Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
Google External Authentication in ASP.NET Core Identity
In this article, I will discuss Integrating Google External Authentication in ASP.NET Core MVC Applications using ASP.NET Core Identity. Please read our previous article discussing the basics of External Identity Providers in ASP.NET Core.
Integrating Google Authentication in ASP.NET Core Identity
ASP.NET Core Identity allows authentication via both local accounts (username/email & password stored in your DB) and external providers like Google, Facebook, or Microsoft. Integrating Google OAuth makes sign-in easier for users because they don’t need to create a separate account; they can use their existing Google credentials.
This enhances user convenience and reduces password management overhead. This process involves:
- Setting up a project in Google Cloud Console
- Enabling the OAuth consent screen
- Registering redirect URIs
- Installing required packages
- Configuring authentication services
- Handling external login callbacks
- Updating views to include Google Sign-in button
We will implement the following:
We want to allow users to log in using local and external accounts like Google. Here, we will set up the UI (i.e., the User Interface) and configure it to redirect the request to Google when the Sign-In with Google button is clicked. So, we want our login page to look like this:
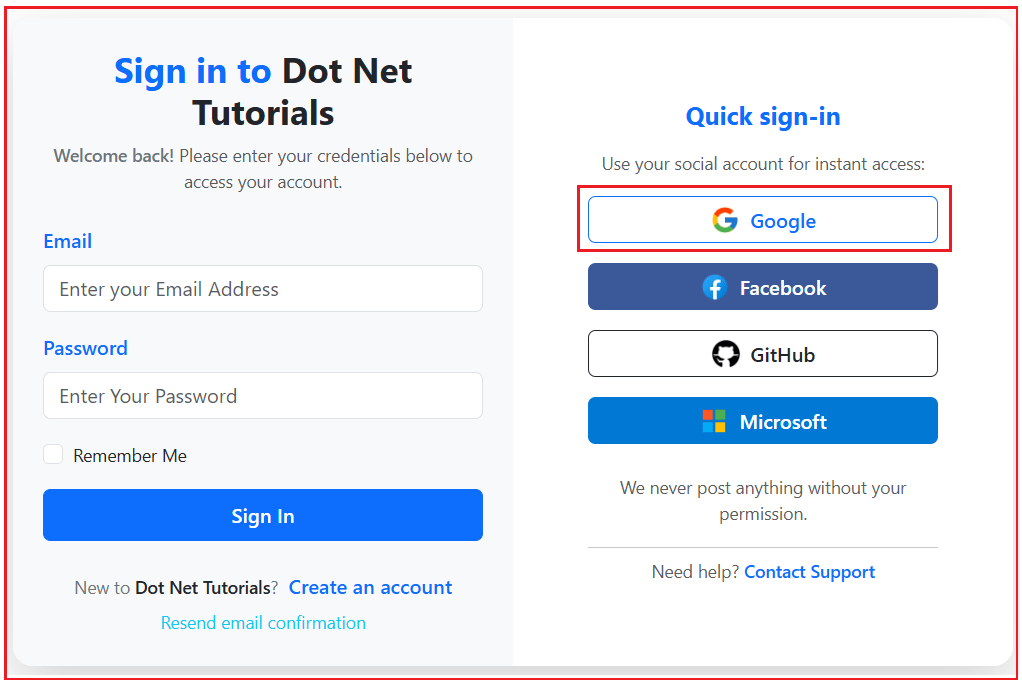
When the user clicks on the Google button, it will open the following page asking the user to log in using his/her Google credentials as follows:
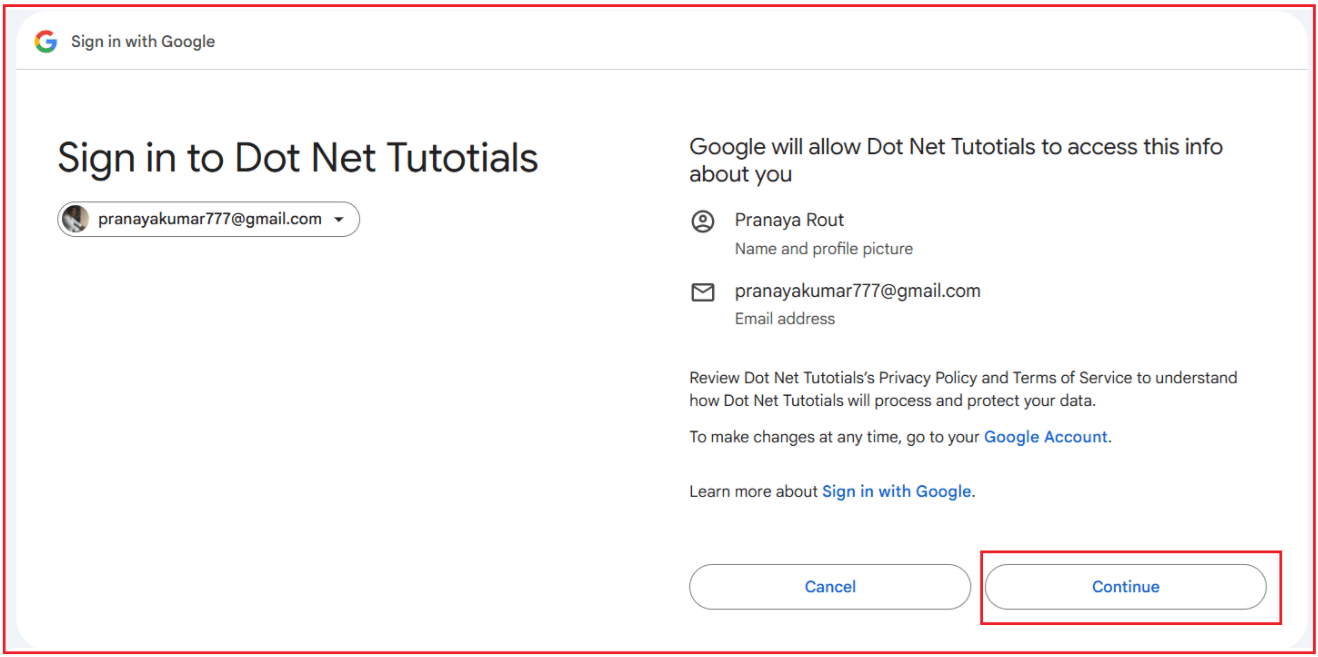
Creating Google OAuth Credentials
Creating Google OAuth credentials is a crucial step for enabling users to authenticate with your application using their Google accounts. This process involves registering your application in the Google Developer Console, configuring the OAuth consent screen, and generating the necessary OAuth 2.0 credentials (Client ID and Client Secret), which are required for your application to authenticate users via Google. The steps are given below:
Create a New Project in Google Cloud Platform
First, visit the URL: https://console.developers.google.com. It will ask you to log in using your Google Credentials, where you need to enter your Gmail ID and password. If you have already logged in, the dashboard will open below.

