Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
ASP.NET Core Web API Versioning using URL Path
In this article, I will discuss how to Implement Web API Versioning using URL Path in ASP.NET Core Web API Applications. Please read our previous article discussing ASP.NET Core Web API Versioning using Query String.
What is URL Path Versioning in Web API?
URL Path Versioning is a method of versioning a Web API by including the API’s version number directly in the URL path. This method is explicit and straightforward, as the version information is directly visible in the endpoint’s URL.
For example, a versioned API path could look like /api/v1.0/products or /api/v2.0/products, where v1.0 and v2.0 indicate different versions of the API. This versioning strategy helps clients know exactly which version they are interacting with, minimizing confusion and compatibility issues.
How Does URL Path Versioning Work in ASP.NET Core Web API?
URL Path Versioning works by embedding the version number in the URL path itself. When a client makes a request, the server parses the URL to determine the requested version of the API. This method ensures that each version of the API has a distinct URL, making it easy to manage and differentiate between different versions.
In ASP.NET Core Web API, URL path versioning is implemented by setting up the API’s routing configuration to recognize and extract version numbers from the URL path. The API can then interpret and route requests to the appropriate controller actions based on the version specified in the URL.
- Routing Configuration: ASP.NET Core Web API uses a middleware pipeline to handle requests, and routing is part of this pipeline. When we configure routing to include version numbers, ASP.NET Core Web API parses the URL path and maps the version part of the URL to a specific controller or action that handles requests for that version.
- Controller and Action Versioning: We can decorate controllers and actions with version attributes that specify which version(s) they apply to. ASP.NET Core’s routing engine uses these annotations to direct incoming requests to the right controllers and actions based on the version specified in the URL.
How Do We Implement URL Path Versioning in ASP.NET Core Web API?
Implementing URL Path Versioning in an ASP.NET Core Web API Application involves defining different versions of API directly in the URL path. This approach makes it clear which version of the API is being called. Let us proceed and understand the step-by-step approach to implementing URL Path Versioning in an ASP.NET Core Web API project. First, create a new ASP.NET Core Web API Project named URLPathAPIVersioning.
Install Necessary Packages
For API versioning, we need the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning package. This can be done via the NuGet Package Manager in Visual Studio or using the following command in the Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning
Configure URL Path API Versioning:
In the Program.cs file, we need to add and configure the URL Path API Versioning services. This configuration includes specifying how the API versions are read (from the URL in this case) and setting default versioning behavior. So, please modify the Program.cs file as follows to configure URL Path API versioning. We are also modifying the Swagger Configuration to show the API versioning without any error.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.OpenApi.Models;
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.SwaggerGen;
using System.Reflection;
namespace URLPathAPIVersioning
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
// Add API Versioning
builder.Services.AddApiVersioning(options =>
{
// Specify the default API version
// Default version: 1.0
options.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0);
// If the client does not specify a version, use the default version
options.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true;
// Optional: to include API versions in the response headers
options.ReportApiVersions = true;
// Read version info from URL segment
options.ApiVersionReader = new UrlSegmentApiVersionReader();
});
// Add Swagger generation
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen(options =>
{
// Defines two Swagger documents, one for API version 1.0 and another for version 2.0.
// Each document includes metadata like the title and version.
// These documents will be accessible in Swagger UI,
// allowing users to view and interact with the different versions of the API
// Define a Swagger document for API version 1.0
options.SwaggerDoc("1.0", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "My API", Version = "1.0" });
// Define a Swagger document for API version 2.0
options.SwaggerDoc("2.0", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "My API", Version = "2.0" });
// Resolving Conflicts
// This resolves conflicts when multiple actions match the same route and HTTP method
// by selecting the first action encountered
options.ResolveConflictingActions(apiDescriptions => apiDescriptions.First());
// Doc Inclusion Predicate
// Define a predicate function to determine which API Endpoints should be included
// in the Swagger documentation based on the version
options.DocInclusionPredicate((version, apiDesc) =>
{
// Attempt to get the MethodInfo for the API Endpoint
if (!apiDesc.TryGetMethodInfo(out MethodInfo method))
return false; //If the MethodInfo for the API description cannot be retrieved, the endpoint is excluded.
// Extracts the versions specified by [ApiVersion] attributes at the method level.
