Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
How to Add or Remove Users from Roles in ASP.NET Core Identity?
In this article, I will discuss how to Manage User-Role Membership, i.e., how to Add or Remove users from a given role using the ASP.NET Core Identity. Please read our previous article discussing How to Customize the AspNetRoles Table in ASP.NET Core Identity. Adding or removing users from roles in ASP.NET Core Identity is a common task that can be achieved using the UserManager and RoleManager services.
Add or Remove Users from Role in ASP.NET Core Identity:
So, what we want to do is, in the Edit Role View, we need to provide a button for Adding or Removing Users from this role, as shown in the image below. If any users have already been added to this role, the list of those users will also be displayed here. We have not added any users to the roles, so it is showing none. Once we add those users, the user list will be displayed here. You can add or remove users from this role using the Add or Remove Users From This Role button.

Once we click on the Add or Remove Users From This Role button, it will open the following page. Here, it will display all the Users. Their checkbox should be selected for those already added to this role, and for those not added, their checkbox will be unselected. We have not added any user with this role, so the checkbox is unselected for all users. If you click on the Cancel button, it will redirect you back to the Edit Role Page.
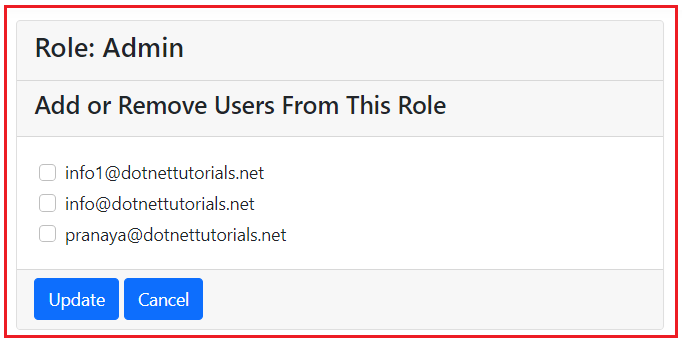
Now, you can select the user’s checkbox you want to add, unselect the one you want to remove from this role, and then click the Update button. Let us select the first two checkboxes and click on the Update button as shown in the below image:

Once you click the Update button, it will add the above two users to the specified Admin Role and redirect you to the Edit Role view, which will show you the following: Now, you can see the users who have the Role Admin showing in the list.

Let us proceed and see how we can implement this in our application.
AspNetUserRoles Identity Database Table
The ASP.NET Core Identity uses the AspNetUserRoles table to manage the User and Role Mapping. The Application Users are stored in the AspNetUsers database table, whereas Application Roles are stored in the AspNetRoles table. UserRoles, i.e., user-to-role mapping data, is stored in the AspNetUserRoles table. The following is the ER Diagram between AspNetUsers, AspNetRoles, and AspNetUserRoles, showing the relationships between these three tables.