Now, to create a new project, click on the Select a Project dropdown list from the dashboard, as shown in the image below.

Once you click on the Select a Project dropdown button, it will open the following pop-up. From this pop-up, click on the New Project button as shown in the image below.

Once you click on the NEW PROJECT button, it will open the page below. From this page, we need to give a meaningful name to our project (I am giving the Project name as MyProject1) and then click on the Create button, as shown in the image below.

Once you click on the CREATE button, it will take a few seconds to create the project. Once the project is created, you will get the following Notification message.

What is OAuth Consent?
When an application (like our ASP.NET Core app) asks a user to log in with Google, the app is requesting access to certain information (such as email, name, profile picture, etc.).
Before Google shares that data, it must ask the user for permission. This “permission request” is shown through the OAuth Consent Screen.
Think of it like this:
- Your app says to Google: “I want access to this user’s email and profile information.”
- Google then asks the user: “Do you allow this app to view your email and profile?”
- The user can either Allow or Deny.
Only if the user consents (agrees), Google will issue an OAuth token that your app can use to fetch the requested information.
How to Configure OAuth Consent
To configure OAuth Consent, from the left-hand navigation menu, select “APIs & Services” > “OAuth Consent Screen” as shown in the image below:

Once you click on the above link, it will open the following page:

Now, click on the Get Started button, which will open the following Project configuration page. Let us proceed and do the required configuration:
App Information:
Here, first provide the App name and select the User Support Email, and click on the Next button as shown in the image below:

This section defines the identity of your application. It’s what users will see when Google asks them to grant permissions.
- App name → The display name (e.g., Dot Net Tutorials).
- User support email → An email where users can contact you if they have issues.
Why it matters: This helps users recognize and trust your app before they share their data.
Audience:
Once you click on the Next button, it will open the following Audience section. Here you decide who can use your app:
- Internal → Only available to users within your Google Workspace organization (useful for company-only apps).
- External → Available to any Google account holder (most common for public websites or apps).
Here, you need to select the External radio button and then click on the Next button as shown in the image below.

Why it matters:
- For our ASP.NET Core MVC site (open to all), we must select External.
- If you’re testing, you can add Test Users (specific Gmail accounts).
Contact Information:
Once you click on the Next button, it will open the following Contact Information section. Please provide your Email address and click on the Next button as shown in the image below.

Here, you need to provide official contact details so Google and users can reach you.
- Developer contact email → For Google to contact you if there are compliance/security issues.
Why it matters: Builds trust and accountability with users and ensures compliance with Google’s policies.
Finish
Once you click on the Next button, it will open the following Finish section. Here, you need to accept the Google service and click on the Continue button as shown in the image below:

This is the final review step where you:
- Accept Google’s terms of service.
- Confirm your entered details.
- Save the configuration.
Why it matters: Once saved, your app can now request OAuth credentials and use the configured consent screen when users log in via Google.
And, finally, click on the Create button as shown in the image below:

What are OAuth Credentials?
OAuth Credentials are the digital keys our application uses to prove its identity when communicating with Google’s servers. They are created in the Google Cloud Console and include:
- Client ID → A public identifier for your app (like an app username).
- Client Secret → A private key (like a password) that must be kept secure.
Together, they allow our ASP.NET Core application to:
- Redirect users to Google for authentication.
- Receive a secure token once the user consents.
- Use that token to fetch user profile information (like email, name, etc.).
Generate Google OAuth Credentials:
With the consent screen configured, you can now create the OAuth 2.0 credentials. Go to the “APIs & Services” > “Credentials” page. On the left side, you will see the Credentials menu, and just click on this Credentials menu as shown in the image below:

Once you click on the Credentials menu, it will open the following page. Here, click on the Create Credentials button and then select the OAuth Client ID option as shown in the image below:

It will open the following page. Do the following:
- Select Web application as the Application type
- Provide a meaningful name for the OAuth client. Here, I am providing the name as MyWebClient1. This option will be visible once you select the Application type.

Authorized JavaScript Origins:
In the Authorized JavaScript origins section, please click on the Add URI button. Here, you need to enter your application URL. Currently, my application is running on a local machine, so I am providing my local host URL (https://localhost:7091). In real-time, you need to give the actual domain URL. You can also set multiple application URIs simply by clicking the Add URI button, as shown in the image below.

Authorized Redirect URIs
In the Authorized Redirect URIs section, please click on the Add URI button. This is the path in our application that users are redirected to after Google authenticates them, i.e., the callback URL. The default path in ASP.NET Core is signin-google. So, the complete redirect URI is Application Root https://localhost:7091/signin-google as shown in the image below.

With the above settings in place, finally click on the Create button. Once you click on the Create button, it will create the OAuth Client ID and Secret, and you will get the following message. Here, you can see the Client ID and Client Secret, and if you want, you can download the credentials (in JSON format) or copy the client ID and client secret from this page. We will use these credentials in our ASP.NET Core Application.