// Ensures that method-level versioning is considered when deciding which endpoints to include in the Swagger documentation
var methodVersions = method.GetCustomAttributes(true)
.OfType<ApiVersionAttribute>()
.SelectMany(attr => attr.Versions);
// Extracts the versions specified by [ApiVersion] attributes at the controller level.
// Ensures that controller-level versioning is considered, allowing for endpoints that might be versioned at the controller level.
var controllerVersions = method.DeclaringType?
.GetCustomAttributes(true)
.OfType<ApiVersionAttribute>()
.SelectMany(attr => attr.Versions);
// Combining Versions
// Combines the versions extracted from both the method and controller levels to create a unified set of versions.
// Ensures that all relevant versions are considered, avoiding duplication by using Distinct()
var allVersions = methodVersions.Union(controllerVersions).Distinct();
// Checks if any of the combined versions match the version specified in the Swagger document
// This determines if the API Endpoint should be included in the current Swagger document based on the version.
return allVersions.Any(v => v.ToString() == version);
});
});
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
// Enable middleware to serve generated Swagger as a JSON endpoint
app.UseSwagger();
// Enable middleware to serve Swagger UI
app.UseSwaggerUI(options =>
{
// Define the Swagger endpoints for each version
options.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/1.0/swagger.json", "My API V1");
options.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/2.0/swagger.json", "My API V2");
});
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}
}
Define the Product Model
To demonstrate how to handle different versions of an API using URL Path Versioning, let’s define a product model and then use some hardcoded data to return from the action methods. So, create a class file named Product.cs within the Models folder and then copy and paste the following code.
namespace URLPathAPIVersioning.Models
{
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
}
}
Define a Versioned API Controller
Create a controller with different versions of the same method using attributes to handle versioning. So, create an Empty API Controller named Products Controller and copy and paste the following code. As you can see, here, define routes that include the API version as part of the URL path.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using URLPathAPIVersioning.Models;
namespace URLPathAPIVersioning.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
// Defines the route template with version parameter for the entire controller.
[Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/products")]
public class ProductsController : ControllerBase
{
// Action method to get a list of products for version 1.0
[HttpGet]
// Specifies that this action only supports API version 1.0.
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsV1()
{
// Returns a hardcoded list of products specifically for version 1.0 of the API.
return new List<Product>
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Apple", Price = 1.50, Category = "Fruit" },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Bread", Price = 2.25, Category = "Bakery" }
};
}
// Action method to get a single product by ID for version 1.0
[HttpGet]
// Specifies the route for this action, appending the Id parameter to the base route.
[Route("{Id}")]
// Specifies that this action only supports API version 1.0.
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public Product GetProductsByIdV1(int Id)
{
// Returns a hardcoded product matching the provided ID.
return new Product { Id = Id, Name = "Apple", Price = 1.50, Category = "Fruit" }; // Returns a Product object.
}
// Action method to get a list of products for version 2.0
[HttpGet]
// Specifies that this action supports API version 2.0.
[ApiVersion("2.0")]
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsV2()
{
// Returns a hardcoded list of products specifically for version 2.0 of the API, with an additional product.
return new List<Product>
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Apple", Price = 1.50, Category = "Fruit" },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Bread", Price = 2.25, Category = "Bakery" },
new Product { Id = 3, Name = "Carrot", Price = 0.75, Category = "Vegetable" }
};
}
}
}
Now, run the application and access the two versions of the endpoint. It should work as expected.
