Back to: ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
ASP.NET Core Minimal API using Entity Framework Core
In this article, I will discuss ASP.NET Core Minimal API Using Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with examples. Please read our previous articles discussing how to Implement Asynchronous Programming in ASP.NET Core Minimal API with Examples. We will be working with the same project that we worked on so far with ASP.NET Core Minimal API.
ASP.NET Core Minimal API using Entity Framework Core
EF Core is an Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) that simplifies database access by allowing us to interact with our database using strongly typed C# classes instead of writing raw SQL queries. When combined with Minimal APIs, EF Core enables us to build efficient, maintainable, and scalable data-driven web APIs.
To integrate Entity Framework Core (EF Core) for managing data (to perform database CRUD Operations) in an SQL Server database within an ASP.NET Core Minimal API, we need to follow the steps below:
- Add EF Core and SQL Server NuGet packages.
- Configure the DbContext.
- Modify the EmployeeRepository to use EF Core.
Add EF Core and SQL Server NuGet Packages:
We will use SQL Server as the database to store employee data, and Entity Framework Core as the Data access technology. So, to use EF Core with SQL Server, we need to install the following two NuGet packages:
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer: Provides EF Core provider to interact with SQL Server databases.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools: Enables EF Core migrations, scaffolding, and other tooling support in Visual Studio.
How to install:
Using Package Manager Console, run:
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Alternatively, use the NuGet Package Manager UI to search and install these packages. These two packages allow us to use EF Core with SQL Server and to perform database migrations.
Define the Employee Model:
The model represents a table in your database. EF Core uses this class to map properties to database columns. If it has not already been defined, create an Employee model that EF Core will use to map to the database table. We have already created the following Employee model:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace MinimalAPIDemo.Models
{
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
// Name is required and cannot exceed 100 characters
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Name is required")]
[StringLength(100, ErrorMessage = "Name cannot exceed 100 characters")]
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
// Position is required and cannot exceed 50 characters
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Position is required")]
[StringLength(50, ErrorMessage = "Position cannot exceed 50 characters")]
public string Position { get; set; } = null!;
// Salary must be within a realistic range
[Range(30000, 200000, ErrorMessage = "Salary must be between 30,000 and 200,000")]
[Column(TypeName = "decimal(18,2)")]
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
}
}
Code Explanation:
- Attributes like [Required], [StringLength], and [Range] enforce validation both in .NET and in the database.
- [Column(TypeName = “decimal(18,2)”)] ensures the Salary column is created with a suitable precision in SQL Server.
Configure the DbContext
Create a class file named ApplicationDbContext.cs within the Models folder and then copy and paste the following code. DbContext is a class that represents a session with the database, allowing querying and saving data. The DbSet property within the DbContext instructs EF Core on which tables or entities to manage. The ApplicationDbContext manages database connections and is the primary EF Core component for performing CRUD operations. Employees will be represented as a table in your SQL Server database.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MinimalAPIDemo.Models
{
public class ApplicationDbContext : DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options) : base(options) { }
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
// Seed initial Employee data
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasData(
new Employee
{
Id = 1,
Name = "John Doe",
Position = "Software Engineer",
Salary = 60000m
},
new Employee
{
Id = 2,
Name = "Jane Smith",
Position = "Project Manager",
Salary = 80000m
}
);
}
}
}
Note: When seeding data with HasData(), you must provide explicit primary key values (e.g., Id = 1). This is required for EF Core to track and insert the data correctly during migrations.
Configure Connection String in appsettings.json:
We will store the connection string in the appsettings.json file. So, please modify the appsettings.json file as follows. Trusted_Connection=True means using Windows Authentication. If you want to use SQL Server Authentication, replace it with User ID=yourUser; Password=yourPassword. Replace the server name and other details according to your environment.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=MinimalAPIDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
}
}
Modify EmployeeRepository to Use EF Core
Instead of working with in-memory lists, use EF Core to interact with the real database asynchronously. So, please modify the EmployeeRepository as follows. Here, we use ToListAsync(), FindAsync(), and SaveChangesAsync() to perform database operations asynchronously. This allows the API to free threads during database I/O.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MinimalAPIDemo.Models
{
public class EmployeeRepository : IEmployeeRepository
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _context;
public EmployeeRepository(ApplicationDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public async Task<List<Employee>> GetAllEmployeesAsync()
{
return await _context.Employees.ToListAsync();
}
public async Task<Employee?> GetEmployeeByIdAsync(int id)
{
return await _context.Employees.FindAsync(id);
}
public async Task<Employee> AddEmployeeAsync(Employee newEmployee)
{
_context.Employees.Add(newEmployee);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return newEmployee;
}
public async Task<Employee?> UpdateEmployeeAsync(int id, Employee updatedEmployee)
{
var employee = await _context.Employees.FindAsync(id);
if (employee == null)
return null;
employee.Name = updatedEmployee.Name;
employee.Position = updatedEmployee.Position;
employee.Salary = updatedEmployee.Salary;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return employee;
}
public async Task<bool> DeleteEmployeeAsync(int id)
{
var employee = await _context.Employees.FindAsync(id);
if (employee == null)
return false;
_context.Employees.Remove(employee);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return true;
}
}
}
Modify Program Class:
Update the Program.cs to use EF Core and register the Employee Repository as a Scoped service. So, modify the Program class as follows.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MinimalAPIDemo.Models;
namespace MinimalAPIDemo
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create the WebApplication builder which prepares the app with default configs
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Configure logging providers
builder.Logging.ClearProviders(); // Remove any default logging providers
builder.Logging.AddConsole(); // Add console logger (shows logs in terminal)
builder.Logging.AddDebug(); // Add debug logger (for IDE/debugging tools)
// Configure JSON serialization options for HTTP responses
builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
{
// Disable camelCase conversion; keep property names as declared (PascalCase)
options.SerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
// Add Swagger/OpenAPI support services for API documentation and UI generation
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
// Register Repository as Scoped
// Scoped lifetime ensures a single instance of ApplicationDbContext is created per web request, avoiding conflicts and ensuring proper resource disposal.