Add Test Users:
For testing purposes, we need to add a few Test Email IDs. Go to Google Cloud Console → OAuth consent screen and select the Audience tab. Please make sure your app is in Testing mode. Add your Gmail(s) under Test Users. Example: youremail@gmail.com and click on the Save button.

Once you click on the Save button, you will see the following.

Delete Projects in Google Cloud Console
If you want to delete any existing project, go to the Google Cloud Console, and navigate to the Manage resources page—or directly visit the IAM & Admin > Manage resources section.
There, you’ll see a list of your projects. For each project you wish to delete:
- Select it.
- Click Delete (or Shut down).
- In the confirmation prompt, type the Project ID.
- Confirm the deletion by clicking Shut down.
The project enters a soft deletion phase:
- It becomes unusable immediately.
- After 30 days, it is automatically and permanently deleted.
Integrating Google Authentication in ASP.NET Core:
We need Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Google package for Google authentication in an ASP.NET Core Web Application. So, please execute the following command in the Visual Studio Package Manager Console. Please install the Package that is compatible with your .NET version.
- Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Google
Step 1: Update appsettings.json
We need to add Google credentials in the appsettings.json file. Please add the following to the appsettings.json file. Also, please use the actual values for [Your Google Client ID] and [Your Google Client Secret].
"Authentication": {
"Google": {
"ClientId": "[Your Google Client ID]",
"ClientSecret": "[Your Google Client Secret]"
}
}
Step 2: Configure Google Authentication Services
In the Program class file, we need to configure the authentication services to include Google Authentication. We need to use the Client ID and Client Secret obtained from Google. So, please add the following code to the Program class.
// External Authentication - Google
builder.Services.AddAuthentication()
.AddGoogle(options =>
{
// Load credentials from appsettings.json
options.ClientId = builder.Configuration["Authentication:Google:ClientId"]!;
options.ClientSecret = builder.Configuration["Authentication:Google:ClientSecret"]!;
});
What is the AddGoogle Method?
In ASP.NET Core, the AddGoogle method is used for integrating Google authentication into our web application. This method’s primary purpose is to configure the necessary services and middleware required for authenticating users via their Google accounts.
- When we call AddGoogle, it registers the Google authentication service with ASP.NET Core’s dependency injection system. This registration tells our application how to handle user sign-ins with Google.
- The method requires a Client ID and Client Secret, which we obtain from the Google Developer Console. These credentials are used to establish a trusted connection between our application and Google’s authentication servers.
- You can also configure additional options in the AddGoogle method, such as the redirect URI, which is the path in your application where users will be redirected after successfully authenticating with Google.
Step 3: Extend the IAccountService Interface
Now, we need to add methods for external login. So, please modify the IAccountService as follows:
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services
{
public interface IAccountService
{
//Existing Methods
Task<IdentityResult> RegisterUserAsync(RegisterViewModel model);
Task<IdentityResult> ConfirmEmailAsync(Guid userId, string token);
Task<SignInResult> LoginUserAsync(LoginViewModel model);
Task LogoutUserAsync();
Task SendEmailConfirmationAsync(string email);
Task<ProfileViewModel> GetUserProfileByEmailAsync(string email);
//New Methods for External Login
AuthenticationProperties ConfigureExternalLogin(string provider, string? redirectUrl);
Task<ExternalLoginInfo?> GetExternalLoginInfoAsync();
Task<SignInResult> ExternalLoginSignInAsync(string loginProvider, string providerKey, bool isPersistent);
Task<IdentityResult> CreateExternalUserAsync(ExternalLoginInfo info);
}
}
Understanding External Authentication Methods:
The following four methods have been added:
ConfigureExternalLogin
The ConfigureExternalLogin method prepares the authentication request before redirecting a user to an external provider like Google. It sets up important details such as the provider’s name (e.g., Google) and the callback URL where the provider should send the user back after login. In short, this method creates the proper configuration needed to start the external login flow.
GetExternalLoginInfoAsync
The GetExternalLoginInfoAsync method retrieves the login details returned by the external provider after a user signs in. This information typically includes the provider’s name, a unique identifier for the user, and claims such as email or profile data. It ensures that your application can read and use the information Google (or another provider) sends back.
