Back to: C++ Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Arrays in C++ with Examples:
Hi, guys welcome back to our next article in the C++ basic module, which is very important from a programming point of view i.e. Arrays in C++ with Examples. Please read our previous article where we discussed Loops in C++. At the end of this article, you will understand the following pointers in detail.
- What is an array?
- Why do we need an Array?
- Declaring an and Initialization of an Array
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Arrays in C++
- What is an Array Index?
- The relation between Array and loops
Arrays in C++:
Let us start with mathematics. In mathematics, there are two types of values. Scaler and Vector.
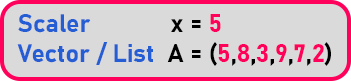
Scalar means magnitude and Vector is a list of values means it is having magnitude as well as dimension. In our example, A has multiple values. So how to differentiate them? We differentiate like this.

In mathematics, we can start from one. But in programming, we have taken it from zero i.e. ‘A0’, ‘A1’, and so on. So instead of writing the name every time, we can say like this i.e. ‘A0’, ‘A1’. These are differentiated by their subscript
So, this is the concept for mathematics that if you have the list of elements, you can give a single name and you differentiate them with their index or subscript that is 0, 1, 2, and so on. The same concept is applied in programming models. Let us come to C++. If we have to store a single value then we have to declare a variable, so the variable will have a data type.
int x = 5;
So, this is an integer type variable ‘x’ having value ‘5’. So, we know very well that an integer takes 2 bytes. We are assuming that the integer takes 2 bytes. This will consume 2 bytes of memory and then in that ’5’ will be stored. If we write with address then,

So let us say the address of the first bite is ‘200’ and the next bite is ‘201’. Now next how to have the list of elements. So, this is the concept of arrays. Arrays in programming or in C++.
What is an Array?
An array is a kind of sequential data structure, which is used to store the collection of items of the same type. I am sure you didn’t get this definition of an array. Let’s discuss the above statement in layman terms rather than programming terms.
We already learned that variables are used to store the value. But variables can hold only one value of a specific type at a time. For a better understanding please have a look at the below diagram. In the below example at any point of time x can hold only one type of value.

Now in real-time programming, there will be a scenario where we need to store a group of values. You didn’t get it, right? Yeah, let’s think in this way. I want to store emp no of 10 employees. Then without array, it is like

I know you already feel this awkward. Yes, if the array kind of data structure is not there then programming would be a bit more complex. For everything we need to define a new variable even if it is of the same type. But let’s see how the array solves this problem.
int employeeno[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
How using [] this work in real memory?
int empno[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
![How using [] this work in real memory? How using [] this work in real memory?](https://dotnettutorials.net/wp-content/plugins/wp-fastest-cache-premium/pro/images/blank.gif)
See using this [] along with the variable name you are informing the compiler that the variable is an array and allocate a block of memory as specified by the array in memory. The normal array is stored in the stack however it is possible to create an array in heap memory also which will be discussed in future articles on dynamic memory allocation.
How to declare an Array in C++?
We have discussed the importance of array over normal variables but now let’s discuss what are ways to declare an Array and initialize an array with examples.
General Syntax: <data type> variablename[size of the array];
Example: int A[5];
Here we have created a variable A with the size of ‘5’. So, you can store 5 values with the same name A. How it looks like in the memory? It will allocate memory for 5 integers. These all ‘5’ are types of ‘int’. For that memory, indexing will start from ‘0’ onwards.

We got an array. So, all these 5 integers are side by side or contiguous. Let us say the first byte’s address is ‘300’ and ‘int’ is taking 2 bytes then,

So here ‘A[0]’ is taking ‘300-301’. ‘A[1]’ is taking ‘302-303’. ‘A[2]’ is taking ‘303-304’ And so on. So how many bytes it is consuming in total? It will consume 10 bytes of memory. This is how we can create 5 variables with one name so we say it is an array. The below is also an example of array declaration by specifying size;
int n=5;
int A[n];
Declare and initialize an array in the same statement
Just like declaring and initializing normal variable in a single statement, we can also follow the same for array if we want to hardcode the input of the array; For example:
int A[]={1,2,3,4,5}
int A[5]={1,2,3,4,5}
Student: Author you said accessing all the elements in an array is easy and it is through the index but I am not getting how to do it?
Author: Yes, don’t be in a hurry our next discussion is all about what is an index of an array? And also, how to access all the elements in an Array. Let us directly get into the details of it.
What is an Array Index?
If I directly explain the concept of array index you might be in some confusion. So, let’s take an example:
int temp[5];
Here temp variable name stores the address of the first element of an array.

