Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
Roles Management in ASP.NET Core Identity
In this article, I will discuss Roles Management, i.e., how to add, update, retrieve, and delete Roles in ASP.NET Core Identity. Please read our previous article discussing ASP.NET Core Remote Validation. At the end of this article, you will understand how to create a new role, fetch all the roles, fetch a specific role, and update and delete an existing role using ASP.NET Core Identity.
Roles Management in ASP.NET Core Identity
Role management in ASP.NET Core Identity is a fundamental feature that helps define and control user permissions within an application. By creating and assigning roles, administrators can determine what actions users are allowed to perform and what resources they can access.
Managing who can do what inside a software application is one of the most important parts of building a secure, efficient, and user-friendly system. This is where roles come into play. In this session, we will cover:
- What a Role is
- Why we need Roles
- Why do applications have different types of Roles
- Why Role Management is essential
What is a Role?
A Role is a named grouping of permissions that defines what a user can and cannot do within an application. Think of a role as a job title in a company. The title itself doesn’t define how you do the job, but it defines what responsibilities you have.
Examples
- School: Teacher can enter marks and view class lists; Student can view assignments but can’t edit marks.
- Hospital: The Doctor can write prescriptions and view patient histories; the Receptionist can schedule appointments but can’t see full medical records.
- E-commerce: CatalogManager can add products; FulfillmentAgent can mark orders as shipped; Customer can place orders and view their own history.
Why Do We Need Roles?
We need roles to make access control simpler, more secure, and easier to manage. Without roles, every time a new person joins, we would have to give them permissions one by one manually. This is time-consuming and error-prone; you might give too many permissions or forget some.
Roles help by acting as permission bundles:
- Assign the bundle once → user gets all required permissions.
- Change the bundle once → all users in that role are updated automatically.
Key reasons we need roles:
- Efficiency – Assigning a role is quicker than assigning individual permissions to every user.
- Consistency – Everyone in the same role gets the same set of permissions.
- Security – Ensures that no one gets extra access accidentally.
- Scalability – Easy to manage when the number of users grows.
Why Do We Have Different Types of Roles?
Not everyone in an application needs the same level of access. Different jobs require different powers. That’s why we have multiple types of roles. If everyone had full access, it would:
- Be risky (someone could accidentally or intentionally harm the system).
- Cause confusion (too many options for people who don’t need them).
- Break the principle of Least Privilege, the idea that users should have only the permissions they need, nothing more.
Different types of roles allow:
- Admins to manage the entire system.
- Managers oversee teams or departments.
- Regular Users are to use the system without touching admin controls.
Example: Think about a hospital:
- Doctors can write prescriptions and access patient records.
- Nurses can give medicines and update patient details, but can’t prescribe new medicines.
- Receptionists can register patients and schedule appointments, but they cannot access medical histories.
If every hospital staff member had doctor-level access, the system would be chaotic and unsafe.
Why Do We Need Role Management?
Roles Management means the ability to create, edit, deactivate, or delete roles in an application. We need role management because:
- Businesses change over time → new job functions appear, old ones disappear.
- Security policies change → some permissions must be restricted or expanded.
- User responsibilities change → a user may get promoted, demoted, or moved to another department.
- Compliance requirements → specific industries (finance, healthcare) require regular review of who has access to what.
Roles management ensures:
- Flexibility – You can add a new “Vendor” role for suppliers without rewriting the system.
- Control – Remove or deactivate roles when they’re no longer needed.
Example: Think about a large mall:
- Initially, there were only Sales Staff and Managers.
- Later, the mall hires Security Staff, Cleaning Staff, and Event Coordinators.
- Without role management, the mall would have to redesign everything from scratch.
With role management, they create new roles and assign them to the right people.
Roles Management Example using ASP.NET Core MVC and Identity:
Now, we will implement the following pages:
Role Index Page:
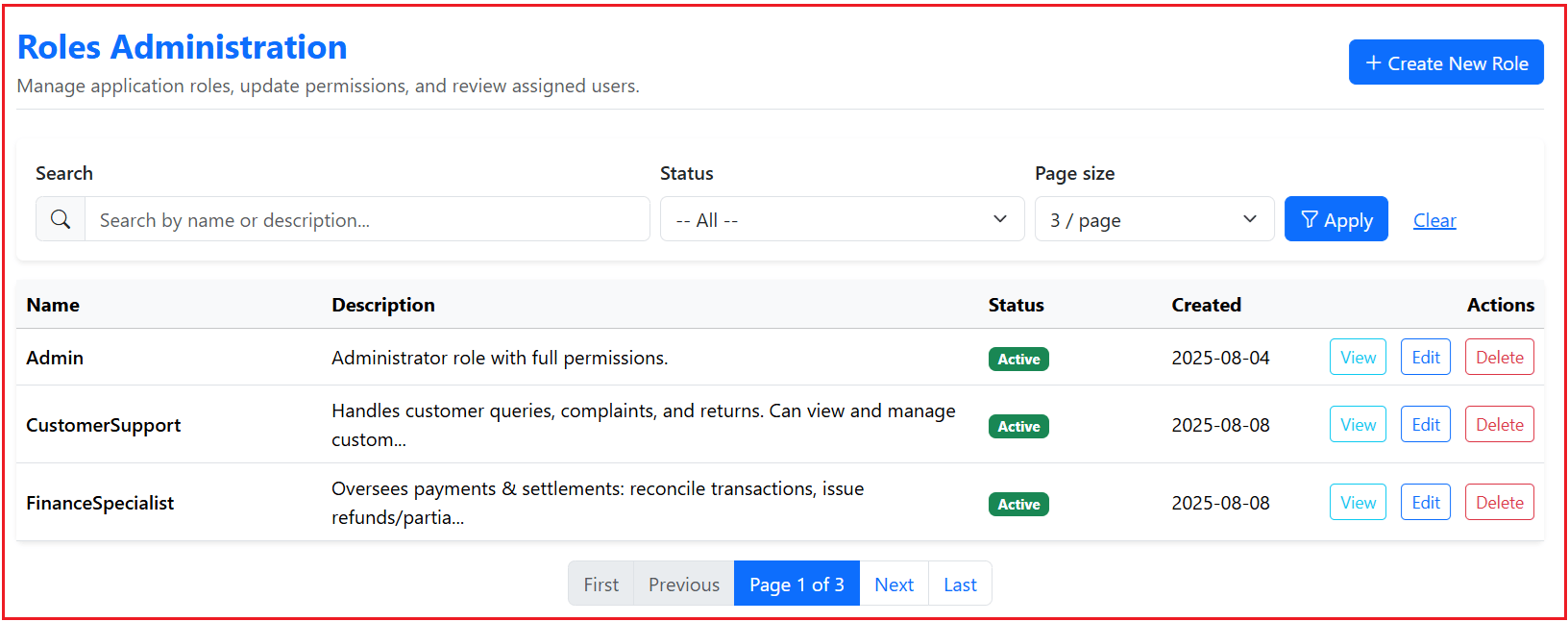
The Role Index page is the starting point for managing roles. It displays a complete list of all roles in the system along with key details like name, description, and status. From here, administrators can search for specific roles, filter the results, and navigate through multiple pages if there are many roles. It also provides quick access to actions like creating a new role, viewing role details, editing existing roles, or deleting roles.
