Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
How to Block Login if Email is not Confirmed in ASP.NET Core Identity
In this article, I will discuss How to Block Login if Email is not Confirmed in ASP.NET Core Identity. Please read our previous article discussing Email Confirmation in ASP.NET Core Identity.
Block Login if Email is not Confirmed in ASP.NET Core Identity:
To block login if the email is not confirmed with ASP.NET Core Identity, we need to modify the login logic to check whether the user’s email address has been confirmed. To do so, we need to follow the below steps:
- Modify the Login Action: In the Account Controller, locate the Login Post action method that handles the login request.
- Check Email Confirmation: After you validate the user’s credentials but before you sign in the user, check if their email address has been confirmed.
- Reject Login if Not Confirmed: If the user’s email address is not confirmed, do not proceed with the login process. Instead, redirect them to a page informing them to confirm their email or resend the confirmation email.
- Resend Confirmation Email: Provide an option for the user to resend the confirmation email if they haven’t received it.
Block Login if Email is not Confirmed Flow:
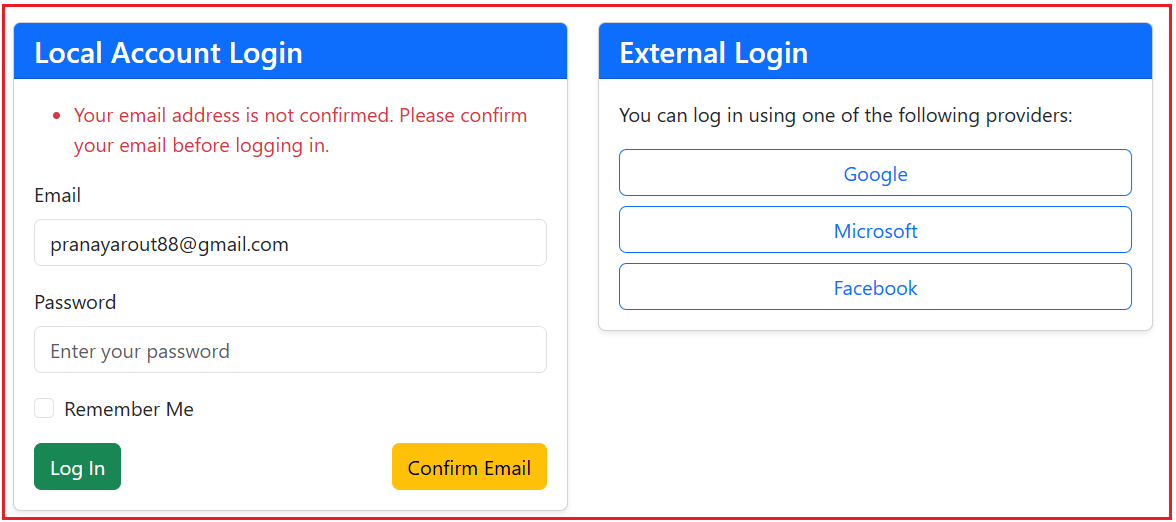
If the email address is not confirmed and if the user tries to log in, we want to display the validation error – Email not confirmed yet, as shown in the image below. Further, if you notice, we provide a Confirm Email button to confirm the user’s email address.
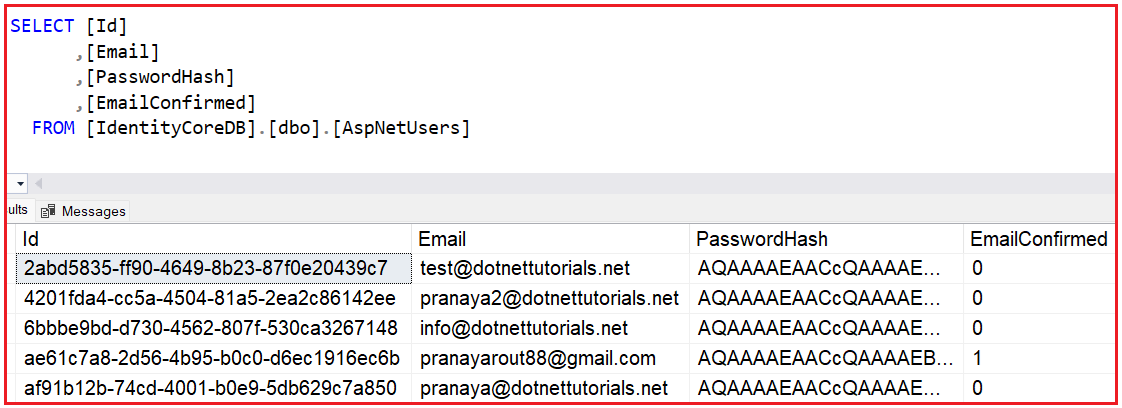
In ASP.NET Core Identity, application users are stored in the AspNetUsers database table. The EmailConfirmed column in this table determines if a given email address is confirmed.
