Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
ASP.NET Core Identity Tables
In this article, I will discuss the ASP.NET Core Identity Tables in detail and try to understand the need and use of each column. Please read our previous article discussing ASP.NET Core Identity Setup step by step.
ASP.NET Core Identity Tables
ASP.NET Core Identity is a system that manages authentication (who you are) and authorization (what you can do) in your app. To do this, it uses several database tables to store info about users, their roles, external logins, claims, tokens, and more. Each table plays a specific role, and together they form a complete identity system. The following are the default database tables generated by ASP.NET Core Identity:
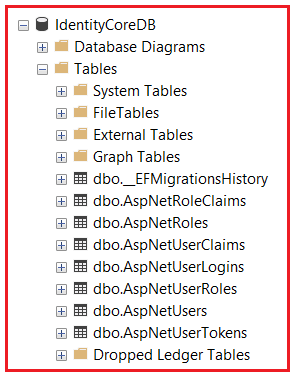
Let us proceed and understand the tables one by one:
AspNetUsers Table:
The AspNetUsers table stores all the essential information about the users of your application. It holds their unique identities, login details, security settings, and contact information. This table acts as the primary source for user-related data in the Identity system. The following are the default columns available in this table:
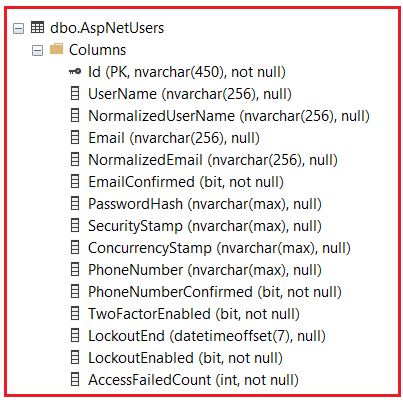
The columns in the AspNetUsers table generally include the following:
- Id: Unique identifier for each user (primary key).
- UserName: The user’s login name.
- NormalizedUserName: Uppercase version of UserName for case-insensitive searches.
- Email: The user’s email address.
- NormalizedEmail: Uppercase version of Email for case-insensitive lookups.
- EmailConfirmed: Indicates if the user’s email is verified.
- PasswordHash: Hashed form of the user’s password (never stored in plain text).
- SecurityStamp: A random value indicates whether any security-related user information has changed. For example, it changes when a user changes their password, resets the password, or adds an external login. Its primary purpose is to invalidate any existing sessions or cookies when security-related information changes. This is a security measure to ensure that the old sessions are no longer valid if credentials are compromised and then changed.
- ConcurrencyStamp: A unique value that changes whenever a user profile is updated, used for optimistic concurrency control, ensuring data integrity. In scenarios where multiple attempts to modify the same user record are made simultaneously, ConcurrencyStamp ensures that changes do not conflict.
- PhoneNumber: User’s phone number.
- PhoneNumberConfirmed: Indicates if the phone number is verified.
- TwoFactorEnabled: Shows if two-factor authentication is active.
- LockoutEnd: Date/time when account lockout ends after failed login attempts.
- LockoutEnabled: Indicates if the lockout feature is enabled for the user.
- AccessFailedCount: Counts failed login attempts to trigger lockout if necessary.
Relationships: The AspNetUsers table is related to most of the other Identity tables. Each user can have multiple roles (via AspNetUserRoles), multiple claims (AspNetUserClaims), multiple external logins (AspNetUserLogins), and multiple tokens (AspNetUserTokens). These relationships use the Id column as a foreign key in the related tables.
AspNetRoles Table:
The AspNetRoles table holds all the defined roles for the application. Roles represent different groups or levels of permissions (e.g., Admin, Moderator, User) that can be assigned to users. The following are the columns available in this table:

The columns in the AspNetRoles table generally include the following:
- Id: Unique identifier for each role (usually a GUID).
- Name: Human-readable name of the role (e.g., “Admin”).
- NormalizedName: Uppercase version of the role name for case-insensitive matching.
- ConcurrencyStamp: Value that changes on updates, used for concurrency control.
Relationships: The AspNetRoles table relates to users through the AspNetUserRoles table (assigning roles to users) and to claims through the AspNetRoleClaims table (assigning claims/permissions to roles).
AspNetUserRoles Table:
The AspNetUserRoles table represents the many-to-many relationship between users and roles. It links users to their respective roles, enabling role-based authorization. The following are the columns available in this table:

The columns in the AspNetUserRoles table generally include the following:
- UserId: The user ID from the AspNetUsers table. Part of the composite primary key. It corresponds to the Id column in the AspNetUsers table. It acts as a foreign key linking to the AspNetUsers table.
- RoleId: The role ID from the AspNetRoles table. Part of the composite primary key. It corresponds to the Id column in the AspNetRoles table. It acts as a foreign key linking to the AspNetRoles table.
Relationships: This table connects AspNetUsers and AspNetRoles, making it possible to look up all roles for a given user or all users for a given role.
AspNetUserLogins Table:
The AspNetUserLogins table stores information about external authentication providers that users use to log in, such as Google or Facebook. It links these external logins to local user accounts. The following are the columns available in this table:

The columns in the AspNetUserLogins table generally include the following:
- LoginProvider: This column stores the name of the external authentication provider (e.g., Google, Facebook, Microsoft, etc.). It is part of the composite primary key for the table.
- ProviderKey: This column stores the unique identifier provided by the external login provider for the user. For example, when a user logs in using Google, this field will store the unique ID assigned to the user by Google. It is also part of the composite primary key.
- ProviderDisplayName: This optional column can store the display name of the login provider (e.g., “Google” instead of “google.com”). It is mainly used for display purposes in the UI.
- UserId: The local user ID that is linked to this login. It acts as a foreign key linking to the Id column in the AspNetUsers table.
Relationships: Each entry in this table connects a user (UserId) to an external authentication provider, allowing users to log in using social logins.
AspNetUserTokens Table:
The AspNetUserTokens table stores tokens for users that can be used for various purposes, like password reset, email confirmation, or two-factor authentication. The following are the columns available in this table:

The columns in the AspNetUserTokens table generally include the following:
- UserId: The User ID from the AspNetUsers table.
- LoginProvider: Name of the provider that generated the token.
- Name: This column stores the name of the token, such as an email confirmation token, password reset token, or two-factor authentication token. It could be something like PasswordReset, EmailConfirmation, AccessToken, etc.
- Value: The value of the token.
Relationships: Each token entry is tied to a user and is typically used for security operations or workflow steps that require a one-time token.
AspNetUserClaims Table:
The AspNetUserClaims table stores additional claims tied to individual users. Claims are key-value pairs that hold extra information about the user, often used in authorization. Each claim is a key-value pair associated with a user and can represent various attributes such as email address, full name, role, or any other custom data relevant to the application. The following are the columns available in this table:

The columns in the AspNetUserClaims table generally include the following:
- Id: The primary key for the user claim. It is an integer.
- UserId: The ID of the user associated with this claim. It acts as a foreign key linking to the Id column in the AspNetUsers table.
- ClaimType: The type of the claim (e.g., “birthdate”).
- ClaimValue: The value of the claim (e.g., “1980-01-01”).
Relationships: Each claim entry links to a user and defines additional properties or access rights unique to that user.
AspNetRoleClaims Table:
The AspNetRoleClaims table stores claims associated with roles. These claims apply to all users who are assigned that role, enabling permission-based claims at the role level. The following are the columns available in this table:

The columns in the AspNetRoleClaims table generally include the following:
- Id: Unique integer identifier for the role claim.
- RoleId: The role ID associated with this claim. A foreign key that links to the Id column in the AspNetRoles table.
- ClaimType: This column stores the type of the claim, such as Permission, AccessLevel, or any other type that makes sense in the context of your application.
- ClaimValue: The actual value of the claim. For example, if the claim type is Permission, the claim value might be Edit_User or View_Reports, etc.
Relationships: Each claim entry is associated with a specific role. All users in that role will inherit the claims defined here.
Note: The structure of the tables is consistent across different database providers (e.g., SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL), but there might be minor differences in types or constraints based on the database system used.
In the next article, I will discuss UserManager, SignInManager, and RoleManager Classes in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain ASP.NET Core Identity Tables in Detail. I hope you enjoy this ASP.NET Core Identity Tables article.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group

Thanks😍😍
Want to master ASP.NET Core Identity?
Check out our latest video: ASP.NET Core Identity Introduction, Setup, and Customization
Learn step-by-step how to set up and customize ASP.NET Core Identity for secure login, role management, and more.
Watch now 👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WGd9nyoQMjg
Boost your .NET skills with practical, easy-to-follow tutorials from Dot Net Tutorials! Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe for more .NET tutorials and videos!