The AspNetUserRoles table has just two columns: UserId and RoleId. Both are foreign keys. The UserId column references the Id column of the AspNetUsers table, and the RoleId column references the Id column of the AspNetRoles table.
Note: The AspNetUserRoles table maintains the many-to-many relationships between the AspNetUsers and AspNetRoles. That means one user can have multiple roles, and one role can assigned to multiple users. Let us proceed and see how we can implement this in our application.
Create UserRoleViewModel:
Create a ViewModel that will be used to pass data between your view and controller. This View model will hold the user information that needs to be added or removed from a given role. Create a class file named UserRoleViewModel.cs within the Models folder and copy and paste the following code:
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models
{
public class UserRoleViewModel
{
public string UserId { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
public bool IsSelected { get; set; }
}
}
In this class,
- The UserId property will hold the user’s ID, which we require while updating the data.
- The UserName property going to display the UserName on the view.
- IsSelected property determines if the user is selected to be a member of the role.
Note: We could include RoleId property in this class, but as far as this view is concerned, there is a one-to-many relationship from Role to Users. So, to avoid repeating RoleId for each User, we will use ViewBag to pass RoleId from the controller to the view.
Adding the Required Manager Class Instances:
Next, please make sure to initialize the RoleManager and UserManager instances through the constructor of your AdministrationController class:
private readonly RoleManager<ApplicationRole> _roleManager;
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager;
public AdministrationController(RoleManager<ApplicationRole> roleManager, UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager)
{
_roleManager = roleManager;
_userManager = userManager;
}
Modifying EditRoleViewModel Class:
Modify the EditRoleViewModel.cs class file as follows. Now, we are adding the Users property, which will hold the list of user names who belong to a role.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models
{
public class EditRoleViewModel
{
[Required]
public string Id { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Role Name is Required")]
public string RoleName { get; set; }
public string? Description { get; set; }
public List<string>? Users { get; set; }
}
}
Modifying EditRole Action Method:
Next, modify the HttpGet version of the EditRole action method of the AdministrationController class as follows. In the following code, we attach all the users assigned the given role. The following code is self-explained, so please go through the comment lines.
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> EditRole(string roleId)
{
//First Get the role information from the database
ApplicationRole? role = await _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(roleId);
if (role == null)
{
// Handle the scenario when the role is not found
return View("Error");
}
//Populate the EditRoleViewModel from the data retrived from the database
var model = new EditRoleViewModel
{
Id = role.Id,
RoleName = role.Name,
Description = role.Description,
Users = new List<string>()
// You can add other properties here if needed
};
// Retrieve all the Users
foreach (var user in _userManager.Users.ToList())
{
// If the user is in this role, add the username to
// Users property of EditRoleViewModel.
// This model object is then passed to the view for display
if (await _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name))
{
model.Users.Add(user.UserName);
}
}
return View(model);
}
In this example,
- _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(roleId): This method will return the Role based on the roleId from the AspNetRoles table.
- _userManager.Users.ToList(): This method will return all the users from the AspNetUsers table.
- _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name): This method will check whether the user is already assigned to this role. If yes, it will return true; else, it will return false. If it returns true, we add that user name to the Users property of the EditRoleViewModel class.
Modifying the EditRole View:
Next, modify the EditRole.cshtml view as follows.
@model EditRoleViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Edit Role";
}
<h1>Edit Role</h1>
<form method="post" class="mt-3">
<div class="form-group row">
<input type="hidden" asp-for="Id" />
<label asp-for="Id" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label"></label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input asp-for="Id" disabled class="form-control">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label asp-for="RoleName" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label"></label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input asp-for="RoleName" class="form-control">
<span asp-validation-for="RoleName" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label asp-for="Description" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label"></label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input asp-for="Description" class="form-control">
</div>
</div>
<div asp-validation-summary="All" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Update</button>
<a asp-action="ListRoles" class="btn btn-primary">Cancel</a>
</div>
</div>
<br/>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
<h3>Users in this role</h3>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
@if (Model.Users != null && Model.Users.Any())
{
foreach (var user in Model.Users)
{
<h5 class="card-title">@user</h5>
}
}
else
{
<h5 class="card-title">None at the moment</h5>
}
</div>
<div class="card-footer">
<a asp-controller="Administration" asp-action="EditUsersInRole"
asp-route-roleId="@Model.Id" class="btn btn-primary">
Add or Remove Users From This Role
</a>
</div>
</div>
</form>
In the above view, apart from the role update and cancel button, we are adding another section that displays the list of users belonging to this particular role. We are also adding one button for Adding or removing users from this role. On clicking the Add or Remove Users from This Role button, we navigate to the EditUsersInRole action method of the Administration controller, passing the Role ID.
EditUsersInRole HttpGet Action Method:
Next, add the following EditUsersInRole HttpGet Action Method within the Administration controller. The following action method first checks whether the Role exists in the database. If it does, it will return all the users from the database. Then, it will loop through all the users and check whether the user is already assigned the given role. If assigned, it will mark the IsSelected property as True, else False.
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> EditUsersInRole(string roleId)
{
ViewBag.roleId = roleId;
var role = await _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(roleId);
if (role == null)
{
ViewBag.ErrorMessage = $"Role with Id = {roleId} cannot be found";
return View("NotFound");
}
ViewBag.RollName = role.Name;
var model = new List<UserRoleViewModel>();
foreach (var user in _userManager.Users.ToList())
{
var userRoleViewModel = new UserRoleViewModel
{
UserId = user.Id,
UserName = user.UserName
};
if (await _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name))
{
userRoleViewModel.IsSelected = true;
}
else
{
userRoleViewModel.IsSelected = false;
}
model.Add(userRoleViewModel);
}
return View(model);
}
In this example,
- _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(roleId): This method will return the Role based on the roleId from the AspNetRoles table.
- _userManager.Users.ToList(): This method will return all the users from the AspNetUsers table.
- _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name): This method will check whether the user is already assigned to this role. If yes, set the IsSelected property of the UserRoleViewModel to true; otherwise, set this property value to false.
- Here, we store the Role ID and Roll Name in the ViewBag.
EditUsersInRole View:
Next, add the EditUsersInRole.cshtml view within the /Views/Administration directory and copy and paste the following code. This is the view that allows us to add or remove users from a role.
@model List<UserRoleViewModel>
@{
var roleId = ViewBag.roleId;
}
<form method="post">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
<h3>Role: @ViewBag.RollName </h3>
</div>
<div class="card-header">
<h4>Add or Remove Users From This Role</h4>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
@for (int i = 0; i < Model.Count; i++)
{
<div class="form-check m-1">
<input type="hidden" asp-for="@Model[i].UserId" />
<input type="hidden" asp-for="@Model[i].UserName" />
<input asp-for="@Model[i].IsSelected" class="form-check-input" />
<label class="form-check-label" asp-for="@Model[i].IsSelected">
@Model[i].UserName
</label>
</div>
}
</div>
<div class="card-footer">
<input type="submit" value="Update" class="btn btn-primary"
style="width:auto" />
<a asp-action="EditRole" asp-route-roleId="@roleId"
class="btn btn-primary" style="width:auto">Cancel</a>
</div>
</div>
</form>
EditUsersInRole Post Action Method:
Next, add the following EditUsersInRole HttpPost Action Method within the Administration controller. The following action method will handle the form submission. The following code is self-explained, so, please go through the comment lines.
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> EditUsersInRole(List<UserRoleViewModel> model, string roleId)
{
//First check whether the Role Exists or not
var role = await _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(roleId);
if (role == null)
{
ViewBag.ErrorMessage = $"Role with Id = {roleId} cannot be found";
return View("NotFound");
}
for (int i = 0; i < model.Count; i++)
{
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(model[i].UserId);
IdentityResult? result;
if (model[i].IsSelected && !(await _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name)))
{
//If IsSelected is true and User is not already in this role, then add the user
result = await _userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, role.Name);
}
else if (!model[i].IsSelected && await _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name))
{
//If IsSelected is false and User is already in this role, then remove the user
result = await _userManager.RemoveFromRoleAsync(user, role.Name);
}
else
{
//Don't do anything simply continue the loop
continue;
}
//If you add or remove any user, please check the Succeeded of the IdentityResult
if (result.Succeeded)
{
if (i < (model.Count - 1))
continue;
else
return RedirectToAction("EditRole", new { roleId = roleId });
}
}
return RedirectToAction("EditRole", new { roleId = roleId });
}
In this example,
- _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(roleId): This method will return the Role based on the roleId from the AspNetRoles table.
- _userManager.FindByIdAsync(model[i].UserId): This method will return the user from the AspNetUsers table based on the UserId.
- _userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role.Name): This method will check whether the user is already assigned to this role.
- _userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, role.Name): This method will add the specified user to the role. It will make an entry into the AspNetUserRoles table where UserId will be the user’s ID, and RoleId will be the ID of the Role.
- _userManager.RemoveFromRoleAsync(user, role.Name): This method will remove the specified user from the role. It will remove the entry in the AspNetUserRoles table for this user and role.
That’s it. Now, run the application and test the functionality, and it should work as expected. After assigning roles with users, you can check the AspNetUserRoles table, and it should have the User ID and Role ID as shown in the image below:

In the next article, I will discuss ASP.NET Core Identity Role-Based Authorization. In this article, I explain how to Add or Remove Users from Roles in ASP.NET Core Identity. I hope you enjoy this article.

@model List
@{
var roleId = ViewBag.roleId;
}
Role: @ViewBag.RollName
Add or Remove Users From This Role
@for (int i = 0; i < Model.Count; i++)
{
@Model[i].UserName
}
Cancel
In this code, “Cancel”
Should be correct this.
asp-route-id => asp-route-roleId
Hi
Thanks for Identifying the type error. We have corrected the same.
Help me understand this logic in the EditUsersInRole Post Action Method.
At the end of the for loop you have:
if (result.Succeeded)
{
if (i < (model.Count – 1))
continue;
else
return RedirectToAction("EditRole", new { roleId = roleId });
}
So if the result is successful, it checks to see if the iteration is at the end of the list,
if not: it continues the loop
if so: it exits the loop and returns the redirect.
But if the result was not successful, it would just continue anyway.
After the loop exits, it returns the same redirect.
Is that right?
If so, I don't see what purpose this if (result.Succeeded) block serves.
For me the method
public async Task EditUsersInRole(List model, string roleId)
was not getting the roleId from the EditUsersInRole view
I fixed this by adding
in the form
meant to say this (without the quotes)
“”
Thanks