
new Product { Id = 3, Name = "Product C", Price = 30.0M, Description = "Test Product C" }
};
private static int _nextId = 4; // To auto-increment product IDs
// Retrieves all products.
[HttpGet("GetAll")]
public ActionResult<List<Product>> GetAllProduct()
{
return Ok(Products);
}
// Retrieves a specific product by ID.
[HttpGet("GetById/{id}", Name = "GetProductById")]
public ActionResult<Product> GetProductById(int id)
{
var product = Products.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Id == id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound(new { message = $"Product with ID {id} not found." });
}
return Ok(product);
}
// Creates a new product.
[HttpPost("Add")]
public IActionResult AddProduct([FromBody] Product product)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
product.Id = _nextId++;
Products.Add(product);
return CreatedAtRoute("GetProductById", new { id = product.Id }, product);
}
// Updates an existing product. Only accessible by Admins.
[HttpPut("Update/{id}")]
public IActionResult UpdateProduct(int id, [FromBody] Product updatedProduct)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
var existingProduct = Products.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Id == id);
if (existingProduct == null)
{
return NotFound(new { message = $"Product with ID {id} not found." });
}
existingProduct.Name = updatedProduct.Name;
existingProduct.Description = updatedProduct.Description;
existingProduct.Price = updatedProduct.Price;
return NoContent();
}
// Deletes a product by ID. Only accessible by Admins.
[HttpDelete("Delete/{id}")]
public IActionResult DeleteProduct(int id)
{
var product = Products.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Id == id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound(new { message = $"Product with ID {id} not found." });
}
Products.Remove(product);
return NoContent();
}
}
}
Obtain a JWT Token to Access the Secured Resources
Authenticates the user and issues a JWT token upon successful login. Please ensure that ClientId corresponds to a valid client in your database (e.g., Client1). This endpoint belongs to the Authentication server.
HTTP Method: POST
Endpoint: /api/Auth/Login
Headers:
Content-Type: application/json
Body (Raw JSON):
{
"Email": "john.doe@example.com",
"Password": "Password@123",
"ClientId": "Client1"
}
Expected Response:
If the provided credentials are valid, you will get a response containing a valid JWT in the token field. You will need this token to authenticate requests.
{
"Token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCIsImtpZCI6IjEyMzQ1NiJ9..."
}
Add a New Product
This endpoint allows the creation of a new product, and it belongs to the Resource server.
HTTP Method: POST
Endpoint: /api/Products/Add
Headers:
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer {JWT Token}}
Body (Raw JSON):
{
"Name": "Test",
"Description": "Test-Product",
"Price": 100
}
Note: You need to replace {JWT Token} with the actual token you received when you call the Login endpoint.
Expected Response:
You will get a response indicating that the product was successfully added, as shown below.
{
"Id": 4,
"Name": "Product D",
"Description": "Test Product D",
"Price": 100
}
Get All Products
This endpoint retrieves all the Products from the Resource server.
HTTP Method: GET
Endpoint: /api/Products/GetAll
Headers:
Authorization: Bearer {JWT Token}}
Note: You need to replace {JWT Token} with the actual token you received when you call the Login endpoint.
Expected Response:
You will get a response containing all the products, as shown below.
[
{
"Id": 1,
"Name": "Product A",
"Description": "Test Product A",
"Price": 10.0
},
//Rest of all Products
]
Update Product
This endpoint updates product information. This belongs to the Resource Server.
HTTP Method: PUT
Endpoint: api/Products/Update/1
Headers:
Authorization: Bearer {JWT Token}}
Body (Raw JSON):
{
"Id": 4,
"Name": "Test",
"Description": "Test-Product",
"Price": 100
}
Note: You need to replace {JWT Token} with the actual token you received when you call the Login endpoint.
Creating Client Application:
Now, we will create a Dot Net Console Application Consuming the Resource Server API Endpoints with JWT Authentication. Let’s create a .NET Console Application named ResourceClient that will perform the following actions:
- Authenticate with the Authentication Server by calling the /api/Auth/Login endpoint to obtain a JWT token.
- Consume the Resource Server’s ProductsController endpoints using the obtained JWT token to perform CRUD operations.
