Back to: SQL Server Tutorial For Beginners and Professionals
Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss the User-Defined Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server with Examples. Please read our previous article where we discussed User-Defined Scalar Valued Functions in SQL Server with Examples. In our previous article, we learned that a scalar user-defined function returns a single (scalar) value. On the other hand, an Inline Table-Valued function returns a table. At the end of this article, you will understand what is Inline Table-Valued Function is and how to create and use Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server with Examples.
What is a Table-Valued Function in SQL Server?
In the case of a Table-Valued Function, we can return a table as an output from the function. These are again of two types.
Note: In this article, we are going to discuss Inline Table-Valued Function and in our next article, we will discuss Multi-Statement Table-valued Functions with Examples.
What are Inline Table-Valued functions in SQL Server?
In the case of an Inline Table-Valued Function, the body of the function will have only a Single Select Statement prepared with the “RETURN” statement. And here, we need to specify the Return Type as TABLE by using the RETURNS TABLE statement. The following image shows the syntax of the Inline Table-Valued Function and how to call an Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server.
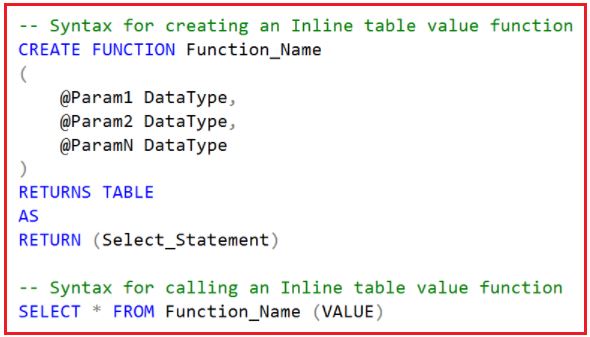
Points to Remember:
- We specify TABLE as the Return Type instead of any scalar data type.
- The function body is not closed between BEGIN and END blocks. This is because the function is going to return a single select statement.
- The structure of the Table that is going to be returned is determined by the select statement used in the function.
Example: Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server
Let us understand the Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server with some examples. We are going to use the following Student table to understand this concept.

Please use the following SQL Script to create and populate the Student table with the required sample data which we are going to use.
-- Create Student Table CREATE TABLE Student ( ID INT PRIMARY KEY, Name VARCHAR(50), Gender VARCHAR(50), DOB DATETIME, Branch VARCHAR(50) ) -- Populate the Student Table with test data INSERT INTO Student VALUES(1, 'Pranaya', 'Male','1996-02-29 10:53:27.060', 'CSE') INSERT INTO Student VALUES(2, 'Priyanka', 'Female','1995-05-25 10:53:27.060', 'CSE') INSERT INTO Student VALUES(3, 'Anurag', 'Male','1995-04-19 10:53:27.060', 'ETC') INSERT INTO Student VALUES(4, 'Preety', 'Female','1996-03-17 10:53:27.060', 'ETC') INSERT INTO Student VALUES(5, 'Sambit', 'Male','1997-01-15 10:53:27.060', 'CSE')
Example:
Create a function that accepts student id as input and returns that student details from the table.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_GetStudentDetailsByID ( @ID INT ) RETURNS TABLE AS RETURN (SELECT * FROM Student WHERE ID = @ID)
Once you create the above function, then call it like below.
SELECT * FROM FN_GetStudentDetailsByID(2)
Once you execute the above SQL Statement, it will give you the following output.

Example:
Create a function to accept branch name as input and returns the list of students who belongs to that branch.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_GetStudentDetailsByBranch ( @Branch VARCHAR(50) ) RETURNS TABLE AS RETURN (SELECT * FROM Student WHERE Branch = @Branch)
Once you create the above function, then call it by executing the below statement.
SELECT * FROM FN_GetStudentDetailsByBranch(‘CSE’)
Once you execute the above SQL Statement, it will give you the following output.

Note: As the inline table-valued user-defined function, is returning a table, issue the select statement against the function, as if we are selecting the data from a TABLE.
Example:
Create a function that returns student Name, DOB, and Branch by GENDER.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_GetStudentDetailsByGender ( @Gender VARCHAR(50) ) RETURNS TABLE AS RETURN (SELECT Name, DOB, Branch FROM Student WHERE Gender = @Gender)
Once you create the above function, then call it by executing the below statement.
SELECT * FROM FN_GetStudentDetailsByGender(‘Male’)
Once you execute the above SQL Statement, it will give you the following output.

Where can we use Inline Table-valued Functions in SQL Server?
The Inline Table-Valued function in SQL Server can be used to achieve the functionalities of parameterized views, and the table returned by the inline table-valued function in SQL Server can also be used in joins with other tables.
Inline Table-Valued Function with JOINs in SQL Server
Let us understand how to use Inline Table-Valued Function with Joins with an example. We are going to use the following Department and Employee tables to understand this concept.

Please use the following SQL Script to create and populate the Department and Employee tables with sample data.
-- Create Department Table CREATE TABLE Department ( ID INT PRIMARY KEY, DepartmentName VARCHAR(50) ) GO -- Populate the Department Table with test data INSERT INTO Department VALUES(1, 'IT') INSERT INTO Department VALUES(2, 'HR') INSERT INTO Department VALUES(3, 'Sales') GO -- Create Employee Table CREATE TABLE Employee ( ID INT PRIMARY KEY, Name VARCHAR(50), Gender VARCHAR(50), DOB DATETIME, DeptID INT FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Department(ID) ) GO -- Populate the Employee Table with test data INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(1, 'Pranaya', 'Male','1996-02-29 10:53:27.060', 1) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(2, 'Priyanka', 'Female','1995-05-25 10:53:27.060', 2) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(3, 'Anurag', 'Male','1995-04-19 10:53:27.060', 2) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(4, 'Preety', 'Female','1996-03-17 10:53:27.060', 3) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(5, 'Sambit', 'Male','1997-01-15 10:53:27.060', 1) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(6, 'Hina', 'Female','1995-07-12 10:53:27.060', 2) GO
Let’s first create an Inline Table-Valued Function that returns the Employees by Gender from the Employees table.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_GetEmployeessByGender ( @Gender VARCHAR(50) ) RETURNS TABLE AS RETURN (SELECT ID, Name, Gender, DOB, DeptID FROM Employee WHERE Gender = @Gender)
Now, let’s join the Employees returned by the inline table-valued function with the Departments table as shown below
SELECT Name, Gender, DOB, DepartmentName
FROM FN_GetEmployeessByGender('Male') Emp
JOIN Department Dept on Dept.ID = Emp.DeptID
When we execute the above query, it will give us the following output.

Example: Table-valued Function Returning data From two Tables using Join in SQL Server
In the below example we are joining the Employee and Department table and returning data from the function body as a single SQL Statement. This is very similar to Views but here we are taking an input parameter and based on the parameter we are returning the result. This is not possible (input parameter) in the case of SQL Server Views.
CREATE FUNCTION FN_EmployeessByGender
(
@Gender VARCHAR(50)
)
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN (
SELECT Emp.ID, Name, Gender, DOB, DepartmentName
FROM Employee Emp
JOIN Department Dept on Emp.DeptId = Dept.Id
WHERE Gender = @Gender)
Once you create the above function, then call it by executing the below statement.
SELECT * FROM dbo.FN_EmployeessByGender(‘Female’);
Once you execute the above SQL Statement, it will give you the following output.

In the next article, I am going to discuss the Multi-Statement Table Valued Function in SQL Server. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Inline Table-Valued Function in SQL Server with Examples. I hope this article will help you with your need. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.

Keep it up sir..you are amazing