Role Details Page:
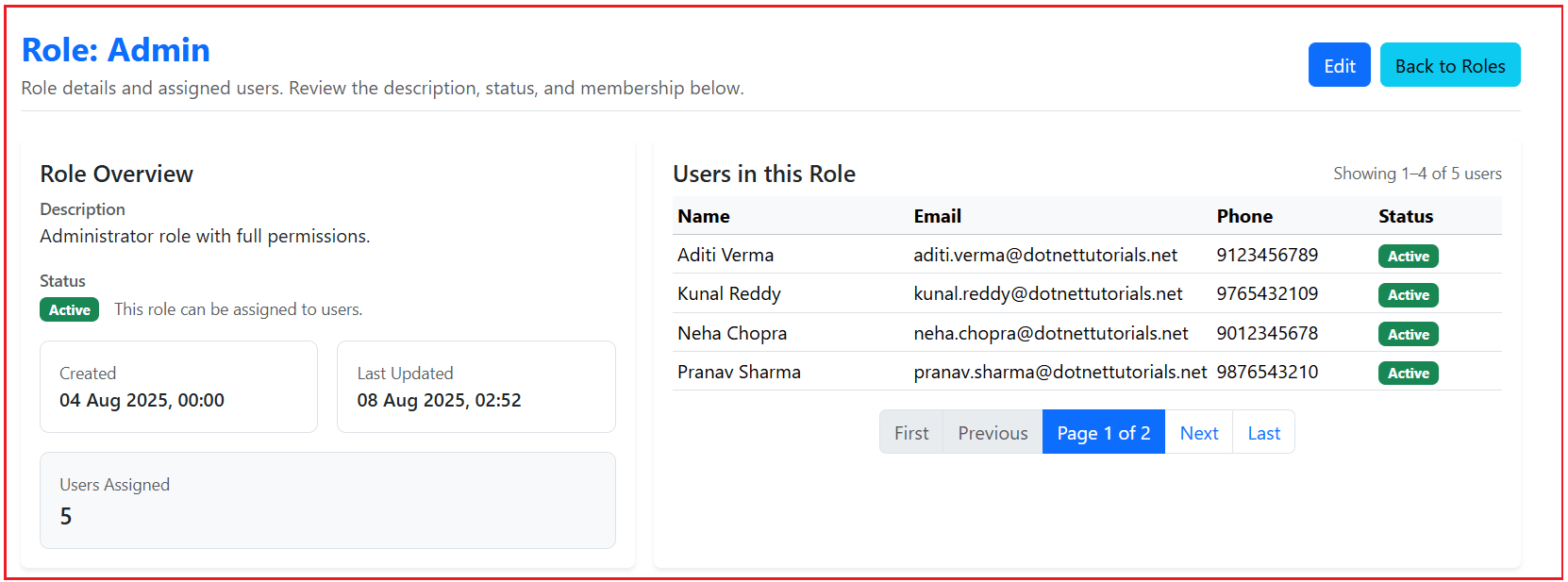
The Role Details page provides a clear view of all information related to a specific role. It shows the role’s name, description, and status, along with a list of users assigned to that role. This page is useful for reviewing a role before making changes, ensuring you understand its current usage and impact in the system.
Role Create Page:
The Role Create page allows administrators to add new roles to the system. It includes fields for entering the role’s name, description, and active status. This page ensures that role names remain unique and provides validation and helper messages to guide the admin while creating a role.

Role Edit Page:
The Role Edit page is designed for updating the details of an existing role. Administrators can change the name, description, and status of the role here. This page also includes validation to prevent errors and uses concurrency checks to ensure no conflicting updates happen at the same time.

Role Delete Modal Popup:
The Role Delete modal popup acts as a confirmation step before removing a role from the system. It clearly warns administrators if the role still has users assigned to it, helping to prevent accidental deletions or actions that could disrupt the application’s workflow.

Let us proceed and implement the above step-by-step in our project.
Creating View Models:
First, create a folder named Roles within the ViewModels folder where we will create all our View Models related to Roles.
PagedResult
PagedResult<T> is a small, reusable wrapper for paginated lists. It carries the current page’s Items, plus metadata such as TotalCount, PageIndex, and PageSize. It also exposes convenience properties like TotalPages, HasPreviousPage, and HasNextPage so your views can easily render “First/Prev/Next/Last” paging controls without recalculating anything. You’ll use this as the model for list pages (roles list, users-in-role list) to make pagination consistent across the app. Create a class file named PagedResult.cs within the ViewModels folder, then copy and paste the following code.
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
{
public class PagedResult<T>
{
public IReadOnlyList<T> Items { get; init; } = Array.Empty<T>();
public int TotalCount { get; init; }
public int PageNumber { get; init; }
public int PageSize { get; init; }
public int TotalPages => (int)Math.Ceiling((double)TotalCount / PageSize);
public bool HasPreviousPage => PageNumber > 1;
public bool HasNextPage => PageNumber < TotalPages;
}
}
RoleListItemViewModel
This model represents one row in the roles list. It includes only what the list needs to render quickly and cleanly: Id, Name, Description, IsActive, and CreatedOn. Keeping it lean prevents over-fetching and keeps your list page fast, while still providing enough data to display status, summarize the role, and link to details/edit/delete. Create a class file named RoleListItemViewModel.cs within the ViewModels\Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
{
public class RoleListItemViewModel
{
public Guid Id { get; init; }
public string Name { get; init; } = string.Empty;
public string? Description { get; init; }
public bool IsActive { get; init; }
public DateTime? CreatedOn { get; init; }
}
}
RoleListFilterViewModel
This model captures the user’s filtering and paging choices on the index page for roles. It includes a free-text Search (matching name/description), an optional IsActive filter, Page number, and page size. Binding this from the query string keeps your lists shareable and bookmarkable (the URL fully describes the state of the grid). Create a class file named RoleListFilterViewModel.cs within the ViewModels\Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
{
public class RoleListFilterViewModel
{
public string? Search { get; set; } // name/description
public bool? IsActive { get; set; }
public int PageNumber { get; set; } = 1;
public int PageSize { get; set; } = 5;
}
}
RoleCreateViewModel
This is the form model for creating a role. It uses data annotations to enforce basic validation. Name is required and length-limited; Description is optional with a max length; IsActive defaults to true. Separating this from the entity avoids over-posting and keeps your create form strictly focused on what an admin can set at creation time. Create a class file named RoleCreateViewModel.cs within the ViewModels\Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
{
public class RoleCreateViewModel
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Name is required.")]
[StringLength(256, ErrorMessage = "Name cannot exceed 256 characters.")]