So, create a Dot Net Console Application named ResourceClient and then modify the Program class as follows:
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json;
namespace ResourceClient
{
public class Program
{
// Configuration settings
private static readonly string AuthServerBaseUrl = "https://localhost:7022"; // Authentication Server URL
private static readonly string ResourceServerBaseUrl = "https://localhost:7267"; // Replace with your Resource Server's URL and port
private static readonly string ClientId = "Client1"; // Must match a valid ClientId in Auth Server
private static readonly string UserEmail = "pranaya@example.com"; // Replace with registered user's email
private static readonly string UserPassword = "Password@123"; // Replace with registered user's password
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Step 1: Authenticate and obtain JWT token
var token = await AuthenticateAsync(UserEmail, UserPassword, ClientId);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(token))
{
Console.WriteLine("Authentication failed. Exiting...");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Authentication successful. JWT Token obtained.\n");
// Step 2: Consume Resource Server's ProductsController endpoints
await ConsumeResourceServerAsync(token);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"An error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Authenticates the user with the Authentication Server and retrieves a JWT token.
private static async Task<string?> AuthenticateAsync(string email, string password, string clientId)
{
using var httpClient = new HttpClient();
var loginUrl = $"{AuthServerBaseUrl}/api/Auth/Login";
var loginData = new
{
Email = email,
Password = password,
ClientId = clientId
};
var content = new StringContent(JsonSerializer.Serialize(loginData), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
Console.WriteLine("Sending authentication request...");
var response = await httpClient.PostAsync(loginUrl, content);
if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Authentication failed with status code: {response.StatusCode}");
var errorContent = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {errorContent}\n");
return null;
}
var responseContent = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var jsonDoc = JsonDocument.Parse(responseContent);
if (jsonDoc.RootElement.TryGetProperty("Token", out var tokenElement))
{
return tokenElement.GetString();
}
Console.WriteLine("Token not found in the authentication response.\n");
return null;
}
// Consumes the Resource Server's ProductsController endpoints using the JWT token.
private static async Task ConsumeResourceServerAsync(string token)
{
using var httpClient = new HttpClient();
// Set the Authorization header with the Bearer token
httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", token);
// Create a new product
var newProduct = new
{
Name = "Smartphone",
Description = "A high-end smartphone with excellent features.",
Price = 999.99
};
Console.WriteLine("Creating a new product...");
var createResponse = await httpClient.PostAsync(
$"{ResourceServerBaseUrl}/api/Products/Add",
new StringContent(JsonSerializer.Serialize(newProduct), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"));
if (createResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var createdProductJson = await createResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Product created successfully: {createdProductJson}\n");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed to create product. Status Code: {createResponse.StatusCode}");
var errorContent = await createResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {errorContent}\n");
}
// Step Retrieve all products
Console.WriteLine("Retrieving all products...");
var getAllResponse = await httpClient.GetAsync($"{ResourceServerBaseUrl}/api/Products/GetAll");
if (getAllResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var productsJson = await getAllResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Products: {productsJson}\n");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed to retrieve products. Status Code: {getAllResponse.StatusCode}");
var errorContent = await getAllResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {errorContent}\n");
}
// Step Retrieve a specific product by ID
Console.WriteLine("Retrieving product with ID 1...");
var getByIdResponse = await httpClient.GetAsync($"{ResourceServerBaseUrl}/api/Products/GetById/1");
if (getByIdResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var productJson = await getByIdResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Product Details: {productJson}\n");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed to retrieve product. Status Code: {getByIdResponse.StatusCode}");
var errorContent = await getByIdResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {errorContent}\n");
}
// Step Update a product
var updatedProduct = new
{
Name = "Smartphone Pro",
Description = "An upgraded smartphone with enhanced features.",
Price = 1199.99
};
Console.WriteLine("Updating product with ID 1...");
var updateResponse = await httpClient.PutAsync(
$"{ResourceServerBaseUrl}/api/Products/Update/1",
new StringContent(JsonSerializer.Serialize(updatedProduct), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"));
if (updateResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode || updateResponse.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NoContent)
{
Console.WriteLine("Product updated successfully.\n");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed to update product. Status Code: {updateResponse.StatusCode}");
var errorContent = await updateResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {errorContent}\n");
}
// Step Delete a product
Console.WriteLine("Deleting product with ID 1...");
var deleteResponse = await httpClient.DeleteAsync($"{ResourceServerBaseUrl}/api/Products/Delete/1");
if (deleteResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode || deleteResponse.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NoContent)
{
Console.WriteLine("Product deleted successfully.\n");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed to delete product. Status Code: {deleteResponse.StatusCode}");
var errorContent = await deleteResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {errorContent}\n");
}
}
}
}
Explanation of the Console Client Code
Configuration Settings:
- AuthServerBaseUrl: URL of the Authentication Server (e.g., https://localhost:7022).
