Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
How to Design and Develop Customer Module in ECommerce Application
In this article, I will discuss How to Design and Develop the Customer Module in our ECommerce Application using ASP.NET Core Web API and EF Core. Please read our previous article discussing the Database Design of our ECommerce Application using ASP.NET Core Web API and EF Core Code First Approach.
The Customer Module serves as the foundational component of the E-Commerce application, responsible for managing all customer-related activities. Its primary functions include facilitating user registration, handling secure authentication processes, and enabling comprehensive profile management. By ensuring the safe storage and validation of sensitive information, such as passwords and personal details, the module enhances user trust and experience.
Key Features of the Customer Module
The following are the Key Features of the Customer Module that we will implement in our Ecommerce Application:
- Customer Registration: Facilitates new users to create accounts by providing necessary personal and contact information. Ensures data validation and secure storage of sensitive information like passwords.
- Customer Authentication: Manages user login processes, verifying credentials to grant access to authenticated features. Ensures secure handling of login data and authentication tokens.
- Profile Management: Allows customers to view and update their personal information. Enables password changes with appropriate security measures.
Creating DTOs for Customer Module Development:
DTOs play a pivotal role in structuring and validating the data exchanged between the client and server. Now, we will create the required request and response DTOs to manage the Customers. First, create a folder named CustomerDTOs within the DTOs folder where we will create all our DTOs related to Customers.
CustomerRegistrationDTO
Create a class file named CustomerRegistrationDTO.cs within the DTOs\CustomerDTOs folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The CustomerRegistrationDTO captures and validates the information required for a new customer to register an account. It is used when a user submits a registration form to create a new customer profile.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs
{
// DTO for customer registration
public class CustomerRegistrationDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "First Name is required.")]
[MinLength(2, ErrorMessage = "First Name must be at least 2 characters.")]
[MaxLength(50, ErrorMessage = "First Name cannot exceed 50 characters.")]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Last Name is required.")]
[MinLength(2, ErrorMessage = "Last Name must be at least 2 characters.")]
[MaxLength(50, ErrorMessage = "Last Name cannot exceed 50 characters.")]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Email is required.")]
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Email Address.")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "PhoneNumber is required.")]
[Phone(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Phone Number.")]
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "DateOfBirth is required.")]
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is required.")]
[MinLength(8, ErrorMessage = "Password must be at least 8 characters.")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}
CustomerResponseDTO
Create a class file named CustomerResponseDTO.cs within the DTOs\CustomerDTOs folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The CustomerResponseDTO Delivers comprehensive customer information, including personal details and associated addresses, in API responses. It is used by the API to fetch detailed customer profiles for display or management purposes.
namespace ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs
{
// DTO for returning customer details.
public class CustomerResponseDTO
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
}
}
CustomerUpdateDTO
Create a class file named CustomerUpdateDTO.cs within the DTOs\CustomerDTOs folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The CustomerUpdateDTO captures and validates the information required to update an existing customer.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs
{
public class CustomerUpdateDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "CustomerId is required.")]
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "First Name is required.")]
[MinLength(2, ErrorMessage = "First Name must be at least 2 characters.")]
[MaxLength(50, ErrorMessage = "First Name cannot exceed 50 characters.")]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Last Name is required.")]
[MinLength(2, ErrorMessage = "Last Name must be at least 2 characters.")]
[MaxLength(50, ErrorMessage = "Last Name cannot exceed 50 characters.")]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Email is required.")]
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Email Address.")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "PhoneNumber is required.")]
[Phone(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Phone Number.")]
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "DateOfBirth is required.")]
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
}
}
LoginDTO
Create a class file named LoginDTO.cs within the DTOs\CustomerDTOs folder and then copy and paste the following code. The LoginDTO Represents the credentials required for a customer to authenticate and log into their account. It is used during the login process, where customers provide their email and password to gain access.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs
{
// DTO for customer login
public class LoginDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Email is required.")]
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Email Address.")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is required.")]
[MinLength(8, ErrorMessage = "Password must be at least 8 characters.")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}
LoginResponseDTO
Create a class file named LoginResponseDTO.cs within the DTOs\CustomerDTOs folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The LoginResponseDTO Provides a structured response after a successful login, including customer identification and a confirmation message. It is used to send back the response to the client upon successful authentication to inform the user of a successful login and provide relevant user details.
namespace ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs
{
public class LoginResponseDTO
{
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
public string CustomerName { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
}
}
ChangePasswordDTO
Create a class file named ChangePasswordDTO.cs within the DTOs\CustomerDTOs folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The CustomerRegistrationDTO will capture the customer’s current password and the new desired password.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs
{
// DTO for changing password
public class ChangePasswordDTO
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "CustomerId is required.")]