ExternalLoginSignInAsync
The ExternalLoginSignInAsync method attempts to sign in a user based on the information from the external provider. If the user has already logged in before, the system finds their record in the Identity database and signs them in directly. This allows returning users to log in smoothly without needing to create a new account each time.
CreateExternalUserAsync
The CreateExternalUserAsync method is used when a user is signing in with Google for the first time. It creates a new user record in the Identity database using the claims provided by the external provider, such as email, first name, and last name. After creating and linking this account, the user is signed in automatically, making the first-time login experience seamless.
Step 4: Implement in AccountService.cs
Extend the service class with external login method implementations. So, please add the following code to the AccountService class file. The following code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
public AuthenticationProperties ConfigureExternalLogin(string provider, string? redirectUrl)
{
// The ConfigureExternalAuthenticationProperties method sets up parameters needed for the external provider,
// such as the login provider name (e.g., Google, Facebook) and the redirect URL to be used after login.
return _signInManager.ConfigureExternalAuthenticationProperties(provider, redirectUrl);
}
public async Task<ExternalLoginInfo?> GetExternalLoginInfoAsync()
{
// Retrieve login information about the user from the external login provider (e.g., Google, Facebook).
// This includes details like the provider's name and the user's identifier within that provider.
return await _signInManager.GetExternalLoginInfoAsync();
}
public async Task<SignInResult> ExternalLoginSignInAsync(string loginProvider, string providerKey, bool isPersistent)
{
// Attempt to sign in the user using their external login details.
// If a corresponding record exists in the UserLogins table, the user will be logged in.
return await _signInManager.ExternalLoginSignInAsync(
loginProvider, // The name of the external login provider (e.g., Google, Facebook).
providerKey, // The unique identifier of the user within the external provider.
isPersistent: isPersistent, // Indicates whether the login session should persist across browser restarts.
bypassTwoFactor: true // Bypass two-factor authentication if enabled.
);
}
public async Task<IdentityResult> CreateExternalUserAsync(ExternalLoginInfo info)
{
// Extract email claim (mandatory for identifying the user)
var email = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.Email);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(email))
return IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError { Description = "Email not received from external provider." });
// Check if user with this email already exists
var existingUser = await _userManager.FindByEmailAsync(email);
if (existingUser != null)
{
// If user already exists, link this external login to the existing account
var loginResult = await _userManager.AddLoginAsync(existingUser, info);
if (loginResult.Succeeded)
{
// Update last login time
existingUser.LastLogin = DateTime.UtcNow;
await _userManager.UpdateAsync(existingUser);
// Sign in the existing user
await _signInManager.SignInAsync(existingUser, isPersistent: false);
}
return loginResult;
}
// Extract optional claims
var firstName = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.GivenName) ?? string.Empty;
var lastName = info.Principal.FindFirstValue(ClaimTypes.Surname);
// Create new ApplicationUser instance
var user = new ApplicationUser
{
UserName = email, // Use email as username (unique in system)
Email = email, // Primary email from Google
FirstName = firstName, // From Google claim (or blank if missing)
LastName = lastName, // From Google claim (nullable)
EmailConfirmed = true, // External providers already confirm email
IsActive = true,
CreatedOn = DateTime.UtcNow,
LastLogin = DateTime.UtcNow
};
// Create the user in Identity DB (Users table)
var result = await _userManager.CreateAsync(user);
if (!result.Succeeded)
return result;
// Link external login info (UserLogins table)
result = await _userManager.AddLoginAsync(user, info);
// Sign in immediately if successful
if (result.Succeeded)
await _signInManager.SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
return result;
}
Step 5: Update AccountController.cs
Please add the following action methods for External Authentication in Account Controller.
ExternalLogin (GET)