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
[StringLength(512, ErrorMessage = "Description cannot exceed 512 characters.")]
public string? Description { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Active?")]
public bool IsActive { get; set; } = true;
}
}
RoleEditViewModel
Similar to the create model, but designed for updates. It includes the Id (so we know which role to update) and a ConcurrencyStamp so the service can perform an optimistic concurrency check (preventing silent overwrites if two admins edit the same role). It carries the editable fields—Name, Description, IsActive—with validation attributes, keeping edit logic safe and intentional. Create a class file named RoleEditViewModel.cs within the ViewModels\Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
{
public class RoleEditViewModel
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Id is required.")]
public Guid Id { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Name is required.")]
[StringLength(256, ErrorMessage = "Name cannot exceed 256 characters.")]
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
[StringLength(512, ErrorMessage = "Description cannot exceed 512 characters.")]
public string? Description { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Active?")]
public bool IsActive { get; set; } = true;
public string? ConcurrencyStamp { get; set; }
}
}
UserInRoleViewModel
This model represents a single user row on the Role Details page. It surfaces only the fields you want to show within that context: Email, PhoneNumber, name parts, IsActive, and Id. It’s purposely read-optimized for the role membership listing, so the details page loads fast and remains easy to format. Create a class file named UserInRoleViewModel.cs within the ViewModels\Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
{
public class UserInRoleViewModel
{
public Guid Id { get; init; }
public string Email { get; init; } = null!;
public string? PhoneNumber { get; init; }
public string? FirstName { get; init; }
public string? LastName { get; init; }
public bool IsActive { get; init; }
}
}
RoleDetailsViewModel
This view model powers the role details screen. It presents the role’s header information, Name, Description, IsActive, audit timestamps, and nests a PagedResult<UserInRoleViewModel> for the associated users list. That nested pager lets you page through members independently while keeping the overall role metadata fixed on the page. Create a class file named RoleDetailsViewModel.cs within the ViewModels\Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
{
public class RoleDetailsViewModel
{
public Guid Id { get; init; }
public string Name { get; init; } = string.Empty;
public string? Description { get; init; }
public bool IsActive { get; init; }
public DateTime? CreatedOn { get; init; }
public DateTime? ModifiedOn { get; init; }
public PagedResult<UserInRoleViewModel> Users { get; init; } = new();
}
}
Role Service Interface
This interface defines all role-related operations, such as: list roles with filtering and paging; create a role and return the result; fetch a role for editing; update with concurrency checks; delete with safety checks; and fetch role details, including paged members. By depending on this interface in controllers, your UI stays decoupled from persistence and is easier to test. Create an interface named IRoleService.cs within the Services folder, then copy and paste the following code.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services
{
public interface IRoleService
{
Task<PagedResult<RoleListItemViewModel>> GetRolesAsync(RoleListFilterViewModel filter);
Task<(IdentityResult Result, Guid? RoleId)> CreateAsync(RoleCreateViewModel model);
Task<RoleEditViewModel?> GetForEditAsync(Guid id);
Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(RoleEditViewModel model);
Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(Guid id);
Task<RoleDetailsViewModel?> GetDetailsAsync(Guid id, int pageNumber, int pageSize);
}
}
Role Service Implementation
This is the concrete business/service layer implementation. It orchestrates RoleManager<ApplicationRole> and your ApplicationDbContext to fulfill the contract in IRoleService. It performs unique-name checks, sets normalized names, manages timestamps, enforces optimistic concurrency via ConcurrencyStamp, and blocks deletion if users still belong to a role. For the details page, it queries the user–role junction table efficiently and returns a paged list of members. Create an interface named RoleService.cs within the Services folder, then copy and paste the following code.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services
{
public class RoleService : IRoleService
{
private readonly RoleManager<ApplicationRole> _roleManager; // Manages roles in ASP.NET Identity
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _dbContext; // For direct DB access
public RoleService(RoleManager<ApplicationRole> roleManager,
ApplicationDbContext dbContext)
{
_roleManager = roleManager;
_dbContext = dbContext;
}
// Retrieves a paginated list of roles based on filter criteria.
public async Task<PagedResult<RoleListItemViewModel>> GetRolesAsync(RoleListFilterViewModel filter)
{
// Start with all roles (No Tracking = better performance for read-only queries)
var query = _roleManager.Roles.AsNoTracking();
// Apply search filter (if provided)
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(filter.Search))
{
var s = filter.Search.Trim();
query = query.Where(r => r.Name!.Contains(s) || (r.Description ?? "").Contains(s));
}
// Apply Active/Inactive filter (if provided)
if (filter.IsActive.HasValue)
query = query.Where(r => r.IsActive == filter.IsActive.Value);
// Get total role count for pagination
var total = await query.CountAsync();
// Get current page of roles
var items = await query
.OrderBy(r => r.Name) // Sort alphabetically
.Skip((filter.PageNumber - 1) * filter.PageSize) // Skip previous pages
.Take(filter.PageSize) // Take only required items
.Select(r => new RoleListItemViewModel
{
Id = r.Id,
Name = r.Name!,
Description = r.Description,
IsActive = r.IsActive,
CreatedOn = r.CreatedOn
})
.ToListAsync();
// Return paginated result
return new PagedResult<RoleListItemViewModel>
{
Items = items,
TotalCount = total,
PageNumber = filter.PageNumber,
PageSize = filter.PageSize
};
}
// Creates a new role.
public async Task<(IdentityResult Result, Guid? RoleId)> CreateAsync(RoleCreateViewModel model)
{
// Ensure the role name is unique
bool roleExists = await _roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(model.Name);
if (roleExists)
{
return (IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError { Description = "Role name already exists." }), null);
}
// Create new ApplicationRole entity
var role = new ApplicationRole
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
Name = model.Name.Trim(),
NormalizedName = model.Name.Trim().ToUpperInvariant(), // For case-insensitive comparison
Description = model.Description?.Trim(),
IsActive = model.IsActive,
CreatedOn = DateTime.UtcNow,
ModifiedOn = DateTime.UtcNow
};
// Save to database
var result = await _roleManager.CreateAsync(role);
return (result, result.Succeeded ? role.Id : null);
}
// Retrieves a role for editing.
public async Task<RoleEditViewModel?> GetForEditAsync(Guid id)
{
var role = await _roleManager.Roles.AsNoTracking().FirstOrDefaultAsync(r => r.Id == id);
if (role == null)
return null;
// Map to edit view model
return new RoleEditViewModel
{
Id = role.Id,
Name = role.Name ?? string.Empty,
Description = role.Description,
IsActive = role.IsActive,
ConcurrencyStamp = role.ConcurrencyStamp // For concurrency checks
};
}
// Updates an existing role.
public async Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(RoleEditViewModel model)
{
var role = await _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(model.Id.ToString());
if (role == null)
{
return IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError
{
Code = "NotFound",
Description = "Role not found."
