Back to: MySQL Tutorials for Beginners and Professionals
Logical AND, OR, NOT Operators in MySQL with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss the Logical AND, OR, NOT Operators in MySQL with Examples. Please read our previous article where we discussed Comparison Operators in MySQL with examples. At the end of this article, you will understand what are logical operators in MySQL and why we need and the different types of logical operators available in MySQL with examples.
What are Logical Operators in MySQL?
If you want to combine more than one condition, then you need to use the Logical Operators in MySQL. The Logical Operators are used to check for the truthness of some conditions. Logical operators return a Boolean data type with a value of TRUE, FALSE, or UNKNOWN. In MySQL, there are three Logical Operators available. They are as follows:
- AND: TRUE if both Boolean expressions are TRUE.
- OR: TRUE if one of the Boolean expressions is TRUE.
- NOT: Reverses the value of any other Boolean operator.
The Logical Operators in MySQL are used to compare two conditions to check whether a row (or rows) can be selected for the output.
Logical Operators Examples in MySQL:
Let us understand how to use Logical Operators in MySQL with Examples. We are going to use the following Employee table to understand the Logical Operators.
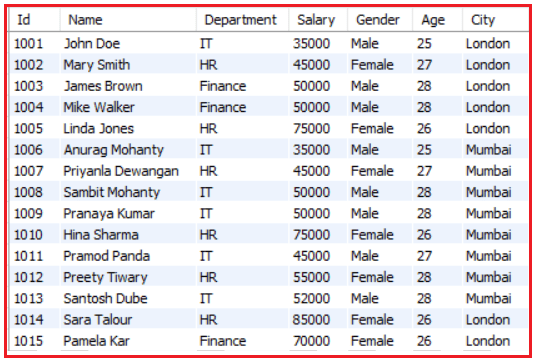
Please use the following SQL Script to create the company database and employee table with the required records.
CREATE DATABASE company; USE company; CREATE TABLE employee ( Id INT PRIMARY KEY, Name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL, Department VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL, Salary FLOAT NOT NULL, Gender VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL, Age INT NOT NULL, City VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1001, 'John Doe', 'IT', 35000, 'Male', 25, 'London'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1002, 'Mary Smith', 'HR', 45000, 'Female', 27, 'London'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1003, 'James Brown', 'Finance', 50000, 'Male', 28, 'London'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1004, 'Mike Walker', 'Finance', 50000, 'Male', 28, 'London'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1005, 'Linda Jones', 'HR', 75000, 'Female', 26, 'London'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1006, 'Anurag Mohanty', 'IT', 35000, 'Male', 25, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1007, 'Priyanla Dewangan', 'HR', 45000, 'Female', 27, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1008, 'Sambit Mohanty', 'IT', 50000, 'Male', 28, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1009, 'Pranaya Kumar', 'IT', 50000, 'Male', 28, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1010, 'Hina Sharma', 'HR', 75000, 'Female', 26, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1011, 'Pramod Panda', 'IT', 45000, 'Male', 27, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1012, 'Preety Tiwary', 'HR', 55000, 'Female', 28, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1013, 'Santosh Dube', 'IT', 52000, 'Male', 28, 'Mumbai'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1014, 'Sara Talour', 'HR', 85000, 'Female', 26, 'London'); INSERT INTO employee (Id, `Name`, Department, Salary, Gender, Age, City) VALUES (1015, 'Pamela Kar', 'Finance', 70000, 'Female', 26, 'London');
Logical AND Operator in MySQL
The Logical AND operator in MySQL compares two conditions and returns TRUE if both of the conditions are TRUE and returns FALSE when either is FALSE. If you want to select rows that must satisfy all the given conditions, then in such cases you need to use the AND operator.
In some cases, there are chances where we will have to use more than one condition to filter the data rows. In such a case, we use some special operators that are useful to create such compound conditions. The AND operator is useful to add multiple conditions in a single SQL statement. It only displays the data rows if all conditions are TRUE. If any one of the conditions is false the SQL statement will return an empty result set. The AND operator can be written as a word AND or && symbols without space.
We can use AND condition with SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statements to test two or more conditions in an individual query.
Syntax to use AND Operator in MySQL:

Examples to Understand Logical AND Operator in MySQL:
Let’s see some examples to understand the need and use of AND operator in MySQL. Adding the conditions in the bracket is optional. Using brackets for the conditions makes the code neat and clean.
Example: Fetch all employees whose Department is IT and Age is 28
Now we want to filter the data rows with two conditions simultaneously using AND operator. Our requirement is to find all the employees from the Employee table where the Department is IT and the employee age is 28, then we need to use the AND operator as shown in the below query.
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE (department = ‘IT’ AND age = 28); OR
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE department = ‘IT’ AND age = 28; — Bracket is optional
When we run the above SQL statement the system evaluates if the first condition, that is department value equal to IT is true. If the first condition is true the system, then evaluates the second condition. If both first and second conditions are true the system returns the data row. If any one of the conditions is false the system won’t return that data row. As in our employee table, three employees satisfy the above two conditions, so when you execute the above query, you will get the following data rows as the output.

