Back to: SQL Server Tutorial For Beginners and Professionals
Inserted and Deleted Tables in SQL Server
In this article, I am going to discuss Inserted and Deleted Tables in SQL Server with examples. Please read our previous article where we discussed the basics of SQL Server Triggers in detail. So, here we will discuss how the inserted and deleted tables are created, what they hold, and how they are being used inside the SQL Server trigger. At the end of this article, you will understand the following pointers in detail.
- What are Inserted and Deleted Tables in SQL Server?
- Understanding the Inserted and Deleted Tables with Examples
- What is Deleted Table in SQL Server?
- How to view the updating data in a table?
- What will happen if we update multiple records at a time?
What are Inserted and Deleted Tables in SQL Server?
Inserted and Deleted tables are temporary tables that are created by SQL Server in the context of a trigger. That means these two tables can only be available as part of a trigger. If you try to access these tables outside of a trigger, then you will get an error. The table structure of both inserted and deleted tables will be exactly the same as the table structure of the table on which the trigger is created.
Whenever you fire any INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statement on a table, all the new records are actually going to the inserted table i.e. all the updated and new records are present in the inserted table. On the other hand, all the old values are present in the deleted table.
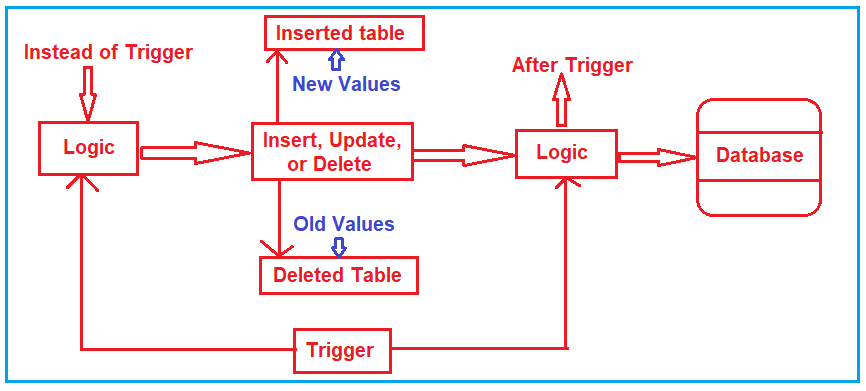
Understanding the Inserted and Deleted Tables with Examples in SQL Server.
Let us understand how we can use Inserted and Deleted tables within a trigger with examples in SQL Server. We are going to use the following Employee table to understand the Inserted and Deleted Tables in the SQL server.

Please use the below SQL Script to create and populate the Employee table with sample data.
-- Create Employee table CREATE TABLE Employee ( Id int Primary Key, Name nvarchar(30), Salary int, Gender nvarchar(10), DepartmentId int ) GO -- Insert data into Employee table INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (1,'Pranaya', 5000, 'Male', 3) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (2,'Priyanka', 5400, 'Female', 2) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (3,'Anurag', 6500, 'male', 1) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (4,'sambit', 4700, 'Male', 2) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (5,'Hina', 6600, 'Female', 3)
Understanding the INSERTED Table in SQL Server:
The Inserted table is created by SQL Server when we perform an INSERT operation and this table has access to the values being inserted into the table. So, whenever we insert the values into a table those values we can see in the inserted magic table. Let us see an example for a better understanding. The following is an example Insert trigger. So, when we insert a record into the Employee table, this trigger is going to be fired after the record inserted. And the inserted data is also stored in the INSERTED magic table and those data stored in the INSERTED magic table are displaying as part of the trigger body.
CREATE TRIGGER trInsertEmployee ON Employee FOR INSERT AS BEGIN SELECT * FROM INSERTED END
Let’s Insert one record into the Employee table
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (6, ‘Saroj’, 7700, ‘Male’, 2)
So when we execute the above insert statement, the data is inserted as expected in the Employee table along with a copy of the inserted new data also available in the Inserted table. So, we get the following output. Please note, the structure of the Inserted table is exactly the same as the structure of the Employee table.

When we add a new row into the Employee table a copy of the row will also be made into the INSERTED table which only a trigger can access. We cannot access this table outside the context of the trigger.
What is Deleted Table in SQL Server?
The Deleted table is created by SQL Server when we perform a delete operation on the table and this table has access to the record being deleted. So, in simple words, we can say that, whenever we delete a record from a table the deleted record information we can view with the help of the deleted table as part of a trigger in SQL Server. Let us understand this with an example. The following is an example delete trigger. So, when we delete a record from the Employee table, this trigger is going to be fired.
CREATE TRIGGER trDeleteEmployee ON Employee FOR DELETE AS BEGIN SELECT * FROM DELETED END
Let’s Delete one record from the Employee table
DELETE FROM Employee WHERE Id = 6
When we execute the above Delete statement, the data gets deleted from the Employee table whose Id is 6 along with it also displays the following deleted data as part of the deleted table.

This proofs that the delete table holds the data that is being deleted from the table. When we delete a row from the Employee table, a copy of the deleted row will be made available in the DELETED table, which only a trigger can access. Just like the INSERTED table, the DELETED table cannot be accessed outside the context of a trigger and the structure of the DELETED table will be identical to the structure of the Employee table.
How to view the updating data in a table?
When we perform an update operation, then we will be having both the inserted and deleted tables. The inserted table will hold the new values being inserted and the deleted table will hold the old values of the table. So in a simple word, we can say that, whenever we update a record in the table, then we can view the new data in the inserted table and the old data in the deleted table. Let us understand this with an example. The following is an example update trigger. So, when we update a record from the Employee table, this trigger is going to be fired.
-- Create Update Trigger CREATE TRIGGER trUpdateEmployee ON Employee FOR UPDATE AS BEGIN SELECT * FROM DELETED SELECT * FROM INSERTED END
Let’s Update one record in the Employee table by executing the following update statement.
UPDATE Employee SET Name = ‘Sharma’, Salary = 8000 WHERE Id = 5
So when we execute the above update statement, the data is updated in the table as expected along with it, it also gives us the following output. So this proves that whenever we perform an update operation then the Deleted Table will hold the OLD Data whereas the InsertedTable will hold the new Data.

What will happen if we update multiple records at a time?
Currently, the employee table holds the below data

Here you can see that the Employee table having three employees whose Gender is Male. Let’s update the Salary of All the Male Employees to 20000 by executing the following SQL query.
UPDATE Employee SET Salary = 20000 WHERE Gender = ‘Male’
So when we execute the above code the data is updated in the Employee table as expected as well as we will also get the following output. As you can see in the below image, all the old records are stored in the Deleted Table whereas all the updated data are stored in the Inserted table.

In the next article, I am going to discuss the Real-Time examples of DML Triggers in SQL Server. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Inserted and Deleted Tables in SQL Server with examples. I hope you enjoy this Inserted and Deleted Tables in SQL Server article.