});
}
// Concurrency check — prevents overwriting changes made by others
if (!string.Equals(role.ConcurrencyStamp, model.ConcurrencyStamp, StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
return IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError
{
Code = "ConcurrencyFailure",
Description = "This role was modified by another user while you were editing. Please reload the page and try again."
});
}
// Ensure name is still unique (excluding current role)
if (!string.Equals(role.Name, model.Name, StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
var dup = await _roleManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Name);
if (dup != null && dup.Id != role.Id)
{
return IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError
{
Code = "DuplicateRoleName",
Description = $"Another role already uses this name: {model.Name}"
});
}
}
// Update properties
role.Name = model.Name.Trim();
role.NormalizedName = role.Name.ToUpperInvariant();
role.Description = model.Description;
role.IsActive = model.IsActive;
role.ModifiedOn = DateTime.UtcNow;
// Save changes — updates ConcurrencyStamp automatically
return await _roleManager.UpdateAsync(role);
}
// Deletes a role if it has no assigned users.
public async Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(Guid id)
{
var role = await _roleManager.FindByIdAsync(id.ToString());
if (role == null)
return IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError { Description = "Role not found." });
// Prevent deletion if any users are assigned to this role
var hasUsers = await _dbContext.Set<IdentityUserRole<Guid>>()
.AsNoTracking()
.AnyAsync(ur => ur.RoleId == id);
if (hasUsers)
return IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError { Description = "Cannot delete a role that still has users. Remove users from the role first." });
// Delete role
return await _roleManager.DeleteAsync(role);
}
// Retrieves details of a role, including paginated list of users in that role.
public async Task<RoleDetailsViewModel?> GetDetailsAsync(Guid id, int pageNumber, int pageSize)
{
var role = await _roleManager.Roles.AsNoTracking().FirstOrDefaultAsync(r => r.Id == id);
if (role == null)
return null;
// Query all users in this role via junction table (IdentityUserRole)
var usersQuery =
from ur in _dbContext.Set<IdentityUserRole<Guid>>().AsNoTracking() //Left table - User Roles
join u in _dbContext.Set<ApplicationUser>().AsNoTracking() //Right table - Users
on ur.UserId equals u.Id
where ur.RoleId == id
select new UserInRoleViewModel
{
Id = u.Id,
Email = u.Email!,
FirstName = u.FirstName,
LastName = u.LastName,
IsActive = u.IsActive,
PhoneNumber = u.PhoneNumber
};
// Get total user count
var total = await usersQuery.CountAsync();
// Get current page of users
var users = await usersQuery
.OrderBy(u => u.Email)
.Skip((pageNumber - 1) * pageSize)
.Take(pageSize)
.ToListAsync();
// Return role details with users
return new RoleDetailsViewModel
{
Id = role.Id,
Name = role.Name ?? string.Empty,
Description = role.Description,
IsActive = role.IsActive,
CreatedOn = role.CreatedOn,
ModifiedOn = role.ModifiedOn,
Users = new PagedResult<UserInRoleViewModel>
{
Items = users,
TotalCount = total,
PageNumber = pageNumber,
PageSize = pageSize
}
};
}
}
}
Register the Role Service into DI:
Please add the following statement to register the Role service into the dependency Injection container within the Program class.
builder.Services.AddScoped<IRoleService, RoleService>();
The above statement wires your service into ASP.NET Core’s DI container so controllers can request an IRoleService and receive a RoleService. The scoped lifetime is appropriate for EF Core and web requests; each HTTP request gets its own clean instance chain.
Creating Roles Controller:
This MVC controller is the entry point for all UI interactions around roles. Index renders the list using RoleListFilterViewModel; Create shows and posts the creation form while mapping identity errors to model-level errors; Edit handles the optimistic concurrency path and duplicates gracefully; Details shows role metadata and a paginated user membership list; and Delete performs a safe delete with feedback via TempData. Create an empty MVC Controller named RolesController within the Controllers folder and then copy and paste the following code.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Controllers
{
[Authorize]
public class RolesController : Controller
{
private readonly IRoleService _roleService;
private readonly ILogger<RolesController> _logger;
public RolesController(IRoleService roleService, ILogger<RolesController> logger)
{
_roleService = roleService;
_logger = logger;
}
// GET: /Roles
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> Index([FromQuery] RoleListFilterViewModel filter)
{
try
{
var result = await _roleService.GetRolesAsync(filter);
ViewBag.Filter = filter;
return View(result);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching roles in Index action.");
return View("Error");
}
}
// GET: /Roles/Create
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Create()
{
try
{
return View(new RoleCreateViewModel());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error rendering Create Role form.");
return View("Error");
}
}
// POST: /Roles/Create
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create(RoleCreateViewModel model)
{
try
{
// DataAnnotations validation first
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return View(model);
}
var (result, id) = await _roleService.CreateAsync(model);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
TempData["Success"] = $"Role '{model.Name}' created successfully.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
// Map IdentityResult errors to MODEL-LEVEL errors
foreach (var e in result.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, e.Description);
}
return View(model);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error creating role '{RoleName}'.", model?.Name);
return View("Error");
}
}
// GET: /Roles/Edit/{id}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(Guid id)
{
try
{
var vm = await _roleService.GetForEditAsync(id);
if (vm == null) return NotFound();
return View(vm);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching role for edit. RoleId: {RoleId}", id);
return View("Error");
}
}
// POST: /Roles/Edit
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(RoleEditViewModel model)
{
try
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return View(model);
}
var result = await _roleService.UpdateAsync(model);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
TempData["Success"] = $"Role '{model.Name}' updated successfully.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
// Map IdentityResult errors to MODEL-LEVEL errors
foreach (var e in result.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, e.Description);
}
return View(model);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error updating role '{RoleName}'.", model?.Name);
return View("Error");
}
}
// GET: /Roles/Details/{id}?page=1&pageSize=4
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> Details(Guid id, int pageNumber = 1, int pageSize = 4)
{
try
{
var vm = await _roleService.GetDetailsAsync(id, pageNumber, pageSize);
if (vm == null) return NotFound();
return View(vm);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching role details. RoleId: {RoleId}", id);
return View("Error");
}
}
// POST: /Roles/Delete/{id}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(Guid id)
{
try
{
var result = await _roleService.DeleteAsync(id);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
TempData["Success"] = "Role deleted.";
}
else
{
TempData["Error"] = string.Join(" ", result.Errors.Select(e => e.Description));
}
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error deleting role. RoleId: {RoleId}", id);
return View("Error");
}
}
}
}
Creating Views:
Shared Pagination Partial View:
This shared partial view renders a standard pagination footer: First, Previous, “Page X of Y”, Next, Last, using the PagedResult<object> metadata. It preserves current query parameters, ensuring filters/search results persist across page navigation, which is crucial for a good user experience. Centralizing the markup here guarantees consistent paging controls across list screens. First, create a partial view named _Pager.cshtml within the Views/Shared folder, then copy and paste the following code.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
