Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
How to Implement CAPTCHA in ASP.NET Core
In this article, I will discuss how to implement CAPTCHA in ASP.NET Core with an Example. Please read our previous article discussing how to implement the Password Change Policy in ASP.NET Core Identity.
CAPTCHA is a simple yet powerful technique to protect web applications from bots and automated abuse. In this tutorial, we learn how to implement a CAPTCHA system in an ASP.NET Core application using a service that generates random text and renders it as an image. This helps ensure that only genuine users can complete critical operations, such as logging in or registering, adding a strong layer of security to your application.
What is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA stands for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart. It is a security mechanism designed to differentiate between human users and automated bots accessing web applications or services.
A CAPTCHA typically appears as a challenge on web forms or login pages, requiring users to perform a task, such as typing distorted text, selecting specific images, or solving a puzzle, that is easy for humans to solve but hard for bots or automated scripts. So, CAPTCHA helps protect websites from various types of malicious activities.
Why Do We Need CAPTCHA Services in Web Applications?
CAPTCHA is essential for enhancing the security of web applications. The following are the primary reasons for its use:
- Prevent Automated Abuse: Without CAPTCHA, malicious bots could repeatedly submit forms, create fake accounts, post spam comments, or attempt brute-force logins. CAPTCHAs handle this automated abuse by introducing a step that is difficult for bots to solve.
- Protect System Resources: Each request to a web application consumes bandwidth and computational resources on the server. By filtering out automated traffic, we save our resources for genuine users and reduce the load on our servers.
How does CAPTCHA work?
Let us understand how the Captcha works in a Web Application.
User Receives a Challenge
When a user attempts to sign up for an account, submit a form, or log in to the application, the site prompts them with a CAPTCHA test. Examples:
- Text-based CAPTCHA: Distorted letters and numbers that users must type correctly.
- Image-based CAPTCHA: Users select images that match a prompt (e.g., “Select all squares with traffic lights”).