- ResourceServerBaseUrl: URL of the Resource Server (e.g., https://localhost:7067).
- ClientId: Must match a valid ClientId registered in the Authentication Server.
- UserEmail & UserPassword: Credentials of a registered user in the Authentication Server. Ensure that this user has the Admin role to perform CRUD operations.
AuthenticateAsync Method:
Sends a POST request to /api/Auth/Login with the user’s email, password, and client ID. If successful, extracts and returns the JWT token from the response. Handles and displays error messages if authentication fails.
ConsumeResourceServerAsync Method:
Sets the Authorization Header: Adds the Bearer token to the Authorization header for authenticated requests. Then perform CRUD Operations:
Create a New Product (POST /api/Products/Add):
- Sends a POST request with product details.
- Displays the created product details upon success.
Retrieve All Products (GET /api/Products/GetAll):
- Sends a GET request to retrieve all products.
- Displays the list of products.
Retrieve a Specific Product by ID (GET /api/Products/GetById/{id}):
- Sends a GET request for a specific product (e.g., ID 1).
- Displays the product details.
Update a Product (PUT /api/Products/Update/{id}):
- Sends a PUT request with updated product details for a specific product.
- Confirm the update upon success.
Delete a Product (DELETE /api/Products/{id}):
- Sends a DELETE request for a specific product.
- Confirms the deletion upon success.
Now, run the above client application, and you should get the following output. Please ensure your Authentication Server and Resource Server Apps are running.
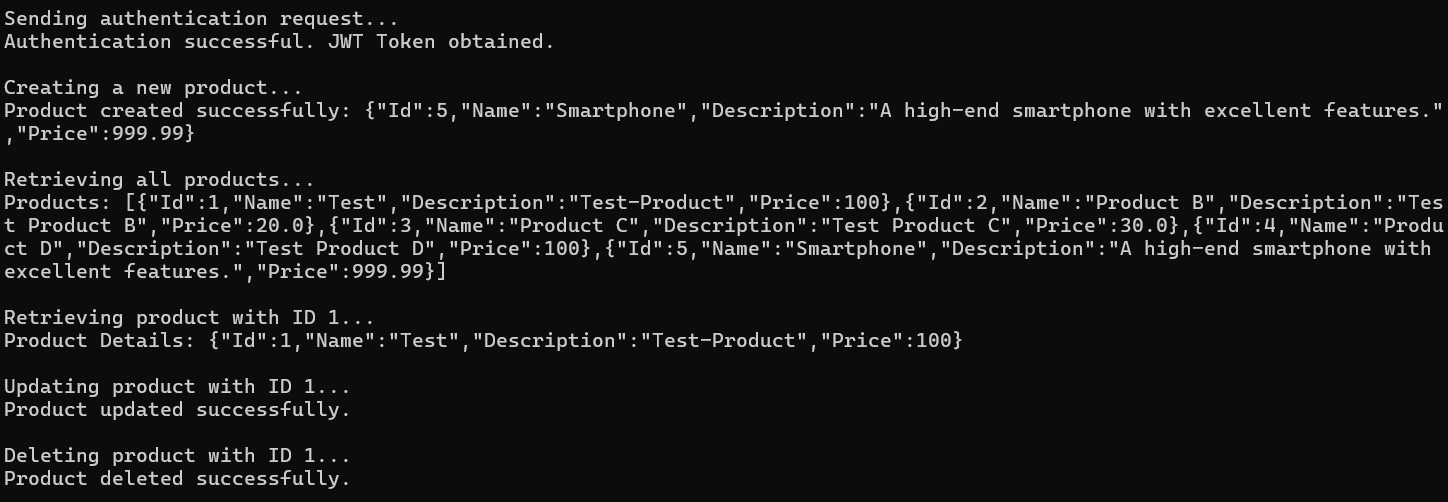
We have successfully created a .NET Console Application that:
- Authenticates with the Authentication Server to obtain a JWT token.
- Consumes the Resource Server’s ProductsController endpoints to perform CRUD operations using the JWT token for authorization.
This setup ensures secure communication between the client and the servers, adhering to modern authentication and authorization practices using JWT tokens.
In the next article, I will discuss implementing Refresh Token in ASP.NET Core Web API using JWT Authentication. In this article, I explain Resource Server and Client Applications with JWT Authentication with Examples. I hope you enjoy this Resource Server and Client Applications with JWT Authentication article.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group

Thanks Pranaya
Your code works perfect, only makin some chamges for OpenApi
Reggards.