Back to: Data Structures and Algorithms Tutorials
Menu Driven Program using Array in C:
In this article, we will write a single Menu Driven Program for all the operations upon an array in C Language. In our previous articles, we have seen various Set Operations on an Array with Examples. First, we will define a list or array in our program as:
struct List {
int* A;
int size;
int length;
};
This List has 3 variables for storing an array, storing the size of an array, and the length of an array. Below is the list of operations that we have discussed in our previous articles:
- Display ()
- Append ()
- Insert ()
- Delete ()
- Swap ()
- LinearSearch ()
- BinarySearch ()
- RecursiveBinarySearch ()
- Get ()
- Set ()
- Max ()
- Min ()
- Average ()
- Reverse ()
- Reverse 2nd method
- Insertion in sorted Array
- isSorted ()
- Merge ()
- Union ()
- Intersection ()
- Difference ()
For our menu-driven program, we will discuss only some operations for giving you an idea of how to write a menu-driven program. You can add more or all operations to your program but here we will include: Insert, Delete, Search, Sum and Display.
Here we will only write the code of these functions and create a menu-driven program. Read our previous articles for a detailed explanation of the above functions. Let’s first see the main function, after that we will add all operation code to our program.
Main Function:
First, create an object of type List. We will ask the user to give input of size of the list or array then we will initialize that array of a given size. After that, we will print some lines on the console and ask from user to enter the appropriate number to perform that operation on the given array. Then we will run a while loop which always checks the value of the ‘ch’ variable. If it is >6 it will stop.
Main() Code:
int main() {
struct List list_1;
int ch;
int x, index;
printf("Enter size of Array: ");
scanf("%d", &list_1.size);
list_1.B = (int*)malloc(list_1.size * sizeof(int));
do{
printf("\nMenu\n");
printf("1. Insert\n");
printf("2. Delete\n");
printf("3. Search\n");
printf("4. Sum\n");
printf("5. Display\n");
printf("6.Exit\n\n");
printf("Enter your choice: ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch(ch){
case 1: printf("Enter an element and index: ");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &index);
Insert(&list_1, index, x);
break;
case 2: printf("Enter index: ");
scanf("%d", &index);
Delete(&list_1, index);
printf("Deleted element is %d\n", x);
break;
case 3: printf("Enter element to search: ");
scanf("%d", &x);
index = LinearSearch(list_1, x);
printf("Element index is %d", index);
break;
case 4: printf("Sum is %d\n", Sum(list_1));
break;
case 5: Display(list_1);
}
}while (ch < 6);
return 0;
}
Full Code of Menu Driven Program in C Language:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct List {
int *B;
int size;
int length;
};
void Display(struct List list) {
int i;
printf("\nElements are\n");
for (i = 0;i<list.length;i++)
printf("%d ", list.B[i]);
}
void Append(struct List* list, int x) {
if (list->length < list->size)
list->B[list->length++] = x;
}
void Insert(struct List* list, int index, int x) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= list->length) {
for (int i = list->length; i > index; i--) {
list->B[i] = list->B[i - 1];
}
list->B[index] = x;
list->length++;
}
}
int Delete(struct List* list, int index) {
int x = 0;
if (index >= 0 && index < list->length) {
x = list->B[index];
for (int i = index; i < list->length - 1; i++)
list->B[i] = list->B[i + 1];
list->length--;
return x;
}
}
void swap(int* x, int* y) {
int temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
int LinearSearch(struct List list, int key) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
if (key == list.B[i])
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int ImprovedLinearSearch(struct List* list, int key) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
if (key == list->B[i]) {
swap(&list->B[i], &list->B[0]);
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int BinarySearch(struct List list, int key) {
int l, mid, h;
l = 0;
h = list.length - 1;
while (l <= h)
{
mid = (l + h) / 2;
if (key == list.B[mid])
return mid;
else if (key < list.B[mid])
h = mid - 1;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
int RBinSearch (int a[], int l, int h, int key){
int mid;
if (l <= h)
{
mid = (l + h) / 2;
if (key == a[mid])
return mid;
else if (key < a[mid])
return RBinSearch (a, l, mid - 1, key);
else
return RBinSearch (a, mid + 1, h, key);
}
return -1;
}
int Get(struct List list,int index){
if(index >= 0 && index < list.length)
return list.B[index];
return -1;
}
void Set(struct List *list,int index,int x){
if(index >= 0 && index < list->length)
list->B[index] = x;
}
int Max(struct List list){