In our application, we will implement a Text-based CAPTCHA, which will be displayed on the Login page as shown in the image below:
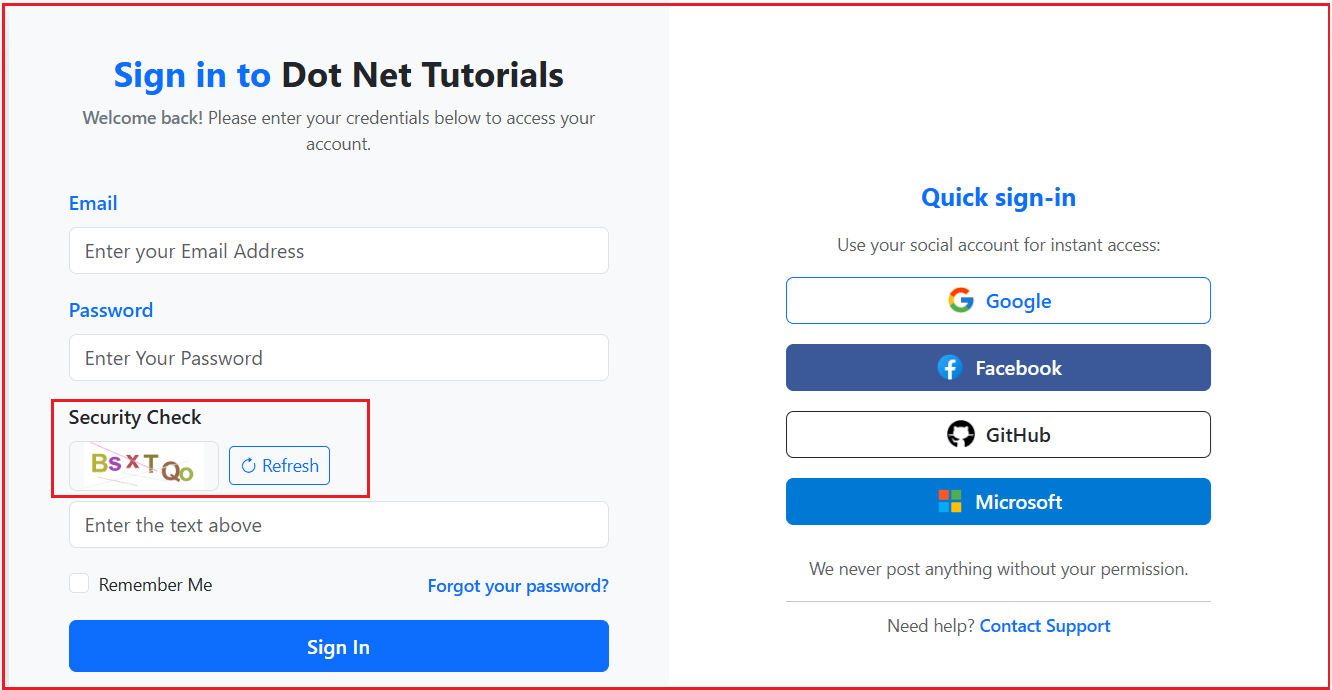
Validation on Server
The user’s response is sent back to the server or a CAPTCHA verification service. The server or third-party CAPTCHA service checks if the response is correct. If the response is correct (or the user’s behavior is deemed human), the user proceeds. If not, the request is blocked or flagged as suspicious.
How to Implement CAPTCHA in ASP.NET Core
We need to add image-based CAPTCHA functionality to our login process. Let us understand the step-by-step process of integrating the CAPTCHA feature into our Local Login process.
Installing Required Packages:
First, we need to install the SixLabors Package. This package provides support for creating and manipulating images, which is essential for generating CAPTCHA images dynamically. So, please install the package by executing the following command in the Package Manager Console:
- Install-Package SixLabors.ImageSharp
- Install-Package SixLabors.ImageSharp.Drawing
- Install-Package SixLabors.Fonts
Add a CAPTCHA Service
This service is responsible for generating the CAPTCHA code and creating the image representation of the CAPTCHA. So, please create a class file named CaptchaService.cs within the Services folder and copy and paste the following code.
using SixLabors.Fonts;
using SixLabors.ImageSharp;
using SixLabors.ImageSharp.Drawing.Processing;
using SixLabors.ImageSharp.Formats.Png;
using SixLabors.ImageSharp.PixelFormats;
using SixLabors.ImageSharp.Processing;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services
{
public static class CaptchaService
{
// Character set for captcha generation.
// Ambiguous characters like 0/O and 1/l/I are excluded to avoid confusion.
private static readonly char[] Alphabet =
"ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyz23456789".ToCharArray();
// Generates a random captcha code of the given length.
// Uses a cryptographically secure random number generator for better unpredictability.
public static string GenerateCaptchaCode(int length = 6)
{
var code = new char[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
code[i] = Alphabet[RandomNumberGenerator.GetInt32(Alphabet.Length)];
return new string(code);
}
// Generates a captcha image (PNG format) from the provided captcha text.
// Includes random rotation, position, color variations, and noise lines to
// make automated recognition more difficult while keeping it human-readable.