builder.Services.AddScoped<IEmployeeRepository, EmployeeRepository>();
//Register ApplicationDbContext
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
// Build the app (finalize service registration and middleware pipeline)
var app = builder.Build();
// Enable Swagger UI only in Development environment to test API endpoints interactively
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger(); // Enable Swagger middleware to generate swagger.json
app.UseSwaggerUI(); // Enable Swagger UI middleware to visualize API docs
}
// Register the custom global error handling middleware in the pipeline
// It will catch exceptions from downstream middleware/endpoints
app.UseMiddleware<ErrorHandlerMiddleware>();
// -------------------- Define Minimal API Endpoints --------------------
// GET /employees - Fetch all employees
app.MapGet("/employees", async (IEmployeeRepository repo, ILogger<Program> logger) =>
{
logger.LogInformation("Fetching all employees asynchronously");
var employees = await repo.GetAllEmployeesAsync();
return Results.Ok(employees);
});
// GET /employees/{id} - Fetch employee by ID
app.MapGet("/employees/{id}", async (int id, IEmployeeRepository repo, ILogger<Program> logger) =>
{
logger.LogInformation($"Fetching employee with ID: {id} asynchronously");
var employee = await repo.GetEmployeeByIdAsync(id);
return employee is not null ? Results.Ok(employee) : Results.NotFound();
});
// POST /employees - Create a new employee
app.MapPost("/employees", async (Employee newEmployee, IEmployeeRepository repo, ILogger<Program> logger) =>
{
if (!ValidationHelper.TryValidate(newEmployee, out var errors))
{
return Results.BadRequest(new
{
Message = "Validation Failed",
Errors = errors.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage)
});
}
var createdEmployee = await repo.AddEmployeeAsync(newEmployee);
logger.LogInformation($"Employee created with ID {createdEmployee.Id} asynchronously");
return Results.Created($"/employees/{createdEmployee.Id}", createdEmployee);
});
// PUT /employees/{id} - Update an existing employee
app.MapPut("/employees/{id}", async (int id, Employee updatedEmployee, IEmployeeRepository repo, ILogger<Program> logger) =>
{
if (!ValidationHelper.TryValidate(updatedEmployee, out var errors))
{
return Results.BadRequest(new
{
Message = "Validation Failed",
Errors = errors.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage)
});
}
var employee = await repo.UpdateEmployeeAsync(id, updatedEmployee);
return employee is not null ? Results.Ok(employee) : Results.NotFound();
});
// DELETE /employees/{id} - Delete an employee by ID
app.MapDelete("/employees/{id}", async (int id, IEmployeeRepository repo, ILogger<Program> logger) =>
{
var deleted = await repo.DeleteEmployeeAsync(id);
return deleted ? Results.NoContent() : Results.NotFound();
});
// Start the web server and listen for incoming HTTP requests
app.Run();
}
}
}
Add Migrations and Update Database:
EF Core Migrations provide a way to incrementally update your database schema, keeping it in sync with your data model, without dropping and recreating the entire database. When we change our models, we add a migration, and EF Core generates the SQL to update our database. So, Open Package Manager Console in Visual Studio and execute the following commands.
- Add-Migration InitialCreate
- Update-Database
The Add-Migration command creates migration files that describe what needs to change in the database, and the Update-Database command actually applies those changes and creates (or updates) the database. Once you execute the above commands, a SQL Server database named MinimalAPIDB with an Employees table is created as shown in the image below.
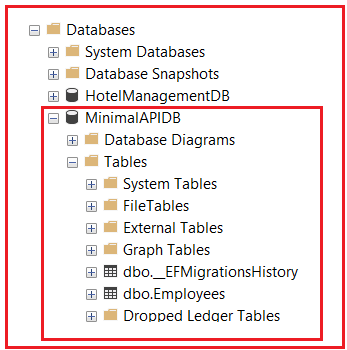
Now, run your application. The Minimal API endpoints perform CRUD operations on the SQL Server database using Entity Framework Core (EF Core). Test endpoints using Swagger UI, Postman, or any HTTP client.
In the next article, I will discuss how to implement Endpoint Filters in ASP.NET Core Minimal API with Examples. In this article, I explain ASP.NET Core Minimal API using Entity Framework Core (EF Core) with Examples. I hope you enjoy this article, ASP.NET Core Minimal API using Entity Framework Core (EF Core).
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