int max = list.B[0];
for(int i = 1;i < list.length; i++){
if(list.B[i] > max)
max = list.B[i];
}
return max;
}
int Min(struct List list){
int min = list.B[0];
for(int i = 1;i < list.length; i++){
if(list.B[i] < min)
min = list.B[i];
}
return min;
}
int Sum(struct List list){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < list.length; i++)
sum+=list.B[i];
return sum;
}
int RSum(struct List list, int n){
if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
return RSum(list, n-1) + list.B[n];
}
float Avg(struct List list){
return (float)Sum(list)/list.length;
}
void Reverse(struct List *list){
int *C;
int i,j;
C=(int *)malloc(list->length*sizeof(int));
for(i=list->length-1,j=0;i>=0;i--,j++)
C[j]=list->B[i];
for(i=0;i<list->length;i++)
list->B[i]=C[i];
}
void Reverse2(struct List *list){
int i,j;
for(i=0,j=list->length-1;i<j;i++,j--){
swap(&list->B[i],&list->B[j]);
}
}
void InsertSort(struct List *list, int x){
int i = list->length-1;
if(list->length == list->size)
return;
while(i >= 0 && list->B[i] > x) {
list->B[i+1] = list->B[i];
i--;
}
list->B[i+1] = x;
list->length++;
}
int isSorted(struct List list){
int i;
for(i=0;i<list.length-1;i++){
if(list.B[i]>list.B[i+1])
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void arrangeNegPos(struct List *list){
int i, j;
i = 0;
j = list->length - 1;
while(i < j){
while (list->B[i] < 0) i++;
while (list->B[j] >= 0) j--;
if (i < j) swap (&list->B[i], &list->B[j]);
}
}
struct List* Merge(struct List *list1, struct List *list2){
int i,j,k;
i = j = k = 0;
struct List *list3=(struct List *)malloc(sizeof(struct List));
while(i < list1->length && j < list2->length){
if(list1->B[i] < list2->B[j])
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i++];
else
list3->B[k++] = list2->B[j++];
}
for(; i < list1->length; i++)
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i];
for(; j < list2->length; j++)
list3->B[k++] = list2->B[j];
list3->length = list1->length + list2->length;
list3->size = 10;
return list3;
}
struct List* Union(struct List *list1, struct List *list2) {
int i, j, k;
i = j = k = 0;
struct List *list3 = (struct List *)malloc(sizeof(struct List));
while (i < list1->length && j < list2->length) {
if (list1->B[i]<list2->B[j])
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i++];
else if (list2->B[j]<list1->B[i])
list3->B[k++] = list2->B[j++];
else {
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i++];
j++;
}
}
for (;i<list1->length;i++)
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i];
for (;j<list2->length;j++)
list3->B[k++] = list2->B[j];
list3->length = k;
list3->size = 10;
return list3;
}
struct List* Intersection(struct List *list1, struct List *list2) {
int i, j, k;
i = j = k = 0;
struct List *list3 = (struct List *)malloc(sizeof(struct List));
while (i < list1->length && j < list2->length) {
if (list1->B[i] < list2->B[j])
i++;
else if (list2->B[j] < list1->B[i])
j++;
else if (list1->B[i] == list2->B[j]) {
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i++];
j++;
}
}
list3->length = k;
list3->size = 10;
return list3;
}
struct List* Difference(struct List *list1, struct List *list2) {
int i, j, k;
i = j = k = 0;
struct List *list3 = (struct List *)malloc(sizeof(struct List));
while (i<list1->length && j<list2->length) {
if (list1->B[i]<list2->B[j])
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i++];
else if (list2->B[j]<list1->B[i])
j++;
else {
i++;
j++;
}
}
for (;i<list1->length;i++)
list3->B[k++] = list1->B[i];
list3->length = k;
list3->size = 10;
return list3;
}
int main() {
struct List list_1;
int ch;
int x, index;
printf("Enter size of Array: ");
scanf("%d", &list_1.size);
list_1.B = (int*)malloc(list_1.size * sizeof(int));
do{
printf("\nMenu\n");
printf("1. Insert\n");
printf("2. Delete\n");
printf("3. Search\n");
printf("4. Sum\n");
printf("5. Display\n");
printf("6.Exit\n\n");
printf("Enter your choice: ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch(ch){
case 1: printf("Enter an element and index: ");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &index);
Insert(&list_1, index, x);
break;
case 2: printf("Enter index: ");
scanf("%d", &index);
Delete(&list_1, index);
printf("Deleted element is %d\n", x);
break;
case 3: printf("Enter element to search: ");
scanf("%d", &x);
index = LinearSearch(list_1, x);
printf("Element index is %d", index);
break;
case 4: printf("Sum is %d\n", Sum(list_1));
break;
case 5: Display(list_1);
}
}while (ch < 6);
return 0;
}
Output:
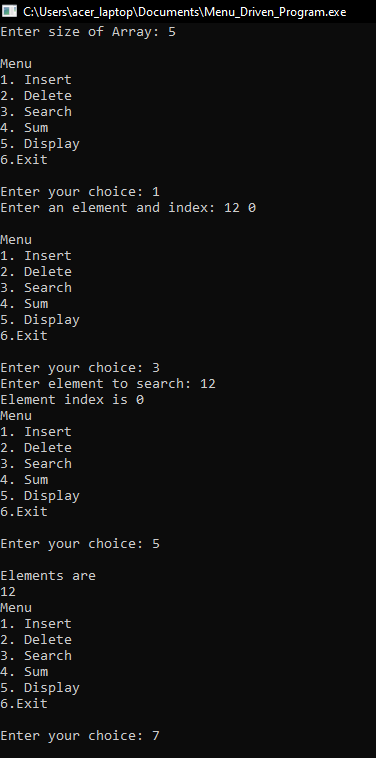
In the next article, I am going to discuss How to Convert Array C Code to C++ Code with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain Menu Driven Program using Array in C Language with Examples and I hope you enjoy this Menu Driven Program using Array in C Language with Examples article.