public static byte[] GenerateCaptchaImage(string captchaCode)
{
int width = 150; // Overall image width in pixels
int height = 60; // Overall image height in pixels
// Create a blank white image
using var image = new Image<Rgba32>(width, height, Color.White);
var random = new Random();
// Choose font style and size for captcha characters
var font = SystemFonts.CreateFont("Arial", 32, FontStyle.Bold);
image.Mutate(ctx =>
{
float x = 8f; // Starting X position for first character
// Render each captcha character with random variations
foreach (char c in captchaCode)
{
var angle = random.Next(-15, 15); // Random tilt to make OCR harder
var color = Color.FromRgb(
(byte)random.Next(50, 200), // Random R
(byte)random.Next(50, 200), // Random G
(byte)random.Next(50, 200)); // Random B
// Random vertical offset (some characters higher/lower)
float y = random.Next(5, 25);
// Draw the character at calculated position
ctx.DrawText(c.ToString(), font, color, new PointF(x, y));
// Move X slightly for the next character (prevent overlap)
x += 22;
}
// Add a few random noise lines across the image
// These lines reduce the success rate of automated captcha solvers
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
var p1 = new PointF(random.Next(width), random.Next(height));
var p2 = new PointF(random.Next(width), random.Next(height));
var lineColor = Color.FromRgb(
(byte)random.Next(150, 255),
(byte)random.Next(150, 255),
(byte)random.Next(150, 255));
ctx.DrawLine(lineColor, 1f, new[] { p1, p2 });
}
});
// Save image into memory as PNG and return as byte array
using var ms = new MemoryStream();
image.Save(ms, new PngEncoder());
return ms.ToArray();
}
}
}
Disable Camel Case in Program.cs
By default, ASP.NET Core uses camel case for JSON property names. This is crucial for consistent property naming between the server and client, especially when dealing with JSON Data (e.g., CacheId remains CacheId instead of becoming cacheId). In Program.cs, where we register the AddControllersWithViews service, please add the AddJsonOptions method to set the PropertyNamingPolicy to null as follows. This will affect all JSON serialization in our application.
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews()
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
// This stops System.Text.Json from converting property names to camelCase
options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null;
});
Creating Captcha Controller
Create a new Empty MVC Controller named CaptchaController within the Controllers folder and then copy and paste the following code. This Controller handles HTTP requests related to CAPTCHA generation and refreshing. This includes generating new CAPTCHA codes, creating corresponding images, storing CAPTCHA codes in memory, and providing endpoints for the frontend to retrieve and refresh CAPTCHA images.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("captcha")]
public class CaptchaController : Controller
{
private readonly IMemoryCache _cache;
public CaptchaController(IMemoryCache cache)
{
_cache = cache;
}
// GET /captcha/generate
[HttpGet("generate")]
public IActionResult GenerateCaptcha()
{
// Generate random CAPTCHA code
var captchaCode = CaptchaService.GenerateCaptchaCode(6);
// Create a new CaptchaId
var CaptchaId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
// Store the code in memory for 10 mins (adjust as needed)
_cache.Set(CaptchaId, captchaCode, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10));
// Generate the image
var captchaImageBytes = CaptchaService.GenerateCaptchaImage(captchaCode);
// Convert to Base64
var base64Image = Convert.ToBase64String(captchaImageBytes);
// Return JSON: { CaptchaId, CaptchaImage }
return Json(new
{
CaptchaId = CaptchaId,
CaptchaImage = $"data:image/png;base64,{base64Image}"
});
}
// GET /captcha/refresh?CaptchaId=<your-guid-here>
[HttpGet("refresh")]
public IActionResult RefreshCaptcha(string CaptchaId)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(CaptchaId))
{
return BadRequest("CaptchaId is required.");
}
// Remove existing captcha code from cache
_cache.Remove(CaptchaId);
// Generate a new code
var newCaptchaCode = CaptchaService.GenerateCaptchaCode(6);
// Store it in memory
_cache.Set(CaptchaId, newCaptchaCode, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10));
// Generate the new image
var captchaImageBytes = CaptchaService.GenerateCaptchaImage(newCaptchaCode);
// Convert to Base64
var base64Image = Convert.ToBase64String(captchaImageBytes);
// Return JSON
return Json(new
{
CaptchaId = CaptchaId,
CaptchaImage = $"data:image/png;base64,{base64Image}"
});
}
}
}
Add In-Memory Caching:
Enable Memory Caching to store CAPTCHA codes temporarily in the server’s Main memory. This ensures that the CAPTCHA validation process can verify user input against the generated code within a specified timeframe. So, please add the following code to the Program class.
builder.Services.AddMemoryCache();
Note: The IMemoryCache enables the application to store data in memory, which is fast and efficient for temporary data, such as CAPTCHA codes. The CaptchaController uses IMemoryCache to store and retrieve CAPTCHA codes based on unique identifiers (CaptchaId).