Testing API Version 1.0:
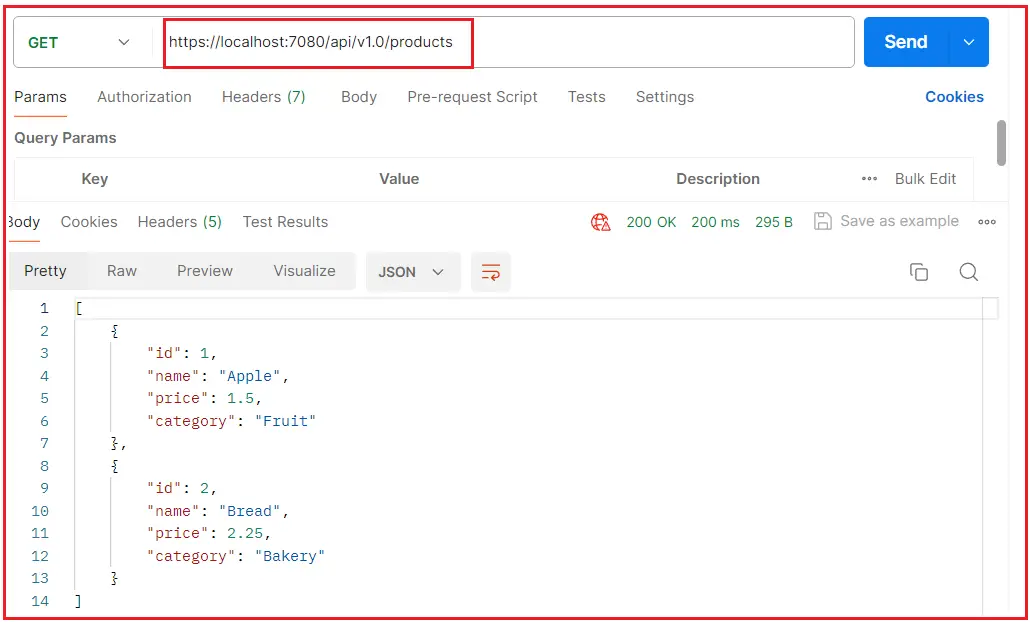
Testing API Version 2.0:

What is ApiVersion Attribute?
This attribute specifies which API version(s) an action method or controller is intended to serve. It can be applied at the controller level to all actions within the controller or to individual actions to specify different versions for each. We use this attribute to declare that certain actions are part of specific API versions.
Applying ApiVersion Attribute at the Controller level:
It is also possible to apply the ApiVersion Attribute at the Controller level. Let us understand this with an example. Let us create two Controllers. So, for simplicity, let us modify the Products Controller as follows. Here, you can see, we have two Controllers, and each controller is annotated with an ApiVersion Attribute with a different version number.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using URLPathAPIVersioning.Models;
namespace URLPathAPIVersioning.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/products")]
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public class ProductsV1Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsV1()
{
// Returns a hardcoded list of products specifically for version 1.0 of the API.
return new List<Product>
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Apple", Price = 1.50, Category = "Fruit" },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Bread", Price = 2.25, Category = "Bakery" }
};
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("{Id}")]
public Product GetProductsByIdV1(int Id)
{
// Returns a hardcoded product matching the provided ID.
return new Product { Id = Id, Name = "Apple", Price = 1.50, Category = "Fruit" }; // Returns a Product object.
}
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/products")]
[ApiVersion("2.0")]
public class ProductsV2Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsV2()
{
// Returns a hardcoded list of products specifically for version 2.0 of the API, with an additional product.
return new List<Product>
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Apple", Price = 1.50, Category = "Fruit" },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Bread", Price = 2.25, Category = "Bakery" },
new Product { Id = 3, Name = "Carrot", Price = 0.75, Category = "Vegetable" }
};
}
}
}
When Should We Use URL Path API Versioning in Real-time Applications?
URL Path Versioning is particularly useful in real-time applications when:
- Backward Compatibility is Required: When we need to support multiple versions of an API simultaneously, allowing clients to upgrade to newer versions at their own pace without breaking existing client functionality.
- Explicit Versioning: When we want to make it clear and explicit which version of the API is being used, making it easier for developers to debug and maintain different versions of the API.
- Isolated Changes: When different versions of the API might have significant differences in structure, behavior, or data contracts, it is necessary to isolate changes to specific versions.
- Multiple Client Versions: If your API serves a variety of client applications, some of which may not be updated as frequently as others, URL path versioning allows clients to choose which API version to call without forcing an upgrade.
- Complex Applications: In large and complex applications, where different clients might depend on different versions of the API, it is important to ensure that changes in one version do not impact other versions.
Let’s say you want to implement URL Path Versioning in a real-time scenario for a product inventory system. Here, version 1 of the API can provide basic product information, while version 2 could include additional details like stock levels and supplier information.
In the next article, I will discuss how to implement Web API Versioning using Header in ASP.NET Core with Examples. In this article, I explain How to Implement ASP.NET Core Web API Versioning using URL Path. I hope you enjoy this ASP.NET Core Web API Versioning using the URL Path article.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