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Current Password is required.")]
public string CurrentPassword { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "New Password is required.")]
[MinLength(8, ErrorMessage = "New Password must be at least 8 characters.")]
public string NewPassword { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Confirm New Password is required.")]
[Compare("NewPassword", ErrorMessage = "New Password and Confirm New Password do not match.")]
public string ConfirmNewPassword { get; set; }
}
}
Service Classes:
Service Classes are dedicated components in an application’s architecture that encapsulate business logic and data processing operations. They act as an intermediary layer between the controller (which handles incoming requests) and the data access layer (such as repositories or the database context). By isolating these operations into separate classes, we achieve a clear separation of concerns and improve the overall maintainability, testability, and scalability of the codebase. First, create a folder named Services in the project root directory, where we will create all our services.
Customer Service Class
Create a class file named CustomerService.cs within the Services folder, and then copy and paste the following code. The CustomerService class is dedicated to encapsulating all business logic and data access operations related to customer management. By centralizing these operations, the service ensures that the controller remains clean, focusing only on handling HTTP requests and responses.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using ECommerceApp.Data;
using ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs;
using ECommerceApp.Models;
using ECommerceApp.DTOs;
namespace ECommerceApp.Services
{
public class CustomerService
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _context;
public CustomerService(ApplicationDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public async Task<ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>> RegisterCustomerAsync(CustomerRegistrationDTO customerDto)
{
try
{
// Check if email already exists
if (await _context.Customers.AnyAsync(c => c.Email.ToLower() == customerDto.Email.ToLower()))
{
return new ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>(400, "Email is already in use.");
}
// Manual mapping from DTO to Model
var customer = new Customer
{
FirstName = customerDto.FirstName,
LastName = customerDto.LastName,
Email = customerDto.Email,
PhoneNumber = customerDto.PhoneNumber,
DateOfBirth = customerDto.DateOfBirth,
IsActive = true,
// Hash the password using BCrypt
Password = BCrypt.Net.BCrypt.HashPassword(customerDto.Password)
};
// Add customer to the database
_context.Customers.Add(customer);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Prepare response data
var customerResponse = new CustomerResponseDTO
{
Id = customer.Id,
FirstName = customer.FirstName,
LastName = customer.LastName,
Email = customer.Email,
PhoneNumber = customer.PhoneNumber,
DateOfBirth = customer.DateOfBirth
};
return new ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>(200, customerResponse);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log the exception (implementation depends on your logging setup)
return new ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>(500, $"An unexpected error occurred while processing your request, Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
public async Task<ApiResponse<LoginResponseDTO>> LoginAsync(LoginDTO loginDto)
{
try
{
// Find customer by email with AsNoTracking for performance since we don't need to track changes
var customer = await _context.Customers
.AsNoTracking()
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(c => c.Email == loginDto.Email);
if (customer == null)
{
return new ApiResponse<LoginResponseDTO>(401, "Invalid email or password.");
}
// Verify password using BCrypt
bool isPasswordValid = BCrypt.Net.BCrypt.Verify(loginDto.Password, customer.Password);
if (!isPasswordValid)
{
return new ApiResponse<LoginResponseDTO>(401, "Invalid email or password.");
}
// Prepare response data
var loginResponse = new LoginResponseDTO
{
Message = "Login successful.",
CustomerId = customer.Id,
CustomerName = $"{customer.FirstName} {customer.LastName}"
};
return new ApiResponse<LoginResponseDTO>(200, loginResponse);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log the exception
return new ApiResponse<LoginResponseDTO>(500, $"An unexpected error occurred while processing your request, Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
public async Task<ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>> GetCustomerByIdAsync(int id)
{
try
{
var customer = await _context.Customers
.AsNoTracking()
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(c => c.Id == id && c.IsActive == true);
if (customer == null)
{
return new ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>(404, "Customer not found.");
}
// Map to CustomerResponseDTO
var customerResponse = new CustomerResponseDTO
{
Id = customer.Id,
FirstName = customer.FirstName,
LastName = customer.LastName,
Email = customer.Email,
PhoneNumber = customer.PhoneNumber,
DateOfBirth = customer.DateOfBirth
};
return new ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>(200, customerResponse);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log the exception
return new ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>(500, $"An unexpected error occurred while processing your request, Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
public async Task<ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>> UpdateCustomerAsync(CustomerUpdateDTO customerDto)
{
try
{
var customer = await _context.Customers.FindAsync(customerDto.CustomerId);
if (customer == null)
{
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(404, "Customer not found.");
}
// Check if email is being updated to an existing one
if (customer.Email != customerDto.Email && await _context.Customers.AnyAsync(c => c.Email == customerDto.Email))
{
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(400, "Email is already in use.");
}
// Update customer properties manually
customer.FirstName = customerDto.FirstName;
customer.LastName = customerDto.LastName;
customer.Email = customerDto.Email;
customer.PhoneNumber = customerDto.PhoneNumber;
customer.DateOfBirth = customerDto.DateOfBirth;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Prepare confirmation message
var confirmationMessage = new ConfirmationResponseDTO
{
Message = $"Customer with Id {customerDto.CustomerId} updated successfully."