The ExternalLogin action is the starting point of the external authentication process. When a user clicks “Sign in with Google”, this method is triggered. It first generates a callback URL (ExternalLoginCallback) where the external provider (Google) should redirect the user after login. Then, it uses the ConfigureExternalLogin method from our service to prepare authentication properties and finally returns a ChallengeResult. This ChallengeResult tells ASP.NET Core to redirect the user to Google’s login page to complete authentication.
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult ExternalLogin(string provider, string? returnUrl = null)
{
// Generate the callback URL for to redirect after login
// This URL includes the returnUrl as a route parameter, which will be used to redirect the user
// back to the original page they were trying to access after a successful external login.
var redirectUrl = Url.Action(
action: "ExternalLoginCallback", // The name of the callback action method.
controller: "Account", // The name of the controller containing the callback method.
values: new { ReturnUrl = returnUrl } // Pass the returnUrl as a parameter to the callback method.
);
// Configure authentication parameters for the external login.
var properties = _accountService.ConfigureExternalLogin(provider, redirectUrl);
// Redirect the user to the external provider's login page (e.g., Google or Facebook).
// The "ChallengeResult" triggers the external authentication process, which redirects the user
// to the external provider's login page using the configured properties.
return new ChallengeResult(provider, properties);
}
ExternalLoginCallback (GET)
The ExternalLoginCallback action is executed after the external provider (Google) redirects the user back to your application. It first checks if any errors occurred during the login attempt. Then, it retrieves the user’s information from Google using GetExternalLoginInfoAsync(). If the user has logged in before, ExternalLoginSignInAsync() signs them in directly. If it’s their first login, the method calls CreateExternalUserAsync() to create a new account in the database using the details from Google. Finally, if the login or account creation succeeds, the user is redirected to their original destination (returnUrl). If anything goes wrong, an error message is shown.
[HttpGet]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<IActionResult> ExternalLoginCallback(string? returnUrl = null, string? remoteError = null)
{
// If no returnUrl is provided, default to the application's home page.
returnUrl = returnUrl ?? Url.Content("~/");
// Check if an error occurred during the external authentication process.
if (remoteError != null)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, $"Error from external provider: {remoteError}");
return RedirectToAction("Login");
}
// Retrieve login information about the user from the external login provider.
var info = await _accountService.GetExternalLoginInfoAsync();
// If the login information could not be retrieved, display an error message
if (info == null)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "Error loading external login information.");
return RedirectToAction("Login");
}
// Attempt to sign in the user using their external login details.
var result = await _accountService.ExternalLoginSignInAsync(info.LoginProvider, info.ProviderKey, false);
// If the external login succeeds, redirect the parent window to the returnUrl
if (result.Succeeded)
{
return LocalRedirect(returnUrl);
}
// If the user does not have a corresponding record in the UserLogins table create a new account
var createResult = await _accountService.CreateExternalUserAsync(info);
if (createResult.Succeeded)
return LocalRedirect(returnUrl);
foreach (var error in createResult.Errors)
ModelState.AddModelError("", error.Description);
return View("Error");
}
Step 6: Update Login.cshtml
Please update the Login view as follows.
@model ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.LoginViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Login";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<div class="container mt-3 mb-3">
<div class="row shadow-lg rounded-4 bg-white overflow-hidden mx-auto" style="max-width: 800px;">
<!-- Left: Login Section -->
<div class="col-md-6 py-4 px-4 bg-light d-flex flex-column justify-content-center">
<h3 class="mb-2 text-center fw-bold text-primary">Sign in to <span class="text-dark">Dot Net Tutorials</span></h3>
<p class="text-center text-muted mb-4 small">
<span class="fw-semibold text-secondary">Welcome back!</span>
Please enter your credentials below to access your account.
</p>
<!-- Messages Section -->
@if (ViewBag.Message != null)
{
<div class="alert alert-info alert-dismissible fade show mb-3 small text-center" role="alert">
@ViewBag.Message
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
@if (!ViewData.ModelState.IsValid)
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show small text-center" role="alert">
<strong>Please fix the errors below and try again:</strong>
<ul class="mb-0 mt-2">
@foreach (var error in ViewData.ModelState.Values.SelectMany(v => v.Errors))