How to Configure Require Confirm Email?
Please modify the Login.cshtml view as follows. Here, we are adding the Confirm Email button. Clicking the Confirm Email button will redirect to the ResendConfirmationEmail action method of the Account Controller.
@model LoginViewModel
<div class="container my-5">
<div class="row">
<!-- Local Account Login -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="card shadow-sm">
<div class="card-header bg-primary text-white">
<h4 class="mb-0">Local Account Login</h4>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<form method="post" asp-action="Login" asp-controller="Account" novalidate>
<input type="hidden" name="ReturnUrl" value="@Model.ReturnUrl" />
<!-- Validation Summary -->
<div asp-validation-summary="All" class="text-danger mb-3"></div>
<!-- Email Field -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Email" class="form-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Email" class="form-control" placeholder="Enter your email" />
<span asp-validation-for="Email" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Password Field -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Password" class="form-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Password" class="form-control" placeholder="Enter your password" />
<span asp-validation-for="Password" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Remember Me -->
<div class="form-check mb-3">
<input asp-for="RememberMe" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="RememberMe" class="form-check-label">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(m => m.RememberMe)
</label>
</div>
<!-- Login Button & Confirm Email Button -->
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">Log In</button>
<a class="btn btn-warning" asp-controller="Account"
asp-action="ResendConfirmationEmail"
asp-route-IsResend="false">Confirm Email</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- External Login -->
<div class="col-md-6 mt-4 mt-md-0">
<div class="card shadow-sm">
<div class="card-header bg-primary text-white">
<h4 class="mb-0">External Login</h4>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
@if (Model.ExternalLogins == null || Model.ExternalLogins.Count == 0)
{
<div class="alert alert-info mb-0">No external logins configured</div>
}
else
{
<p class="mb-3">You can log in using one of the following providers:</p>
<div class="d-grid gap-2">
@foreach (var provider in Model.ExternalLogins)
{
<button type="button"
class="btn btn-outline-primary external-login-btn"
data-provider="@provider.Name"
data-url="@Url.Action("ExternalLogin", "Account", new { provider = provider.Name, returnUrl = Model.ReturnUrl })"
title="Log in using your @provider.DisplayName account">
@provider.DisplayName
</button>
}
</div>
}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<script type="text/javascript">
document.querySelectorAll('.external-login-btn').forEach(button => {
button.addEventListener('click', function () {
var provider = this.getAttribute('data-provider');
var url = this.getAttribute('data-url');
// Define popup window size
var width = 500;
var height = 600;
var left = (window.innerWidth / 2) - (width / 2);
var top = (window.innerHeight / 2) - (height / 2);
// Open the popup window
var popup = window.open(url, provider, `width=${width},height=${height},top=${top},left=${left},resizable=yes`);
// Monitor the popup to check if it closes
var checkPopup = setInterval(function () {
if (popup.closed) {
clearInterval(checkPopup);
// Optionally, reload or fetch updated user state
location.reload(); // Refresh the parent window to reflect login state
}
}, 500); // Check every 500ms if the popup is closed
});
});
</script>
}
Modifying Login Post Action Method
We need to implement the following functionalities in the Login Post Action method to block the user from login correctly:
- Find User by Email: First, we need to fetch the user entity from the database using the email address provided in the login form. If the email doesn’t exist in the database, a generic error message is returned to avoid account enumeration attacks, which could allow attackers to discover valid email addresses.
- Check Password: Then we need to validate the provided password against the hashed password stored in the database. This is to ensure that the credentials are correct before proceeding with further checks (e.g., email confirmation).
- Check if Email is Confirmed: This will ensure that only users with confirmed email addresses can access their accounts. If the email isn’t confirmed, a clear message informs the user of the issue and how to resolve it.
