Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity
In this article, I will discuss How to Implement Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity. Please read our previous article discussing How to Add or Remove User Claims in ASP.NET Core Identity.
What is Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity?
Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity provides a way to handle authorization decisions based on claims associated with the authenticated user. This approach focuses on verifying if the user is assigned specific claims that permit them to perform certain actions within an application. In Claims-Based Authorization, rights are granted to users based on the claims they possess rather than their roles alone.
Example to Understand Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity:
In our previous article, we have seen that whenever we add claims for a user, those claims will be stored in the following AspNetUserClaims identity database table.

Business Requirement:
Now, our requirement is that to DELETE a Role, the logged-in user must have a Delete Role Claim or Policy. Otherwise, access should be denied. Similarly, the logged-in user must have an Edit Role claim to Edit a Role. Otherwise, access should be denied.
Implementing Claims-Based Authorization using ASP.NET Core Identity:
We need to follow the below steps to Implement Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity:
- Define Claims: Determine what information about users is relevant for authorization decisions in your application. Common claims might include User ID, Role, Permission Levels (Edit, Delete, etc.), etc.
- Generate Claims During Authentication: When a user logs in, ensure that the necessary claims are generated and included in the user’s identity. This can be handled within the user login process, often in the SignInManager or when generating the user’s ClaimsIdentity.
- Create Authorization Policies or Claim Policy: Use the Policy-Based Authorization capabilities in ASP.NET Core to define policies that rely on specific claims. Policies are registered in the Program configuration class and can be applied to controllers or actions.
What is the Claim Policy?
In ASP.NET Core Identity, a Claim Policy is a specific set of requirements that defines how authorization decisions are made based on the claims associated with a user’s identity. Claim policies are part of the policy-based authorization strategy. Policies can enforce access control based on any information embedded within the user’s identity claims, such as roles, permissions, or other custom data.
- Defining a Policy: Policies are defined in the Program.cs class file of our ASP.NET Core application. Here, we can create a policy and specify the claims requirements it enforces.
- Using the Policy: Once a policy is defined, it can be applied to controllers, actions, or Razor Pages in our application. This is done using attributes like [Authorize(Policy = “PolicyName”)].
Creating a Claim Policy in ASP.NET Core
To define a claim policy, we need to specify the required claims and their values that users must possess to satisfy the policy. In the Program.cs class file, we need to define the Claim Policy using the AddAuthorization service. We need to use the AddPolicy method of the AuthorizationOptions object to define the Claim Policies. Please add the following code to the Program class for a better understanding.
builder.Services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("DeleteRolePolicy",
policy => policy.RequireClaim("Delete Role"));
});
Here,
- AddAuthorization() Method: The AddAuthorization service is used to set up policy-based authorization in ASP.NET Core applications.
- AddPolicy() Method: The AddPolicy() method of the AuthorizationOptions class in ASP.NET Core Identity defines authorization policies. These policies are essentially sets of requirements that specify what is needed for a user to be authorized to access certain resources or execute specific actions within an application.
- RequireClaim() Method: The RequireClaim() method in ASP.NET Core Identity implements claims-based authorization. This method creates authorization policies that specify a user’s claims to access certain resources.
In the above code, we are creating a policy named DeleteRolePolicy with the Claim Delete Role. Now, we can apply this DeleteRolePolicy to controllers or action methods, and when it applies, it will check whether the logged-in user has the Delete Role claim. If the user has the Delete Role claim, authorization will be successful, and the action method will be executed. If not, it redirects the request to the access denied page.
Using the Policy
Apply the DeleteRolePolicy to controllers or actions using the [Authorize] attribute. To access the DeleteRole action, the logged-in user must have a Delete Role claim. So, decorate the DeleteRole action method with the [Authorize(Policy = “DeleteRolePolicy”)] attribute as shown below:
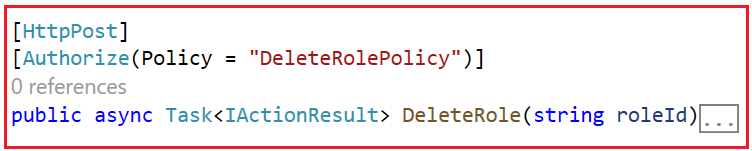
Now, run the application and try deleting a user without the Delete Role Policy. It should redirect you to the access denied page.
Adding Multiple Claims to a Policy in ASP.NET Core Identity
To add multiple claims to a given policy, we must chain the RequireClaim() method as follows. Here, we add Delete Role and Create Role claims to the DeleteRolePolicy policy. To satisfy this policy requirement, the logged-in user must have both claims.
builder.Services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("DeleteRolePolicy",
policy => policy.RequireClaim("Delete Role")
.RequireClaim("Create Role"));
});
In the next article, I will discuss Role-Based Authorization vs Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain How to Implement Claims-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity. I hope you enjoy this article, Claims Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity.


what if we have more then 50 claims???, then we need to create 50 polices because each claim is using for different-different methods im i right or not ??????.