Modifying LoginViewModel (Add Captcha Fields)
We need to extend the existing login form model to include fields necessary for CAPTCHA validation. This ensures that the user’s input for CAPTCHA can be captured and validated during the login process. So, please modify the LoginViewModel as follows:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
{
public class LoginViewModel
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Email Id is Required")]
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Email Address")]
public string Email { get; set; } = null!;
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password Id is Required")]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
public string Password { get; set; } = null!;
[Display(Name = "Remember Me")]
public bool RememberMe { get; set; }
public string? ReturnURL { get; set; }
// Captcha fields
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please enter the CAPTCHA text.")]
[Display(Name = "Enter CAPTCHA")]
// 1) Must be exactly 6 length
// 2) Must be alphanumeric (case-insensitive)
[StringLength(6, MinimumLength = 6, ErrorMessage = "The CAPTCHA code must be 6 alphanumeric characters.")]
[RegularExpression("^[A-Za-z0-9]{6}$", ErrorMessage = "CAPTCHA must be exactly 6 alphanumeric characters.")]
public string CaptchaCode { get; set; } = null!;
// CaptchaId from Captcha
public string? CaptchaId { get; set; }
}
}
Login View (Add Captcha UI Elements)
Next, we need to integrate CAPTCHA UI elements into the login form, allowing users to view the CAPTCHA image, refresh it if necessary, and input the CAPTCHA code. This ensures that each login attempt includes a CAPTCHA verification step. So, please modify the Login.cshtml view as follows:
@model ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.LoginViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Login";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<div class="container-xxl pt-3 pb-4">
<div class="row justify-content-center">
<div class="col-12 col-lg-11 col-xl-10 col-xxl-10">
<div class="card border-0 shadow-lg rounded-4 overflow-hidden">
<div class="row g-0">
<!-- Left: Login Section -->
<div class="col-md-6 bg-light d-flex align-items-center">
<div class="w-100 p-4 p-lg-5">
<h3 class="mb-2 text-center fw-bold text-primary">
Sign in to <span class="text-dark">Dot Net Tutorials</span>
</h3>
<p class="text-center text-muted mb-4 small">
<span class="fw-semibold text-secondary">Welcome back!</span>
Please enter your credentials below to access your account.
</p>
<form asp-action="Login" method="post" novalidate>
<!-- Messages Section -->
@if (!ViewData.ModelState.IsValid)
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show small" role="alert">
<strong>Please fix the errors below and try again:</strong>
<div asp-validation-summary="All" class="mb-0 mt-1"></div>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<input type="hidden" name="ReturnUrl" value="@Model.ReturnURL" />
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Email" class="form-label fw-semibold text-primary"></label>
<input asp-for="Email" class="form-control" placeholder="Enter your Email Address" autocomplete="username" />
<span asp-validation-for="Email" class="text-danger small"></span>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Password" class="form-label fw-semibold text-primary"></label>
<input asp-for="Password" class="form-control" type="password" placeholder="Enter Your Password" autocomplete="current-password" />
<span asp-validation-for="Password" class="text-danger small"></span>
</div>
<!-- Captcha Section -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="CaptchaCode" class="form-label fw-semibold">Security Check</label>
<div class="d-flex align-items-center gap-2 mb-2">
<img id="captcha-image" alt="captcha"
class="rounded border"
style="width: 120px; height: 40px; object-fit: contain;" />
<button type="button" class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-primary" id="refresh-captcha">
<i class="bi bi-arrow-clockwise"></i> Refresh
</button>
</div>
<!-- Hidden field for CaptchaId -->
<input asp-for="CaptchaId" type="hidden" id="CaptchaId" />
<input asp-for="CaptchaCode" class="form-control"
placeholder="Enter the text above" />
<span asp-validation-for="CaptchaCode" class="text-danger small"></span>
</div>
<!-- Remember + Forgot -->
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center mb-3">
<div class="form-check">
<input asp-for="RememberMe" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="RememberMe" class="form-check-label small"></label>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-action="ForgotPassword" class="text-decoration-none small text-primary fw-semibold">
Forgot your password?