- If the Email is Confirmed, Manually Sign-in the User: Then we need to sign in the user manually after all checks (password, email confirmation) have passed. The manual sign-in step allows more control over login criteria before establishing the session. This also ensures that only fully validated users are signed in
- Redirect User After Successful Sign-in: Then we need to redirect the user to the appropriate page after a successful login.
So, please modify the Login Post Action method of the Account Controller as follows. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding:
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Login(LoginViewModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
// 1. Find user by email
var user = await userManager.FindByEmailAsync(model.Email);
if (user == null)
{
// Avoid enumerating which part is invalid, just show generic error
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "Invalid login attempt.");
model.ExternalLogins = (await signInManager.GetExternalAuthenticationSchemesAsync()).ToList();
return View(model);
}
// 2. Check password
var result = await signInManager.CheckPasswordSignInAsync(user, model.Password, lockoutOnFailure: false);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
// 3. Now that we know the password is correct, check if email is confirmed
if (!user.EmailConfirmed)
{
// Show a specific error message
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "Your email address is not confirmed. Please confirm your email before logging in.");
model.ExternalLogins = (await signInManager.GetExternalAuthenticationSchemesAsync()).ToList();
return View(model);
}
// 4. If email is confirmed, manually sign-in the user
await signInManager.SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: model.RememberMe);
// 5. Redirect user after successful sign in
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(model.ReturnUrl) && Url.IsLocalUrl(model.ReturnUrl))
{
return Redirect(model.ReturnUrl);
}
return RedirectToAction(nameof(HomeController.Index), "Home");
}
if (result.RequiresTwoFactor)
{
// Handle two-factor authentication case
}
if (result.IsLockedOut)
{
// Handle lockout scenario
}
else
{
// Generic failure message for invalid credentials
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "Invalid login attempt.");
}
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay the login form
model.ExternalLogins = (await signInManager.GetExternalAuthenticationSchemesAsync()).ToList();
return View(model);
}
With the above changes in place, the Email not confirmed yet error message is displayed only if the Email is not confirmed and the user has provided the correct username and password. Otherwise, it will display an Invalid Login Attend error message.
Now, if the user wants to confirm his email, then he needs to click on the Confirm Email button on the Login Page as shown in the below image:

Once the user clicks on the Confirm Email button, it will open the following page, where the user needs to enter his email address and then click on the Send Confirmation Email button, as shown in the below image.

Once the user clicks on the Send Confirmation Email button, it will send the Email Confirmation link to the user’s email address, and on clicking that, the user’s email address will be confirmed; we have already discussed this in our previous article.
What about External Login?
If you want, you can also block the login if the external login account (like Facebook, Google, Microsoft, Twitter, etc.) is used and the email address associated with that external account is not confirmed in our database. So, modify the ExternalLoginCallback action method as follows:
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<IActionResult> ExternalLoginCallback(string? returnUrl, string? remoteError)
{
// If no returnUrl is provided, default to the application's home page.
returnUrl = returnUrl ?? Url.Content("~/");
// Check if an error occurred during the external authentication process.
// If so, display an alert to the user and close the popup window.
if (remoteError != null)
{
return Content($"<script>alert('Error from external provider: {remoteError}'); window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
// Retrieve login information about the user from the external login provider (e.g., Google, Facebook).
var info = await signInManager.GetExternalLoginInfoAsync();
// If the login information could not be retrieved, display an error message and close the popup.
if (info == null)
{
return Content($"<script>alert('Error loading external login information.'); window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
// Attempt to sign in the user using their external login details.
// If a corresponding record exists in the AspNetUserLogins table, the user will be logged in.
var signInResult = await signInManager.ExternalLoginSignInAsync(
info.LoginProvider, // The name of the external login provider (e.g., Google, Facebook).
info.ProviderKey, // The unique identifier of the user within the external provider.
isPersistent: false, // Indicates whether the login session should persist across browser restarts.
bypassTwoFactor: true // Bypass two-factor authentication if enabled.