Logical NOT Operator Example in MySQL:
We can also use the NOT keyword in the statement to revert one of the conditions. Suppose our requirement is to fetch all the employees whose Department is IT and Age does not equal to 28. Then in that case we can use NOT Operator along as shown in the below query.
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE department = ‘IT’ AND NOT age = 28;
When you execute the above query, you will get the following output. And this time, the result set contains only the data rows where the age column value is not equal to 28 and the department column value is IT as shown in the below image.

False Condition Example using AND Operator in MySQL:
Let’s modify the SQL statement so that the second condition becomes false. As in our employee table, there is no employee in the IT department whose age is 28. Now, in the below SQL Statement, the second condition becomes false.
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE department = ‘IT’ AND age = 26;
When you execute the above SQL Statement, then you will not get any data rows. And this time you can see, even though we have data rows with department value equal to IT, we got an empty result set, as the second condition age=26 was never true for any row.
Logical OR Operator in MySQL
In some cases, we will have to evaluate only one of the conditions is TRUE to return the result set. In such a case, the logical OR operator is useful to create such compound conditions. Similar to AND operator, The OR operator is useful to add multiple conditions in a single SQL statement. It displays the data rows if any one of the multiple conditions is TRUE. If all the conditions are false the SQL statement won’t return any result set.
The OR operator can be written as a word “OR” or “||” two pipe symbols without space. Adding the conditions in the bracket is optional. Using brackets for the conditions makes the code neat and clean. The following is the syntax to use the logical OR operator in MySQL.

Example: Fetch all the employees whose age is either 25 or 26 from the employee table.
Now we will filter the data rows with two conditions simultaneously using the “OR” operator. Our requirement is to fetch all the employees from the Employee table whose age is either 25 or 26, then we need to use the OR operator as shown in the below query.
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE age = 25 OR age = 26; — OR
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE (age = 25 OR age = 26); — Bracket is optional
When we run the above SQL statement the system evaluates if the first condition, that is age = 25 is true. Whether the condition is true or false, the system evaluates the second condition. If any of the condition is true the system returns the data row. If all the conditions are false the system won’t return that data row.
Now run the statement, and you can see, the system returned only the data rows where the age value is 25 or 26 as shown in the below image.

Let’s modify the SQL statement so that both conditions become FALSE. We will change the first condition to age = 10 and the second condition to age = 15. There is no record with the “age” column with a value of 10 or 15, so both the conditions will be false.
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE age = 10 OR age = 15;
Run the SQL statement again. And this time we got an empty result set.
Logical NOT Operator in MySQL:
The Logical NOT Operator in MySQL takes a single Boolean as an argument and changes its value from false to true or from true to false. If we want to select rows that do not satisfy a condition, then you need to use the logical NOT operator. NOT results in the reverse of a condition. That is, if a condition is satisfied, then the row is not returned. For example, if we want to fetch the Employees who do not belong to the IT Department, then we need to use the NOT Operator as shown in the below SQL query.
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE NOT Department = ‘IT’;
When you execute the above SQL Query, it will give you the below result set. As you can see, the result set excludes the IT Department employees.

AND OR Condition in MySQL
We can also use AND & OR condition together to select, insert, update and delete the statements. But while using these conditions together we must use round brackets so that the database evaluates each condition in order. The syntax to use AND OR condition is given below.

Now we will filter the data rows with multiple conditions simultaneously using the “AND” & “OR” operator. For example, if we want to select all the employees whose Salary is between 50000 and 60000, or those whose City is Mumbai, then we need to write the below query
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE (Salary >= 50000 AND Salary <= 60000) OR (CITY = ‘Mumbai’);
Once you execute the above SQL Query, you will get the following result set as per our requirement.

In this case, the filter works as follows:
- First, all the Employees, whose Salary between 50000 and 60000 are selected.
- Second, all the Employees who belong to Mumbai City are selected.
- And finally, the result is the rows that satisfy at least one of the above conditions are returned.
Note: The order of the condition is important, if the order changes we may get a different result.
In the next article, I am going to discuss LIKE Operator in MySQL with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Logical AND, OR, & NOT operators in MySQL with Examples. I hope you enjoy these Logical AND, OR, NOT Operators in MySQL article.