</a>
</div>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary w-100 fw-semibold py-2 mb-2">Sign In</button>
<p class="mt-3 text-center mb-1">
<span class="text-secondary small">New to <span class="fw-semibold text-dark">Dot Net Tutorials</span>?</span>
<a asp-action="Register" class="text-primary ms-1 text-decoration-none fw-semibold">Create an account</a>
</p>
<p class="text-center mb-0">
<a asp-action="ResendEmailConfirmation" class="text-info text-decoration-none small">Resend email confirmation</a>
</p>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Right: External Authentication -->
<div class="col-md-6 bg-white d-flex align-items-center">
<div class="w-100 p-4 p-lg-5 d-flex flex-column align-items-center">
<div class="w-100" style="max-width: 340px;">
<h5 class="mb-3 fw-bold text-primary text-center">Quick sign-in</h5>
<div class="mb-3 text-center text-muted small">Use your social account for instant access:</div>
<div class="d-grid gap-3 mb-3">
<a asp-controller="Account" asp-action="ExternalLogin" asp-route-provider="Google"
class="btn btn-outline-primary d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/color/32/000000/google-logo.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="Google" />
Google
</a>
<a asp-controller="Account" asp-action="ExternalLogin" asp-route-provider="Facebook"
class="btn d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold"
style="background-color: #3b5998; color: #fff;">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/fluency/32/000000/facebook-new.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="Facebook" />
Facebook
</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-outline-dark d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/ios-filled/32/000000/github.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="GitHub" />
GitHub
</a>
<a href="#" class="btn d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold"
style="background-color: #0078d4; color: #fff;">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/color/32/000000/microsoft.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="Microsoft" />
Microsoft
</a>
</div>
<div class="text-center text-muted small mt-4 mb-2">
<span>We never post anything without your permission.</span>
</div>
<hr class="mb-2" />
<div class="text-center text-muted small">
Need help? <a href="mailto:support@dotnettutorials.net" class="text-decoration-none fw-semibold">Contact Support</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- End right -->
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
<script>
function loadCaptcha() {
$.getJSON('/captcha/generate', function (data) {
$('#captcha-image').attr('src', data.CaptchaImage);
$('#CaptchaId').val(data.CaptchaId);
$('#CaptchaCode').val('');
});
}
function refreshCaptcha(captchaId) {
$.getJSON('/captcha/refresh', { CaptchaId: captchaId }, function (data) {
$('#captcha-image').attr('src', data.CaptchaImage);
$('#CaptchaId').val(data.CaptchaId);
$('#CaptchaCode').val('');
});
}
$(function () {
// Initial load
loadCaptcha();
// Refresh click
$('#refresh-captcha').on('click', function () {
var id = $('#CaptchaId').val();
if (id) refreshCaptcha(id); else loadCaptcha();
});
});
</script>
}
Inject Memory Cache into Account Controller:
Next, we need to inject the Memory Cache instance into the Account Controller as follows:
private readonly IAccountService _accountService;
private readonly ILogger<AccountController> _logger;
//_memoryCache hold the MemoryCache instance
private readonly IMemoryCache _memoryCache;
public AccountController(IAccountService accountService,
ILogger<AccountController> logger,
IMemoryCache memoryCache)
{
_accountService = accountService;
_logger = logger;
_memoryCache = memoryCache;
}
Modifying Login Post Action Method:
Next, we need to integrate CAPTCHA validation into the login process. This involves verifying that the user has entered the correct CAPTCHA code before proceeding with the authentication process. When redisplaying the form after a failed CAPTCHA validation, it’s essential to clear the previous CaptchaCode from the model and ModelState to prevent the old input from being shown again. So, please modify the Login Post action method as follows.
