Back to: AWS Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
AWS Cloud History
In this article, I am going to discuss AWS Cloud History. Please read our previous article where we discussed Types of Cloud Computing.
AWS Cloud History
It was launched in 2002 internally at amazon.com. Because they realized that the IT departments could be externalized. Their Amazon infrastructure was one of their core strengths and they said, “You know what “maybe we can do IT for someone else, “for other people.” they launched their first offering publicly which was SQS in 2004. In 2006, they expanded their offering and re-launched with the availability of SQS, S3, and EC2. Then they expanded and said, “You know what? “We don’t have to be just in America. “We could be in Europe.” And then fast forward to today, we have so many applications that used to run or are still running on AWS, such as Dropbox, Netflix, Air BNB, or even NASA.

AWS Cloud Number Facts:
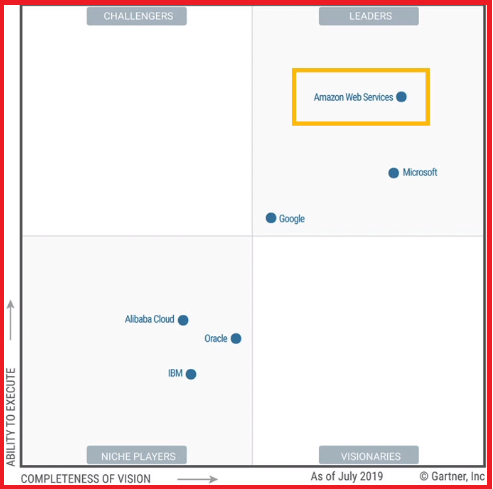
If we look at the Gartner magic quadrants, which sort of rank the cloud providers, as we can see AWS is on the top right corner, which is a leader. It’s able to execute really well. And it has really great completeness of vision. It is followed closely by Microsoft and Google. But still, in 2019, AWS had $35 billion in annual revenue, which is huge and accounted for 47% of the market 2019. With Microsoft being second with 22% by learning AWS you are learning a tool that is widely used. It is a pioneer and leader of the AWS Cloud Markets for the ninth consecutive year. And it has over 1 million active users.
AWS Cloud Uses Cases:
AWS will enable you to build sophisticated and scalable applications that are applicable to diverse sets of industries. Every company has a use case for the cloud. So, Netflix, McDonald’s, 21st Century Fox, and Activision, they’re all using the cloud. And use cases can include just transferring your enterprise IT or using the cloud as a backup and storage, or doing some big data analytics. You can also host a website or create a backend for your mobile and your social applications. Or you could have your entire gaming servers running on the clouds. The applications are endless.

AWS Global Infrastructure:
AWS is global. And this is where we are going to learn a bit more specifics about how it works. We have an AWS region, we have availability zones, data centers, edge locations, and points of presence. And all of these can be represented on the map right here. https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/regions_az/

Let us go on this website to have a quick look at it. This is a cool map, because on this website how AWS is global. If I click on it, I can, you know, scroll through the world, and see what is happening. AWS has multiple regions and they are in orange and they are all around the world. For example, Paris, Spain, Ohio, Sao Paulo, Cape Town, Mumbai, and everywhere else. AWS truly is a global service. On top of it, each region is going to be connected through the network. These are the network reconnecting the regions and this is a private network of AWS. And then within each region, for example, the Cape Town region, we can see that we have blue dots. And each Blue Dot will be availability zones that we will be described in the next image. What I want to get you out of this, is that AWS is truly global. And we can leverage the infrastructure of a cloud provider to make ourselves, and our application global.

AWS Regions:
The first important concept in AWS is regions. Regions are all around the world and we saw it on the map before the regions have a name, it could be us-east-1, EU-west-3, and we can see the mapping of the name of the region to their code on the console that we will see in a minute. Now a region, what is it? It is going to be a cluster of data centers. Any different data centers. Look at it (indistinct) for example, Ohio or Singapore or Sydney, or Tokyo. When we use AWS services, most services are going to be linked and scoped to a specific region. That means that if we use a service in one region and we try to use it in another region, it will be like a new time of using the service.

How to Choose an AWS Region?
A Question that may come up in the exam is how do you choose an AWS region?
You are launching a new application. Where should you do it? Should you do it in America, in Europe in South America, or in Australia? Well, the answer is, of course, it depends. Some factors that may impact your choice of an AWS region. The first one is compliance. Sometimes governments want the data to be local to the country you are deploying the application. For example, France, data in France may have to stay in France and therefore you should launch your application in the French region. Then, there is also a concept of latency. If most of your users are going to be in America, it makes a lot of sense to deploy your application in America, close to your users, because they will have a reduced latency. If you deploy your application in Australia and your users are in America, they will have a lot of lags in using your application. Also, not all regions have all services. Some regions do not have services. And so obviously if you are leveraging a service with your application, you need to make sure that the region you are deploying into is available and does have that service. And finally, pricing does vary from region to region and you need to consult the applicant, the services, and pricing, (indistinct) to see what the differences are between the regions. But this could be obviously a factor that could impact your deployment of an application into a specific region. Now, availability zones are what actually is going into the region.

AWS Availability Zones:
Each region will have many availability zones. Usually three, the minimum is two, and the max is six. But really the usual is three. Let us take the Sydney region as an example. The senior region code is ap-southeast-2. We can have two have three availability zones in Sydney, ap-southeast-2a, ap-southeast-2b, and ap-southeast-2c. Each of these availability zones is going to be one or more, just create data centers that will have redundant power, networking, and connectivity. That means that in southeast-2a, I can have two data centers may be, as well as two in 2b and two in 2c. But it could be one, it could be three, it could be four. We do not really know. AWS does not tell us that. What we know is that these availability zones are separate from each other that they will be isolated from disasters. If something happens to ap-southeast-2a, we know that it is designed not to cascade into ap-southeast-2b or ap-southeast-2c. They are really isolated from disasters. And then these data centers, these availability zones, are connected with high bandwidth, ultra-low latency networking and therefore altogether being linked together, it will form a region.

AWS Points of Presence (Edge Locations):
Next, the only thing we need to know about AWS for the global infrastructure is the points of presence or edge locations. You should know that AWS has more than 200 points of presence in 84 cities across 42 countries. And this will be very helpful when we deliver content to the end users with the lowest latency possible. And this is what you see on this map.

How about we just play around and do a tour of the console?
We will see that AWS has global services such as IAM, Route 53, Cloud Front, and WAF, most AWS services are going to be regions scoped, such as Amazon EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, and REKOGNITION.

Finally, to know if a service is available in your region, there is a region table you should check out right here.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Console and Services in AWS. Here, in this article, I try to explain AWS Cloud History and I hope you enjoy this AWS Cloud History article.