@model PagedResult<object>
@* The pager works with any list wrapped inside a PagedResult<T> model *@
@{
// Get the current action and controller name from the route
var action = ViewContext.RouteData.Values["action"]?.ToString();
var controller = ViewContext.RouteData.Values["controller"]?.ToString();
// This dictionary will hold all query string parameters from the current URL
// except the "pagenumber" parameter (so we can replace it with a new one later)
var routeValues = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
// Loop through all query parameters from the current request URL
foreach (var kv in ViewContext.HttpContext.Request.Query)
{
// Skip the "page" parameter because we'll manually set it later for each link
if (!string.Equals(kv.Key, "pagenumber", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
// Store the query parameter and its value in the dictionary
// Example: search=Admin, isActive=true, pagesize=5
routeValues[kv.Key] = kv.Value.ToString();
}
}
// Calculate the first and previous page numbers
var firstPage = 1;
var prevPage = Math.Max(1, Model.PageNumber - 1); // Never go below page 1
// Ensure we have a valid total page count
var totalPages = Model.TotalPages;
// Calculate the next and last page numbers
var nextPage = Math.Min(totalPages, Model.PageNumber + 1); // Never go beyond last page
var lastPage = totalPages;
}
<!-- Pagination Navigation -->
<nav aria-label="Pagination" class="mt-3">
<ul class="pagination justify-content-center">
<!-- First Page Button -->
<!-- Use current controller -->
<!-- Use current action -->
<!-- Preserve all current filters except 'page' -->
<!-- Set page=1 -->
<li class="page-item @(Model.HasPreviousPage ? "" : "disabled")">
<a class="page-link"
asp-controller="@controller"
asp-action="@action"
asp-all-route-data="routeValues"
asp-route-pagenumber="@firstPage">First</a>
</li>
<!-- Previous Page Button -->
<li class="page-item @(Model.HasPreviousPage ? "" : "disabled")">
<a class="page-link"
asp-controller="@controller"
asp-action="@action"
asp-all-route-data="routeValues"
asp-route-pagenumber="@prevPage">
<!-- Set page to previous page -->
Previous
</a>
</li>
<!-- Current Page Display (Not clickable) -->
<li class="page-item active">
<span class="page-link">
Page @Model.PageNumber of @Model.TotalPages
</span>
</li>
<!-- Next Page Button -->
<li class="page-item @(Model.HasNextPage ? "" : "disabled")">
<a class="page-link"
asp-controller="@controller"
asp-action="@action"
asp-all-route-data="routeValues"
asp-route-pagenumber="@nextPage">
<!-- Set page to next page -->
Next
</a>
</li>
<!-- Last Page Button -->
<li class="page-item @(Model.HasNextPage ? "" : "disabled")">
<a class="page-link"
asp-controller="@controller"
asp-action="@action"
asp-all-route-data="routeValues"
asp-route-pagenumber="@lastPage">
<!-- Set page to last page -->
Last
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
Index View:
This is the roles listing UI. It presents a professional header, filter bar (search, active status, page size), success/error alerts, and the grid itself with “View / Edit / Delete” actions. It uses Bootstrap tooltips and a confirmation modal for deletes, and includes the shared _Pager to navigate pages. The view binds to PagedResult<RoleListItemViewModel> and reads the filter back from ViewBag.Filter to keep the form fields in sync with the current query. Create a view named Index.cshtml within the Views/Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
@model PagedResult<RoleListItemViewModel>
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Roles";
var filter = (RoleListFilterViewModel)ViewBag.Filter;
}
<div class="container mt-1">
<!-- Page Header -->
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap align-items-center justify-content-between gap-2 mb-4 pb-2 border-bottom">
<div>
<h1 class="h3 mb-1 fw-bold text-primary">Roles Administration</h1>
<p class="text-muted mb-0">
Manage application roles, update permissions, and review assigned users.
</p>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-action="Create" class="btn btn-primary">
<i class="bi bi-plus-lg me-1"></i>Create New Role
</a>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Alerts -->
@if (TempData["Success"] is string sMsg)
{
<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-check-circle me-2"></i>@sMsg
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
@if (TempData["Error"] is string eMsg)
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-exclamation-triangle me-2"></i>@eMsg
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<!-- Filter Bar -->
<form method="get" asp-action="Index" asp-controller="Roles" class="row g-2 align-items-end mb-3">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label class="form-label">Search</label>
<input name="Search" value="@filter.Search" class="form-control"
placeholder="Search by name or description..." />
</div>
<div class="col-md-3">
<label class="form-label">Status</label>
<select name="IsActive" class="form-select">
<option value="">All Status</option>
<option value="true" selected="@(filter.IsActive == true)">Active</option>
<option value="false" selected="@(filter.IsActive == false)">Inactive</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="col-md-3">
<label class="form-label">Page Size</label>
<select name="PageSize" class="form-select">
@foreach (var size in new[] { 5, 10, 20, 50 })
{
<option value="@size" selected="@(filter.PageSize == size)">@size / page</option>
}
</select>
</div>
<div class="col-md-2 d-grid d-sm-flex gap-2">
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">
<i class="bi bi-funnel me-1"></i> Apply
</button>
<!-- Clear = go to Index without query string -->
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">
<i class="bi bi-x-circle me-1"></i> Clear
</a>
</div>
</form>
<!-- Table / Empty state -->
@if (Model.Items.Any())
{
<div class="card shadow border-0 rounded">
<div class="card-body p-0">
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table align-middle mb-0">
<thead class="table-dark">
<tr>
<th style="width: 20%;">Name</th>
<th style="width: 43%;">Description</th>
<th style="width: 12%;">Status</th>
<th style="width: 10%;">Created</th>
<th class="text-end" style="width: 15%;">Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var r in Model.Items)
{
var desc = r.Description ?? "";
var shortDesc = desc.Length > 80 ? desc.Substring(0, 77) + "..." : desc;
<tr>
<td class="fw-semibold">@r.Name</td>
<td>
<span data-bs-toggle="tooltip" title="@desc">@shortDesc</span>
</td>
<td>
@if (r.IsActive)
{
<span class="badge bg-success">Active</span>
}
else
{
<span class="badge bg-danger">Inactive</span>
}
</td>
<td>@(r.CreatedOn?.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd") ?? "-")</td>
<td class="text-end">
<a asp-action="Details" asp-route-id="@r.Id"
class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-info me-2">View</a>
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@r.Id"
class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-primary me-2">Edit</a>
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-danger"
type="button"
data-bs-toggle="modal"
data-bs-target="#confirmDeleteModal"
data-role-id="@r.Id"
data-role-name="@r.Name">
Delete
</button>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Pager -->
<partial name="~/Views/Shared/_Pager.cshtml"
model="new PagedResult<object> { Items = Array.Empty<object>(), TotalCount = Model.TotalCount, PageNumber = Model.PageNumber, PageSize = Model.PageSize }" />
}
else
{
<div class="card border-0 shadow-sm">
<div class="card-body text-center py-5">
<div class="display-6 mb-2">No roles to display</div>
<p class="text-muted mb-4">Try adjusting filters or create your first role.</p>
<a asp-action="Create" class="btn btn-primary">
<i class="bi bi-plus-lg me-1"></i>Create Role
</a>
</div>
</div>
}
</div>
<!-- Delete Confirmation Modal (centered) -->
<div class="modal fade" id="confirmDeleteModal" tabindex="-1" aria-labelledby="confirmDeleteLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-dialog-centered">
<div class="modal-content border-0 shadow">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="confirmDeleteLabel">Delete Role</h5>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
Are you sure you want to delete role <strong id="delRoleName"></strong>?