{
<li>@error.ErrorMessage</li>
}
</ul>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<form asp-action="Login" method="post" validate>
<input type="hidden" name="ReturnUrl" value="@Model.ReturnURL" />
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Email" class="form-label fw-semibold text-primary"></label>
<input asp-for="Email" class="form-control" placeholder="Enter your Email Address" autocomplete="username" />
<span asp-validation-for="Email" class="text-danger small"></span>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label asp-for="Password" class="form-label fw-semibold text-primary"></label>
<input asp-for="Password" class="form-control" type="password" placeholder="Enter Your Password" autocomplete="current-password" />
<span asp-validation-for="Password" class="text-danger small"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-check mb-3">
<input asp-for="RememberMe" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="RememberMe" class="form-check-label small"></label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary w-100 fw-semibold py-2 mb-2">Sign In</button>
<p class="mt-3 text-center mb-1">
<span class="text-secondary small">New to <span class="fw-semibold text-dark">Dot Net Tutorials</span>?</span>
<a asp-action="Register" class="text-primary ms-1 text-decoration-none fw-semibold">Create an account</a>
</p>
<p class="text-center mb-0">
<a asp-action="ResendEmailConfirmation" class="text-info text-decoration-none small">Resend email confirmation</a>
</p>
</form>
</div>
<!-- Right: External Authentication -->
<div class="col-md-6 py-4 px-4 d-flex flex-column justify-content-center align-items-center bg-white">
<div class="w-100" style="max-width: 280px;">
<h5 class="mb-3 fw-bold text-primary text-center">Quick sign-in</h5>
<div class="mb-3 text-center text-muted small">Use your social account for instant access:</div>
<div class="d-grid gap-3 mb-3">
<a asp-controller="Account" asp-action="ExternalLogin" asp-route-provider="Google" asp-route-returnUrl="@Model.ReturnURL"
class="btn btn-outline-primary d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/color/32/000000/google-logo.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="Google" />
Google
</a>
<a href="#" class="btn d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold" style="background-color: #3b5998; color: #fff;">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/fluency/32/000000/facebook-new.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="Facebook" />
Facebook
</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-outline-dark d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/ios-filled/32/000000/github.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="GitHub" />
GitHub
</a>
<a href="#" class="btn d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fw-semibold" style="background-color: #0078d4; color: #fff;">
<img src="https://img.icons8.com/color/32/000000/microsoft.png" class="me-2" style="width:24px" alt="Microsoft" />
Microsoft
</a>
</div>
<div class="text-center text-muted small mt-4 mb-2">
<span>We never post anything without your permission.</span>
</div>
<hr class="mb-2" />
<div class="text-center text-muted small">
Need help? <a href="mailto:support@dotnettutorials.net" class="text-decoration-none fw-semibold">Contact Support</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
Now, run the application and check the functionality, and it should work as expected. Now, if you verify the UserLogins table, you will see the following.

Integrating Google Authentication into an ASP.NET Core MVC application not only simplifies the login process for users but also enhances the overall security and trustworthiness of our system. By using Google’s OAuth 2.0, we allow users to sign in quickly with their existing accounts, reducing the need for new account creation. At the same time, ASP.NET Core Identity manages both external and local accounts, ensuring flexibility and scalability.
In the next article, I will discuss how to integrate Facebook External Authentication in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain how to integrate Google External Authentication in ASP.NET Core MVC using Identity. I hope you enjoy this article, Integrating Google Authentication in ASP.NET Core.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group

Watch the Full Video Tutorial
Want to see this implementation in action? Check out our step-by-step video guide on integrating Google Authentication in ASP.NET Core Identity. It covers everything from setting up Google OAuth credentials to configuring your ASP.NET Core MVC application for secure external login.
👉 Watch on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vVwugea58WM
This video is perfect for developers who prefer visual learning or want to follow along with real-time coding. Don’t miss it!