};
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(200, confirmationMessage);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log the exception
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(500, $"An unexpected error occurred while processing your request, Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
public async Task<ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>> DeleteCustomerAsync(int id)
{
try
{
var customer = await _context.Customers
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(c => c.Id == id);
if (customer == null)
{
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(404, "Customer not found.");
}
//Soft Delete
customer.IsActive = false;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Prepare confirmation message
var confirmationMessage = new ConfirmationResponseDTO
{
Message = $"Customer with Id {id} deleted successfully."
};
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(200, confirmationMessage);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log the exception
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(500, $"An unexpected error occurred while processing your request, Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// Changes the password for an existing customer.
public async Task<ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>> ChangePasswordAsync(ChangePasswordDTO changePasswordDto)
{
try
{
var customer = await _context.Customers.FindAsync(changePasswordDto.CustomerId);
if (customer == null || !customer.IsActive)
{
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(404, "Customer not found or inactive.");
}
// Verify current password
bool isCurrentPasswordValid = BCrypt.Net.BCrypt.Verify(changePasswordDto.CurrentPassword, customer.Password);
if (!isCurrentPasswordValid)
{
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(401, "Current password is incorrect.");
}
// Hash the new password
customer.Password = BCrypt.Net.BCrypt.HashPassword(changePasswordDto.NewPassword);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
// Prepare confirmation message
var confirmationMessage = new ConfirmationResponseDTO
{
Message = "Password changed successfully."
};
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(200, confirmationMessage);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log the exception (implementation depends on your logging setup)
return new ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>(500, $"An unexpected error occurred while processing your request, Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Registering the CustomerService:
Please modify the Program class as follows to register the CustomerService.
using ECommerceApp.Data;
using ECommerceApp.Services;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace ECommerceApp
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers()
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
// This will use the property names as defined in the C# model
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
// Configure EF Core with SQL Server
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("EFCoreDBConnection")));
// Registering the CustomerService
builder.Services.AddScoped<CustomerService>();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Creating Customers Controller
The CustomersController manages all customer-related operations, including registration, authentication, profile management, etc. It is the central point for handling HTTP requests related to customers in the E-Commerce Application.
The CustomersController will use the CustomerService class to handle customer-related operations. This results in a cleaner controller that delegates the business logic to the appropriate service classes. So, create a new API Empty Controller named CustomersController within the Controllers folder and copy and paste the following code.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using ECommerceApp.DTOs;
using ECommerceApp.DTOs.CustomerDTOs;
using ECommerceApp.Services;
namespace ECommerceApp.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class CustomersController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly CustomerService _customerService;
// Injecting the services
public CustomersController(CustomerService customerService)
{
_customerService = customerService;
}
// Registers a new customer.
[HttpPost("RegisterCustomer")]
public async Task<ActionResult<ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>>> RegisterCustomer([FromBody] CustomerRegistrationDTO customerDto)
{
var response = await _customerService.RegisterCustomerAsync(customerDto);
if (response.StatusCode != 200)
{
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, response);
}
return Ok(response);
}
// Logs in a customer.
[HttpPost("Login")]
public async Task<ActionResult<ApiResponse<LoginResponseDTO>>> Login([FromBody] LoginDTO loginDto)
{
var response = await _customerService.LoginAsync(loginDto);
if (response.StatusCode != 200)
{
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, response);
}
return Ok(response);
}
// Retrieves customer details by ID.
[HttpGet("GetCustomerById/{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<ApiResponse<CustomerResponseDTO>>> GetCustomerById(int id)
{
var response = await _customerService.GetCustomerByIdAsync(id);
if (response.StatusCode != 200)
{
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, response);
}
return Ok(response);
}
// Updates customer details.
[HttpPut("UpdateCustomer")]
public async Task<ActionResult<ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>>> UpdateCustomer([FromBody] CustomerUpdateDTO customerDto)
{
var response = await _customerService.UpdateCustomerAsync(customerDto);
if (response.StatusCode != 200)
{
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, response);
}
return Ok(response);
}
// Deletes a customer by ID.
[HttpDelete("DeleteCustomer/{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>>> DeleteCustomer(int id)
{
var response = await _customerService.DeleteCustomerAsync(id);
if (response.StatusCode != 200)
{
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, response);
}
return Ok(response);
}
// Changes the password for an existing customer.