<div class="text-muted small mt-2">This action cannot be undone.</div>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<form id="delForm" method="post" asp-action="Delete" asp-controller="Roles">
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<input type="hidden" name="id" id="delId" />
<button type="button" class="btn btn-info" data-bs-dismiss="modal">Cancel</button>
<button class="btn btn-danger" type="submit">Delete</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
<script>
$(function () {
// Enable Bootstrap tooltips
$('[data-bs-toggle="tooltip"]').tooltip();
// Show delete modal with populated role info
$('#confirmDeleteModal').on('show.bs.modal', function (event) {
var button = $(event.relatedTarget);
var roleId = button.data('role-id');
var roleName = button.data('role-name');
$('#delRoleName').text(roleName || '');
$('#delId').val(roleId || '');
});
});
</script>
}
Create View:
This form collects the minimal inputs to define a new role: Name, Description, and Active status. It shows a model-level validation summary for general errors (e.g., duplicate name) plus per-field validation messages. The right-hand guidance card explains naming, description, and deactivation best practices to keep admin actions consistent and clear. Create a view named Create.cshtml within the Views/Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
@model RoleCreateViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create Role";
}
<div class="container mt-1">
<!-- Page Header -->
<div class="mb-4 border-bottom pb-2">
<h1 class="h4 fw-bold text-primary mb-1">Create Role</h1>
<p class="text-muted small mb-0">Add a new role with a clear name and helpful description. You can mark it inactive if you’re planning ahead.</p>
</div>
<!-- Two-column Layout -->
<div class="row g-4">
<!-- Left Column: Form -->
<div class="col-lg-8">
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0 h-100">
<div class="card-body">
<!-- Model-level and field errors (visible only when there are errors) -->
@if (!ViewData.ModelState.IsValid && ViewData.ModelState.Values.Any(v => v.Errors.Count > 0))
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-1">We couldn’t create the role.</div>
<div class="small text-muted mb-2">Please review the messages below and try again.</div>
<div asp-validation-summary="All"></div>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<form asp-action="Create" method="post" novalidate>
<!-- Name -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Name" class="form-label fw-semibold">Role Name</label>
<input asp-for="Name" class="form-control" placeholder="e.g., Admin, Manager, Support" />
<div class="form-text">Role names must be unique. Use descriptive and consistent naming.</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Name" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Description -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Description" class="form-label fw-semibold">Description</label>
<textarea asp-for="Description" rows="4" class="form-control" maxlength="1000" placeholder="Describe what this role can do"></textarea>
<div class="form-text">Brief, admin-facing note about this role’s purpose and typical permissions. Max 1000 characters.</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Description" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Active Status -->
<div class="form-check form-switch mb-3">
<input asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-label fw-semibold">Active</label>
<div class="form-text">
Inactive roles remain in the system but should not be assigned to new users.
</div>
</div>
<!-- Actions -->
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap gap-2">
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">Create Role</button>
<button class="btn btn-dark" type="reset">Reset</button>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">Back to Roles</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Right Column: Guidance -->
<div class="col-lg-4">
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0">
<div class="card-body">
<h6 class="fw-bold mb-3">Guidelines</h6>
<ul class="small mb-0 ps-3">
<li>Pick a clear, unique name (e.g., <em>SupportAgent</em>, <em>ContentManager</em>).</li>
<li>Use the description to help other admins understand the scope of this role.</li>
<li>Prefer deactivating over deleting to keep an audit trail.</li>
<li>You can edit or deactivate the role at any time after creation.</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
Edit View:
This form lets admins modify an existing role’s name, description, and active flag. It includes hidden fields for Id and ConcurrencyStamp to support safe updates. Create a view named Edit.cshtml within the Views/Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
@model RoleEditViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Edit Role";
}
<div class="container mt-1">
<!-- Page Header -->
<div class="mb-4 border-bottom pb-2">
<h1 class="h4 fw-bold text-primary mb-1">Edit Role</h1>
<p class="text-muted small mb-0">Update the role’s name, description, and status. All changes take effect immediately.</p>
</div>
<!-- Alerts -->
@if (TempData["Success"] is string sMsg)
{
<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-check-circle me-2"></i>@sMsg
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
@if (TempData["Error"] is string eMsg)
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-exclamation-triangle me-2"></i>@eMsg
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<!-- Two-column Layout -->
<div class="row g-4">
<!-- Left Column: Form -->
<div class="col-lg-8">
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0 h-100">
<div class="card-body">
<!-- Model-level and field errors (visible only when there are errors) -->
@if (!ViewData.ModelState.IsValid && ViewData.ModelState.Values.Any(v => v.Errors.Count > 0))
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-1">We couldn’t save your changes.</div>
<div class="small text-muted mb-2">Please review the messages below and try again.</div>
<div asp-validation-summary="All"></div>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<form asp-action="Edit" method="post" novalidate>
<input type="hidden" asp-for="Id" />
<input type="hidden" asp-for="ConcurrencyStamp" />
<!-- Name -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Name" class="form-label fw-semibold">Role Name</label>
<input asp-for="Name" class="form-control" placeholder="e.g., Admin, Manager, Support" />
<div class="form-text">Role names must be unique. Use descriptive and consistent naming.</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Name" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Description -->
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Description" class="form-label fw-semibold">Description</label>
<textarea asp-for="Description" rows="4" class="form-control" maxlength="1000" placeholder="Describe what this role can do"></textarea>
<div class="form-text">Brief, admin-facing note about this role’s purpose and permissions.</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Description" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Active Status -->
<div class="form-check form-switch mb-3">
<input asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-label fw-semibold">Active</label>
<div class="form-text">
Inactive roles will remain in the system but cannot be assigned to new users.
