Back to: SQL Server Tutorial For Beginners and Professionals
How Index impacts DML Operations in SQL Server
In this article, I am going to discuss how SQL Server Index impacts DML Operations such as Insert, Update and Delete with examples. Please read our previous article, where we discussed the Non-Clustered Index and the difference between Clustered and Non-Clustered Index in detail.
In our previous three articles, we saw how indexes make our search operations faster. As we know whenever a product comes into the market, there should be some advantages as well as disadvantages that exist in that product. This is also the same in the case of Indexes. In this article, we will discuss in detail, how indexes impact the insert, update and delete operations in SQL Server.
Example to understand how Index impacts DML Operations in SQL Server:
In order to understand this, we are going to use the following Employee table. As you can see, the following Employee table has two columns i.e. EmployeeId, and AddressLine. Here, EmployeeId is of type integer and as it is marked as Primary Key, so by default it will create a clustered index. The column AddressLine1 is of type varchar with size 2000.
-- Create Employee table with EmployeeId as Primary Key CREATE TABLE Employee ( EmployeeId INT Primary Key, AddressLine1 Varchar(2000) );
Once you created the Employee table, now insert four records into the table by executing the below query.
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (101, 'Address1') INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (102, 'Address2') INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (103, 'Address3') INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (104, 'Address4')
Now let us understand, for this type of data type and this type of table, how will internal index structure is formed. To make things simple and easy to understand, I have put the entire thing together (table, data, and index structure) in a single image as shown below. As we already discussed index is created based on the nodes i.e. we have a root node, intermediate nodes (non-leaf nodes), and leaf nodes. And in the case of a clustered index, the leaf node actually contains the data which you can see in the below image.
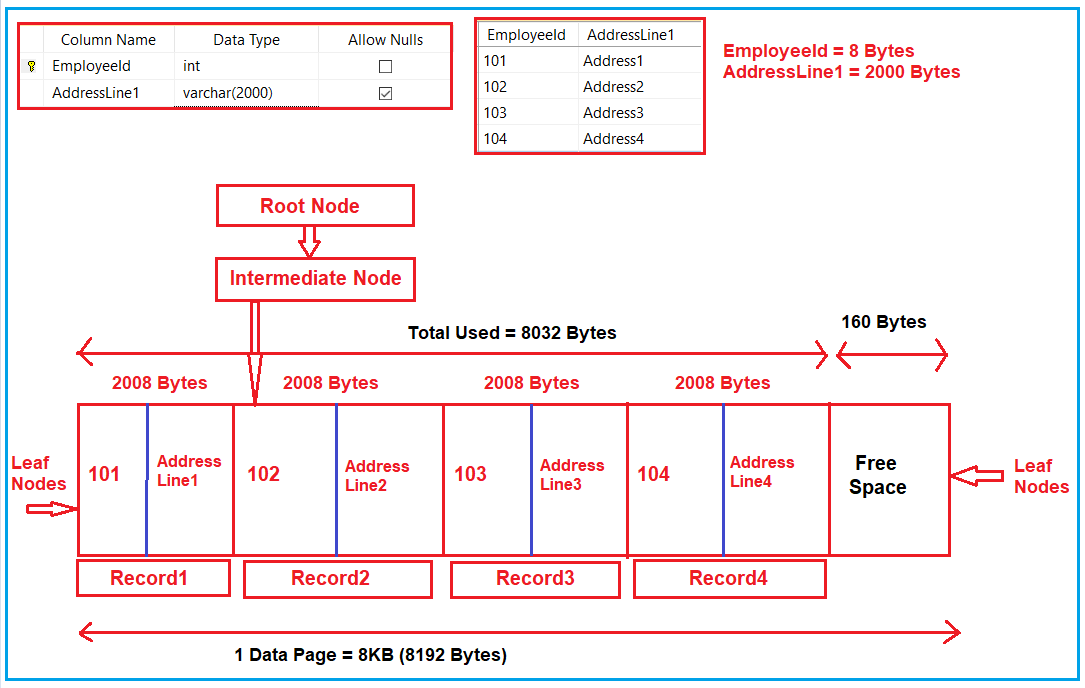
As you can see in the above image, currently the employee table is having two columns. The EmployeeId column is of type integer and hence its size is 8 Bytes and the AddressLine1 column size is 2000 Bytes as declared. That means one record will take 2008 bytes of memory space and currently we have four records, so a total of 8032 bytes of memory space will be consumed.
The leaf nodes actually store the data in 8KB (approximately 8192 Bytes) pages. So, from the 8192 Bytes, the four records actually consume 8032 Bytes i.e. 160 Bytes are free from the above data page.
Now, if you insert the fifth record into the table, then what will happen?
In order to insert a record, it requires 2008 Bytes. But currently, on the current data page, only 160 Bytes are available. So, what it will do is, it will create another data page with a size of 8KB. That means a page split happens. To understand this better please have a look at the following image.
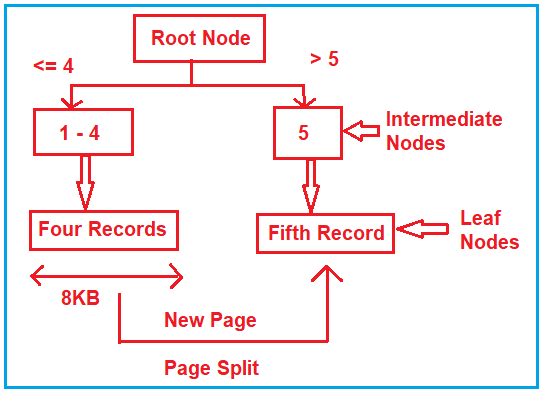
Page split is nothing but when the current data page is filled with space or space is not enough for the record to insert it will create a new data page and insert that record into the new data page. This is called a Page Split. So, when your table has too many indexes, then you have too many page splits which affect the performance of your application.
Another Drawback of Index in SQL Server:
Suppose you modify any data using the Update or you delete some data using the Delete statement, then the updated information needs to be updated in the leaf node of all the indexes (i.e. in the index table) where the data has been changed. Indexes can help us to search and locate the data faster. However, too many indexes in a table can actually hurt the performance of DML operations. So, you need to use the indexes properly to balance the performance.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Unique and Non-Unique Index in SQL Server with examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain how Index Impacts the DML (Insert, Update, and Delete) operations in SQL Server step by step with one example. I hope you enjoy this How Index impacts DML Operations article.


Nice Explanation of impact on DML. if possible explain the concept on index table vs actual table