);
// If the external login succeeds, redirect the parent window to the returnUrl and close the popup window.
if (signInResult.Succeeded)
{
var user = await userManager.FindByLoginAsync(info.LoginProvider, info.ProviderKey);
if (user != null)
{
if (user.EmailConfirmed)
{
// Email is confirmed; redirect to returnUrl
return Content($"<script>window.opener.location.href = '{returnUrl}'; window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
else
{
// Email not confirmed; send confirmation email and redirect to RegistrationSuccessful
await SendConfirmationEmail(user.Email, user);
await signInManager.SignOutAsync(); // Ensure the user is not signed in
var registrationSuccessfulUrl = Url.Action("RegistrationSuccessful", "Account");
return Content($"<script>window.opener.location.href = '{registrationSuccessfulUrl}'; window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
}
}
// If the user does not have a corresponding record, proceed to create one.
// Retrieve the user's email from the external login provider.
var email = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.Email);
if (email != null)
{
// Check if a local user account with the retrieved email already exists.
var user = await userManager.FindByEmailAsync(email);
// If no local account exists, create a new user in the AspNetUsers table.
if (user == null)
{
user = new ApplicationUser
{
UserName = email, // Set the username to the user's email.
Email = email, // Set the email.
FirstName = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.GivenName), // Retrieve and set the user's first name.
LastName = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.Surname) // Retrieve and set the user's last name.
};
// Create the new user in the database.
await userManager.CreateAsync(user);
}
// Link the external login to the newly created or existing user account.
// This inserts a record into the AspNetUserLogins table.
await userManager.AddLoginAsync(user, info);
// Check if the user's email is confirmed
if (user.EmailConfirmed)
{
// Email is confirmed; sign in the user and redirect
await signInManager.SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
return Content($"<script>window.opener.location.href = '{returnUrl}'; window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
else
{
// Email not confirmed; send confirmation email and redirect
await SendConfirmationEmail(user.Email, user);
var registrationSuccessfulUrl = Url.Action("RegistrationSuccessful", "Account");
return Content($"<script>window.opener.location.href = '{registrationSuccessfulUrl}'; window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
}
// If the email claim is not provided by the external login provider,
// display an error message and close the popup window.
return Content($"<script>alert('Email claim not received. Please contact support.'); window.close();</script>", "text/html");
}
RegistrationSuccessful Action Method:
Also, add the following RegistrationSuccessful Action Method within the Account Controller. This will render the Email Confirmation message when the user registers themselves using External Accounts.
public IActionResult RegistrationSuccessful()
{
return View("RegistrationSuccessful");
}
Now, run the application, and it should work as expected.
Test Cases
Case1:
Is Local Account Exist: Yes
Is Email Confirmed: No
Is External Account Exist: Yes
Objective: Send Confirmation Email
Case2:
Is Local Account Exist: Yes
Is Email Confirmed: Yes
Is External Account Exist: Yes
Objective: Login Success
Case3:
Is Local Account Exist: Yes
Is Email Confirmed: Yes
Is External Account Exist: No
Objective: Login Success and New Entry in External Login Table
Case4:
Is Local Account Exist: N0
Is External Account Exist: No
Objective: Make entry to the Local and External Login Table. Send Confirmation Email
In the next article, I will discuss Forgot Password in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain How to Block Login if Email is not Confirmed in ASP.NET Core Identity. I hope you enjoy this article, Block Login if Email is not Confirmed in ASP.NET Core Identity.

I have a bug with external login providers.
“””
// Email Confirmation Section
// Get the email claim from external login provider (Google, Facebook etc)
var email = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.Email);
ApplicationUser? user;
if (email != null)
{
// Find the user
user = await _userManager.FindByEmailAsync(email);
// If the user exists in our database and email is not confirmed,
// display login view with validation error
if (user != null && !user.EmailConfirmed)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, “Email not confirmed yet”);
return View(“Login”, loginViewModel);
}
}
“””
This code located in ExternalLoginCallback() action;
“””
[HttpGet]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task ConfirmEmail(string UserId, string Token)
{
if (UserId == null || Token == null)
{
ViewBag.Message = “The link is Invalid or Expired”;
}
// find user
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync(UserId);
if (user == null)
{
ViewBag.Message = $”The User ID {UserId} is Invalid”;
return View(“NotFound”);
}
// Call the ConfirmEmailAsync method which will mark the Email is Confirmed
var result = await _userManager.ConfirmEmailAsync(user, Token);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
ViewBag.Message = “Thank you for confirming your email”;
return View();
}
ViewBag.Message = “Email cannot be confirmed”;
return View();
}
“””
In the arguments to this action, the token comes with the value “null”.
As a result, the email was not confirmed.
But in other cases it works successfully.