</div>
</div>
<!-- Save Button -->
<div class="d-flex gap-2">
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">
Save Changes
</button>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">Back to Roles</a>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-secondary">View Details</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Right Column: Role Info & Guidelines -->
<div class="col-lg-4">
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0 mb-4">
<div class="card-body">
<h6 class="fw-bold mb-3">Role Status</h6>
@if (Model.IsActive)
{
<span class="badge bg-success px-3 py-2">Active</span>
}
else
{
<span class="badge bg-secondary px-3 py-2">Inactive</span>
}
<div class="mt-3 small text-muted">
<strong>Role ID:</strong> @Model.Id
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0">
<div class="card-body">
<h6 class="fw-bold mb-3">Guidelines</h6>
<ul class="small mb-0 ps-3">
<li>Ensure the name is unique and descriptive.</li>
<li>Keep descriptions concise but informative.</li>
<li>Deactivate roles instead of deleting for record-keeping.</li>
<li>Review permissions before making the role active.</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
Details View:
This page gives a concise “Role Overview” (description, active badge, created/updated times, member count) alongside a paginated table of users assigned to the role. It uses the nested PagedResult<UserInRoleViewModel> to display members and reuses the _Pager partial to navigate pages of users. If there are no users, it shows a helpful empty state so admins know what to do next. Create a view named Details.cshtml within the Views/Roles folder, then copy and paste the following code.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Roles
@model RoleDetailsViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Role Details";
var totalUsers = Model.Users.TotalCount;
var start = totalUsers == 0 ? 0 : ((Model.Users.PageNumber - 1) * Model.Users.PageSize) + 1;
var end = Math.Min(Model.Users.PageNumber * Model.Users.PageSize, totalUsers);
string FormatDate(DateTime? dt) => dt.HasValue ? dt.Value.ToString("dd MMM yyyy, HH:mm") : "-";
}
<div class="container mt-3">
<!-- Page Header -->
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap align-items-center justify-content-between gap-2 mb-4 pb-2 border-bottom">
<div>
<h1 class="h3 mb-1 fw-bold text-primary">
Role: @Model.Name
</h1>
<p class="text-muted mb-0">
Role details and assigned users. Review the description, status, and membership below.
</p>
</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-2">
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@Model.Id" class="btn btn-primary">Edit</a>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">Back to Roles</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row g-3">
<!-- Role Overview -->
<div class="col-lg-5">
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0 h-100">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title mb-2">Role Overview</h5>
<div class="mb-3">
<div class="fw-semibold text-muted small">Description</div>
<div>@(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(Model.Description) ? "No description provided." : Model.Description)</div>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<div class="fw-semibold text-muted small">Status</div>
@if (Model.IsActive)
{
<span class="badge bg-success">Active</span>
<span class="text-muted ms-2 small">This role can be assigned to users.</span>
}
else
{
<span class="badge bg-secondary">Inactive</span>
<span class="text-muted ms-2 small">This role is currently disabled.</span>
}
</div>
<div class="row g-3">
<div class="col-6">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-3">
<div class="text-muted small">Created</div>
<div class="fw-semibold">@FormatDate(Model.CreatedOn)</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-6">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-3">
<div class="text-muted small">Last Updated</div>
<div class="fw-semibold">@FormatDate(Model.ModifiedOn)</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="mt-3 border rounded-3 p-3 bg-light">
<div class="text-muted small mb-1">Users Assigned</div>
<div class="h5 mb-0">@totalUsers</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Users in Role -->
<div class="col-lg-7">
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0 h-100">
<div class="card-body">
<div class="d-flex align-items-center justify-content-between flex-wrap gap-2 mb-2">
<h5 class="card-title mb-0">Users in this Role</h5>
@if (totalUsers > 0)
{
<div class="text-muted small">Showing @start–@end of @totalUsers users</div>
}
</div>
@if (Model.Users.Items.Any())
{
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table table-sm table-hover align-middle mb-0">
<thead class="table-light">
<tr>
<th style="width: 30%;">Name</th>
<th style="width: 34%;">Email</th>
<th style="width: 20%;">Phone</th>
<th style="width: 16%;">Status</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var u in Model.Users.Items)
{
var fullName = $"{u.FirstName} {u.LastName}".Trim();
<tr>
<td>
@(!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(fullName) ? fullName : "—")
</td>
<td>
<span title="@u.Email">@u.Email</span>
</td>
<td>@(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(u.PhoneNumber) ? "—" : u.PhoneNumber)</td>
<td>
@if (u.IsActive)
{
<span class="badge bg-success">Active</span>
}
else
{
<span class="badge bg-secondary">Inactive</span>
}
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<partial name="~/Views/Shared/_Pager.cshtml"
model="new PagedResult<object> { Items = Array.Empty<object>(), TotalCount = Model.Users.TotalCount, PageNumber = Model.Users.PageNumber, PageSize = Model.Users.PageSize }" />
}
else
{
<div class="border rounded-3 p-4 text-center bg-light mt-2">
<div class="h5 mb-1">No users assigned to this role yet</div>
<div class="text-muted">Add users to <strong>@Model.Name</strong> from your user management page.</div>
</div>
}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Modifying Layout View:
Please modify the Layout View as follows.
@{
ViewData["Title"] = ViewData["Title"] ?? "Dot Net Tutorials";
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - Dot Net Tutorials</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap-icons@1.11.3/font/bootstrap-icons.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="d-flex flex-column min-vh-100">
<!-- Dark Navbar -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark">
<div class="container">
<a class="navbar-brand fw-bold" href="@Url.Action("Index", "Home")">Dot Net Tutorials</a>
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-bs-toggle="collapse" data-bs-target="#navbarContent"
aria-controls="navbarContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarContent">
<ul class="navbar-nav me-auto mb-2 mb-lg-0">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("Index", "Home")">Home</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("About", "Home")">About</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="SecureMethod">Secure</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="NonSecureMethod">Non Secure</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Roles" asp-action="Index">Roles</a>
</li>
</ul>
<ul class="navbar-nav mb-2 mb-lg-0">
@if (User.Identity?.IsAuthenticated == true)
{
<li class="nav-item dropdown">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle" href="#" id="userDropdown" role="button"
data-bs-toggle="dropdown" aria-expanded="false">
<i class="bi bi-person-circle me-1"></i>
Hello, @User.Identity.Name
</a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu dropdown-menu-end" aria-labelledby="userDropdown">
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="@Url.Action("Profile", "Account")">
<i class="bi bi-person-lines-fill me-2"></i> Profile
</a>
</li>
<li><hr class="dropdown-divider" /></li>
<li>
<form method="post" asp-controller="Account" asp-action="Logout" class="px-3 py-1">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-link text-decoration-none w-100 text-start">
<i class="bi bi-box-arrow-right me-2"></i> Logout
</button>
</form>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
}
else
{
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("Login", "Account")">Login</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("Register", "Account")">Register</a></li>
}
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
<!-- Main Content -->
<main class="container flex-grow-1 py-3">
@RenderBody()
</main>
<!-- Footer -->
<footer class="bg-dark text-light py-4 mt-auto">
<div class="container d-flex flex-column flex-md-row justify-content-between align-items-center">
<div>
© @DateTime.Now.Year Dot Net Tutorials. All rights reserved.