In the above example to access all the elements in an array, we need the address of temp[0] and that address is stored in the temp variable. So, the array name gives the address of the first element in an array. Since I know the address of the first element of an array it is easy to access the second element in an array through an index of an array.
What is an index of an array?
The index of an array is basically a pointer that is used to indicate which element in the array will be used. The array is sequential starting at zero to n-1 you can easily access any element in a small array with the index. For example:
int empno[5]={1,2,3,4,5};

In the above example to print the value 4 if I just use the below instruction is enough.
cout<<empno[3];
Note: Array index is an integer starting from 0. And zero index will always be given by the name of the array.
How to store elements in an Array in C++?
Now we will store all those elements one by one.
int x = 5;
Here we have assigned ‘5’ to ‘x’. It is declaration + Initialization. In the same way, we will initialize the whole array. So here only assign in braces that are in curly braces,
int A [10] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
These values will be filled in memory as,

This is how values will be stored in the array. Now how do you differentiate with the values? We will do it as,
A [0] = 2,
A [1] = 4
And so on.
So, we can access each value by using their index.
How to access Array Elements in C++?
Suppose we want to print ‘8’, so for that, we will write,
cout << A [3];
So individual all the elements we can print whichever one we want. We have to use the array name and the index for the value which we want to access. Now if we write,
cout << A;
Will it print the whole array? No, we have to print each and every element one by one separately, whichever one you want you to print. Or if we want to print all, then we can print them. Now we’ll explain to you how to print all these elements one by one.
How to print all elements in an array in C++?
Let us write a piece of code,
int main(){
int A[5] = {2,4,6,8,10};
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
cout << A[i] << endl;
}
}
In this code, first, we have declared an array of size ‘5’ and at the same time, we have initialized it with some values. Next, we want to print all the values of the array, so here we used the ‘for’ loop. We can also use other loops also but here we have used the ‘for’ loop.
In the ‘for’ loop, we are starting from ‘0’ to ‘size – 1’ as array indexing starts from ‘0’ in C / C++. Then inside ‘for’ loop, we just write a statement ‘cout << A[i] << endl’. So, it will print the whole array. And as we created an array of size ‘5’ then memory will allocate inside stack as shown in the below image.

This is the memory allocation of the array. The iteration of for loop will be as,

So, by using loops we can access every element of the array. After accessing we can perform various operations on the array-like, addition subtraction, and more. So, this is how all the array elements are displayed in C++.
Program to Understand Arrays in C++:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int A[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
cout << "to print value 1\t" << A[0] << endl;
cout << "to print value 2\t" << A[1] << endl;
cout << "to print value 3\t" << A[2] << endl;
cout << "to print value 4\t" << A[3] << endl;
cout << "to print value 5\t" << A[4] << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:

In the above program, you came to know that using array index we can get the value associated with that index but the program looks awkward when I try to print all the elements in an array.
Yes, you’re right I have used five cout statements to print the five elements of an array. This looks similar to declaring five new variables and initializing them and printing them separately. To avoid multiple cout and also to read multiple input from the user for an array we need to use counter loops. Yes, you guessed it right counter loops are nothing but for loop and for each loop.
Relation between counter loops and Array in C++
Since we know the first index of an array from the array name and also, we know the array is contiguous and hence index is also contiguous from 0 to the size of an array-1. We can make use of Counter loops for traversal purposes. Let’s modify the above example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int empno[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
cout << "printing all the elements using for loop" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << "to print the element at index\t" << i << "\tvalue at index is\t" << empno[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output:

Summary.
We have learned how to declare an array, how to initialize an array and how to access all the elements of an array in C++. Now the next thing I will show you how you can declare and initialize an array with different data types, we will look at
int A[5];
float B[5];
char C[5];
Here we have declared 3 types of arrays i.e. ‘int’, ‘float’, and ‘char’. So, you can have any data for an array. The array can be of any type. And if it is ‘Int’, all five elements are ‘int’ only. So similar data elements, all are float, all are characters. Next, we can initialize these as,
int A[5] = {2, 5, 7, 9, 3}
float B[5] = {2.2, 4.3, 7.6, 9.1, 1.1}
char C[5] = {‘D’, ‘W’, ‘S’, ’V’, ‘A’};
So, this is declaration plus initialization. Now one more thing I will show you, can we have an array of size ‘5’ and we mentioned only two or four elements? Yes, we can mention as,
float num[5] = {3.0, 3.5};
Now only ‘3.0’ and ‘3.5’ will be filled, all the other values will be automatically zero. Next, can we create an array without giving size and give the value? Yes.
float numbers = {2.0, 2.4, 5.3, 6.4};
So, what size of the array will be created? 4 Elements we have given. So, the array of size 4 will be created.
Advantages of Arrays in C++:
- We can access any element in an array using the array index.
- Sorting in an array is easy
- Easily we can access all the elements through the traversal in a single loop
Disadvantages of Arrays in C++:
- Array in C++ is fixed size and we need to define the size of an array while declaration.
- Insertion and deletion of an array could be a costly operation.
Note: To know more about time complexity and more insight into an array as a data structure please refer to the Data Structure and Algorithm course by DotNetTutorials.
This was the introduction to the Arrays in C++. In our upcoming articles, we will write programs using the arrays, and also, we will discuss the different types of arrays in C++ with examples. In the next article, I am going to discuss For Each Loop in C++ with Examples.