[HttpPost("ChangePassword")]
public async Task<ActionResult<ApiResponse<ConfirmationResponseDTO>>> ChangePassword([FromBody] ChangePasswordDTO changePasswordDto)
{
var response = await _customerService.ChangePasswordAsync(changePasswordDto);
if (response.StatusCode != 200)
{
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, response);
}
return Ok(response);
}
}
}
Testing the Customers Module Endpoints of our ECommerce Application:
Register Customer:
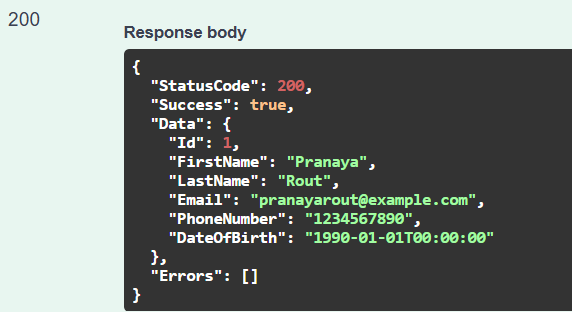
Handles the registration of new customers by validating input data, creating customer records, and ensuring email uniqueness. Invoked when a user submits a registration form to create a new account. This endpoint Registers a new customer by providing necessary personal and contact information.
Endpoint: POST /api/Customers/RegisterCustomer
URL: http://localhost:5000/api/Customers/RegisterCustomer
Method: POST
Headers: Content-Type: application/json
Request Body:
{
"FirstName": "Pranaya",
"LastName": "Rout",
"Email": "pranayarout@example.com",
"PhoneNumber": "1234567890",
"DateOfBirth": "1990-01-01",
"Password": "Password@456"
}
Response in Swagger:
Login:
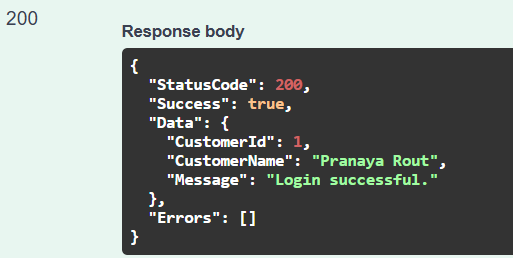
Authenticates customers by verifying their email and password and responds to successful or failed login attempts. Triggered when a customer attempts to log into their account. This endpoint Authenticates a customer using their email and password.
Endpoint: POST /api/Customers/Login
Method: POST
URL: http://localhost:5000/api/Customers/Login
Headers: Content-Type: application/json
Request Body:
{
"Email": "pranayarout@example.com",
"Password": "Password@456"
}
Response in Swagger:
Get Customer by ID:
Retrieves detailed information of a specific customer, including their addresses and orders. Used when fetching a customer’s profile details for viewing or administrative purposes. This endpoint Retrieves detailed information about a specific customer, including their addresses.
Endpoint: GET /api/Customers/GetCustomerById/{id}
Method: POST
URL: http://localhost:5000/api/Customers/GetCustomerById/1
Response in Swagger:

Update Customer:
Updates existing customer information, ensuring data integrity and handling password changes securely. Called when a customer edits their profile information. This endpoint updates existing customer information, including optional password changes.
Endpoint: PUT /api/Customers/UpdateCustomer
Method: PUT
URL: http://localhost:5000/api/Customers/UpdateCustomer
Headers: Content-Type: application/json
Request Body:
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"FirstName": "Pranaya",
"LastName": "Kumar",
"Email": "Pranaya.Kumar@example.com",
"PhoneNumber": "9876543210",
"DateOfBirth": "1990-01-01"
}
Response in Swagger:

Change Password:
This endpoint will receive the ChangePasswordDTO, invoke the service method, and return the appropriate response. That means this endpoint changes the password for an existing customer.
Endpoint: POST /api/Customers/ChangePassword
URL: http://localhost:5000/api/Customers/ChangePassword
Method: POST
Headers: Content-Type: application/json
Request Body:
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"CurrentPassword": "Password@456",
"NewPassword": " Password@123",
"ConfirmNewPassword": " Password@123"
}
Response in Swagger:

Delete Customer:
Removes a customer and all associated data (addresses and orders) from the system. It is used when a customer requests account deletion or for administrative account removal.
Endpoint: DELETE /api/Customers/DeleteCustomer/{id}
URL: http://localhost:5000/api/Customers/DeleteCustomer/1
Method: DELETE
Note: We are not deleting the customer.
So, we have done with our Customer Module Implementation in our Ecommerce Application using ASP.NET Core Web API and Entity Framework Core. In the next article, we will discuss How to Implement the Address Module of our ECommerce Application for Managing the Billing and Shipping addresses. In this article, we discussed How to Design and Develop the Customer Module for our ECommerce Application using ASP.NET Core Web API and EF Core.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