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Login(LoginViewModel model)
{
try
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
// Retrieve the cached captcha code from memory
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(model.CaptchaId)
|| !_memoryCache.TryGetValue(model.CaptchaId, out string? storedCaptchaCode))
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Captcha has expired or is invalid. Please refresh and try again.");
// Clear the user's CaptchaCode property in the model
model.CaptchaCode = string.Empty;
// ALSO remove the CaptchaCode entry from ModelState so it won't rebind
// the old posted value into the form field.
ModelState.Remove(nameof(model.CaptchaCode));
return View(model);
}
// Compare codes
if (storedCaptchaCode != model.CaptchaCode)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Invalid CAPTCHA. Please try again.");
// Clear the user's CaptchaCode property in the model
model.CaptchaCode = string.Empty;
// ALSO remove the CaptchaCode entry from ModelState so it won't rebind
// the old posted value into the form field.
ModelState.Remove(nameof(model.CaptchaCode));
return View(model);
}
// Remove it from memory
_memoryCache.Remove(model.CaptchaId);
// Clear the user's CaptchaCode property in the model
model.CaptchaCode = string.Empty;
// ALSO remove the CaptchaCode entry from ModelState so it won't rebind
// the old posted value into the form field.
ModelState.Remove(nameof(model.CaptchaCode));
// Proceed with the existing login logic
var (result, isPasswordExpired, failedAttempts, remainingAttempts, lockoutEndUtc, maxAttempts) = await _accountService.LoginUserAsync(model);
if (result.Succeeded && isPasswordExpired)
{
// Credentials ok, but password is expired -> DO NOT sign in.
TempData["ForceChangeEmail"] = model.Email;
TempData["Message"] = "Your password has expired. Please change it to continue.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(ForceChangePassword));
}
if (result.Succeeded)
{
// Redirect back to original page if ReturnUrl exists and is local
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(model.ReturnURL) && Url.IsLocalUrl(model.ReturnURL))
return Redirect(model.ReturnURL);
// Otherwise, redirect to a default page (like user profile)
return RedirectToAction("Profile", "Account");
}
// Handle login failure (e.g., account locked out, invalid credentials or unconfirmed email)
if (result.IsLockedOut)
{
ViewBag.FailedCount = failedAttempts;
ViewBag.MaxAttempts = maxAttempts;
ViewBag.LockoutEndUtc = lockoutEndUtc; // DateTimeOffset? (UTC)
ViewBag.SupportEmail = "support@dotnettutorials.net"; // optional config value
// Redirect to friendly lockout page
return View("AccountLocked");
}
if (result.IsNotAllowed)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Email is not confirmed yet.");
}
else
{
// Show attempts info
ModelState.AddModelError("", $"Invalid login attempt. " +
$"Failed Attempts: {failedAttempts}. Remaining Attempts: {remainingAttempts}.");
}
return View(model);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error during login for email: {Email}", model.Email);
ModelState.AddModelError("", "An unexpected error occurred. Please try again later.");
return View(model);
}
}
Note: When an ASP.NET Core form is re-displayed after a failed validation, the Razor engine re-populates form fields from the ModelState (not just from your model object). That’s why even if we set model.CaptchaCode = string.Empty;, the old value can still show up in the input field. So, we need to remove or update the ModelState entry for CaptchaCode right after we set model.CaptchaCode = string.Empty;. This way, Razor will not rebind the stale value.
By integrating CAPTCHA into our ASP.NET Core application, we can significantly reduce the risk of automated submissions and malicious bot activity. This additional layer of security ensures that only genuine users can access protected resources, thereby safeguarding sensitive operations such as login, registration, and password resets. With a properly implemented CAPTCHA system, we strike a balance between usability and protection, making our application more reliable and secure.
In the next article, I will discuss How to Configure SMS Service in ASP.NET Core. In this article, I explain how to implement Captcha in ASP.NET Core Identity. I hope you enjoy this article on implementing Captcha in ASP.NET Core Identity.