</div>
<div>
<a href="@Url.Action("Contact", "Home")" class="text-light me-3 text-decoration-none">Contact</a>
<a href="@Url.Action("Privacy", "Home")" class="text-light me-3 text-decoration-none">Privacy Policy</a>
<a href="@Url.Action("Terms", "Home")" class="text-light text-decoration-none">Terms of Service</a>
</div>
</div>
</footer>
<!-- Scripts -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/js/site.js" asp-append-version="true"></script>
<script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
@await RenderSectionAsync("Scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
Adding Seed Users:
This utility seeds dummy users tied to specific role names (Admin/Manager/User) for demos and testing. It ensures a user exists (creating one with a default password if not) and then ensures they are in the specified role. It also populates profile fields (name, phone, date of birth) so your UI has realistic data. This is especially useful to validate pagination, filters, and membership lists on the details page. Create a class file named IdentityUserSeeder.cs within the Data folder and then copy and paste the following code.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data
{
public static class IdentityUserSeeder
{
// Adjust this to your policy (must satisfy your password rules)
private const string DefaultPassword = "Test@1234";
// Predefined dummy users for each role
private static readonly Dictionary<string, List<(string FirstName, string LastName, string Phone, DateTime DOB)>> RoleUsers =
new()
{
["Admin"] = new List<(string, string, string, DateTime)>
{
("Pranav", "Sharma", "9876543210", new DateTime(1985, 5, 12)),
("Aditi", "Verma", "9123456789", new DateTime(1990, 3, 8)),
("Rohan", "Iyer", "9988776655", new DateTime(1988, 7, 21)),
("Neha", "Chopra", "9012345678", new DateTime(1992, 11, 15)),
("Kunal", "Reddy", "9765432109", new DateTime(1986, 9, 30))
},
["Manager"] = new List<(string, string, string, DateTime)>
{
("Arjun", "Mehta", "9823456780", new DateTime(1984, 4, 17)),
("Sneha", "Kapoor", "9345678901", new DateTime(1991, 6, 9)),
("Vikram", "Patel", "9456789012", new DateTime(1989, 1, 25)),
("Pooja", "Nair", "9567890123", new DateTime(1993, 8, 14)),
("Anil", "Deshmukh", "9678901234", new DateTime(1987, 2, 19))
},
["User"] = new List<(string, string, string, DateTime)>
{
("Rahul", "Singh", "9789012345", new DateTime(1994, 12, 4)),
("Priya", "Menon", "9890123456", new DateTime(1995, 10, 22)),
("Siddharth", "Joshi", "9901234567", new DateTime(1992, 9, 18)),
("Ananya", "Pillai", "9812345678", new DateTime(1996, 5, 5)),
("Manoj", "Bose", "9923456789", new DateTime(1991, 3, 29))
}
};
public static async Task SeedUsersAsync(IServiceProvider services)
{
using var scope = services.CreateScope();
var userManager = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<UserManager<ApplicationUser>>();
foreach (var role in RoleUsers.Keys)
{
foreach (var (firstName, lastName, phone, dob) in RoleUsers[role])
{
var email = $"{firstName.ToLower()}.{lastName.ToLower()}@dotnettutorials.net";
await EnsureUserInRoleAsync(userManager, firstName, lastName, email, phone, dob, role, DefaultPassword);
}
}
}
private static async Task EnsureUserInRoleAsync(
UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager,
string firstName,
string lastName,
string email,
string phone,
DateTime dob,
string role,
string password)
{
var user = await userManager.FindByEmailAsync(email);
if (user == null)
{
user = new ApplicationUser
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
UserName = email,
NormalizedUserName = email.ToUpperInvariant(),
Email = email,
NormalizedEmail = email.ToUpperInvariant(),
EmailConfirmed = true,
FirstName = firstName,
LastName = lastName,
PhoneNumber = phone,
DateOfBirth = dob, // Ensure this property exists in ApplicationUser
IsActive = true,
CreatedOn = DateTime.UtcNow,
ModifiedOn = DateTime.UtcNow
};
var createResult = await userManager.CreateAsync(user, password);
if (!createResult.Succeeded)
{
// Optional: log error
return;
}
}
if (!await userManager.IsInRoleAsync(user, role))
{
await userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, role);
}
}
}
}
Data Seeding API Controller:
This lightweight API controller exposes a POST endpoint you can call from Postman or Swagger to seed dummy users on demand. It delegates to IdentityUserSeeder.SeedUsersAsync returns a simple success message when finished. Using a dedicated endpoint keeps seeding out of your app startup, giving you explicit control over when demo data appears. Create an empty API Controller named DataSeedingController within the Controllers folder and then copy and paste the following code.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DataSeedingController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IServiceProvider _services;
public DataSeedingController(IServiceProvider services)
{
_services = services;
}
[HttpPost("seed-dummy-users")]
public async Task<IActionResult> SeedDummyUsers()
{
await IdentityUserSeeder.SeedUsersAsync(_services);
return Ok("Dummy users have been seeded successfully.");
}
}
}
Seeding Dummy Users:
Invoke the following endpoint to seed the data from Postman using a POST Request.
https://localhost:7091/api/DataSeeding/seed-dummy-users
By invoking this endpoint (e.g., https://localhost:7091/api/DataSeeding/seed-dummy-users), you trigger the seeding process only when you want it. This avoids re-running seeding every time the app starts and keeps production safer. Because the seeder is idempotent, you can call it more than once without creating duplicates, and your role-based demos will immediately have realistic data to showcase.
Adding New Roles:
For an E-Commerce application, you can introduce the following roles to cover common business, operational, and customer service needs beyond Admin, Manager, and User:
- CustomerSupport: Handles customer queries, complaints, and returns. Can view and manage customer tickets, issue refunds (within allowed limits), and escalate issues to higher management.
- InventoryManager: Manages product stock levels, updates inventory details, and coordinates with suppliers. Has access to inventory reports and restocking tools.
- OrderProcessor: Processes and fulfills orders, manages shipping labels, updates order status, and ensures timely dispatch to customers.
- MarketingManager: Create coupons & campaigns, schedule banners, manage cross-sell/upsell rules, set homepage/landing content.
- Vendor: For third-party sellers who manage their own product listings, prices, and stock. Limited access to sales reports and order fulfillment for their products only.
Effective role management is essential for maintaining both security and usability in an application. It not only helps prevent unauthorized access but also simplifies administrative tasks by grouping users according to their roles and responsibilities. ASP.NET Core Identity offers built-in support to create, edit, assign, and manage roles within an MVC application.
With these changes in place, run the application and test the functionalities, and it should work as expected.
In the next article, I will discuss User Management in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain Role Management in ASP.NET Core Identity. I hope you enjoy this Roles Management article, which covers how to add, update, retrieve, and Delete Roles in ASP.NET Core Identity.

🎥 Watch the Complete Video Tutorial on YouTube
Want to see Roles Management in ASP.NET Core Identity explained step-by-step with real-time examples? In this video, I walk you through creating, editing, deleting roles, assigning users, and applying role-based access control in ASP.NET Core MVC — all with best practices.
📺 Click here to watch now: https://youtu.be/FIxFlY6kGRc
If you find the video helpful, don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe to my YouTube channel Dot Net Tutorials for more ASP.NET Core content.