Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
ASP.NET Core Remote Validation
In this article, I will discuss ASP.NET Core Remote Validation. Please read our previous article discussing how to redirect to ReturnUrl After Login in ASP.NET Core. Remote Validation in ASP.NET Core allows your web application to check input data on the server without requiring a full page reload. This means users get immediate feedback when, for example, entering an email or username that’s already taken. It improves user experience by making validations faster and more dynamic, especially for checks that need access to server data like a database.
What is Remote Validation in ASP.NET Core?
Remote Validation is a powerful feature in ASP.NET Core that enables client-side validation to communicate asynchronously with the server without a full page reload. Unlike typical client-side validation (which checks data using JavaScript on the browser) or server-side validation (which checks data after a form is submitted), Remote Validation sends an AJAX request to a server endpoint to validate input data on the fly.
This is especially useful for validations that require access to server data or complex business logic, which cannot be validated purely on the client side. A common example is validating whether a username or email is already registered in the database.
Why Use Remote Validation?
- To improve user experience by providing immediate feedback without submitting the entire form.
- To reduce unnecessary full-page postbacks, making the app more responsive and faster.
- To validate data that depends on server-side information, such as database lookups or external service calls.
Example Scenario: Validating if an Email Is Already Taken
Usually, when registering a user, the email uniqueness can only be verified on the server. Without remote validation, this check occurs after the user submits the registration form, causing a full-page reload if the email is taken.
Let us understand the Remote Validation in an ASP.NET Core MVC Application with an example. Now, when we register a new user with an existing email, we will get the following error message only when we submit the Register button:
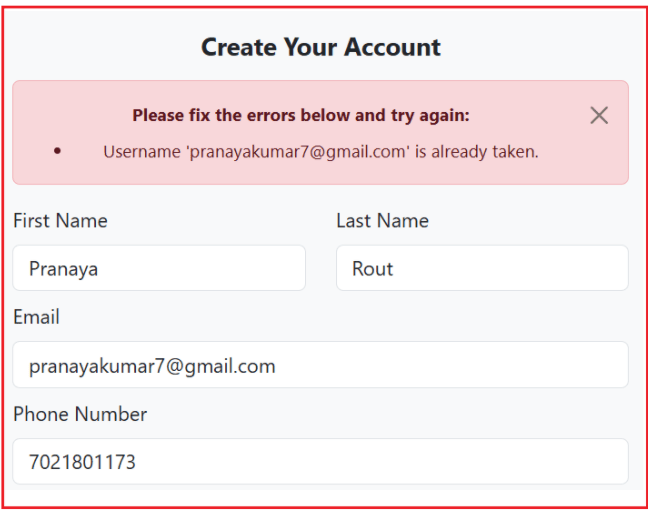
With Remote Validation, the email field can be checked in real-time against the database via an asynchronous call, preventing the user from submitting the form until a unique email is provided.
How to Implement Remote Validation in ASP.NET Core
Let us proceed and understand how to implement the Remote Validation step by step in an ASP.NET Core MVC Application.
Step 1: Create a Validation Action in a Controller
We need an action method that the client-side script will call to verify the input asynchronously. This action method should return a JSON result indicating whether the validation is successful or not. Create an Empty MVC Controller named RemoteValidationController within the Controllers folder, and then copy and paste the following code.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Controllers
{
public class RemoteValidationController : Controller
{
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager;
public RemoteValidationController(UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager)
{
_userManager = userManager;
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> IsEmailAvailable(string Email)
{
//Check If the Email Id is Already in the Database
var user = await _userManager.FindByEmailAsync(Email);
if (user == null)
{
return Json(true);
}
else
{
return Json($"Email {Email} is already in use.");
}
}
}
}
Code Explanations:
- The method supports both GET and POST (usually GET is enough for validation).
- The parameter name (Email) must match the property name in your view model for the model binder to work correctly.
- Returning Json(true) means validation passed.
- Returning a string means validation failed, and the string is the error message displayed.
Step 2: Apply the [Remote] Attribute on the Model Property:
Next, we need to apply the Remote attribute to the property we want to validate. To validate the Email property with Remote Validation, please modify the RegisterViewModel as follows. As you can see, we have applied the Remote Data Annotation Attribute with the Email Property and specified the controller and action name.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
{
public class RegisterViewModel
{
[Required]
[Display(Name = "First Name")]
[StringLength(50, ErrorMessage = "First Name cannot be longer than 50 characters.")]
public string FirstName { get; set; } = null!;
[Display(Name = "Last Name")]
[StringLength(50, ErrorMessage = "Last Name cannot be longer than 50 characters.")]
public string? LastName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage ="Email Id is Required")]
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Invalid Email Address")]
[Remote(action: "IsEmailAvailable", controller: "RemoteValidation")]
public string Email { get; set; } = null!;
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
[Display(Name = "Date of Birth")]
public DateTime? DateOfBirth { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "PhoneNumber is Required")]
[Phone(ErrorMessage = "Please enter a valid Phone number")]
[Display(Name = "Phone Number")]
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; } = default!;
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[StringLength(100, MinimumLength = 8, ErrorMessage = "Password must be at least 8 characters.")]
public string Password { get; set; } = null!;
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "Password and confirmation password do not match.")]
[Display(Name = "Confirm Password")]
public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; } = null!;
}
}
Code Explanation:
- The Remote attribute specifies which controller action should be called for validation (IsEmailAvailable in RemoteValidationController).
- This triggers an AJAX call whenever the Email field loses focus or changes, validating the email in real-time.
Step 3: Include Required Client-Side Validation Scripts
Make sure your view includes the necessary JavaScript files for unobtrusive validation (usually _ValidationScriptsPartial):
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
This enables ASP.NET Core’s built-in client-side validation infrastructure, which supports remote validation out of the box.
ASP.NET Core Remote Validation Testing
With the above changes in place, run the application, click the Register link, and give an existing email ID. You will immediately see the error message, as shown in the image below:
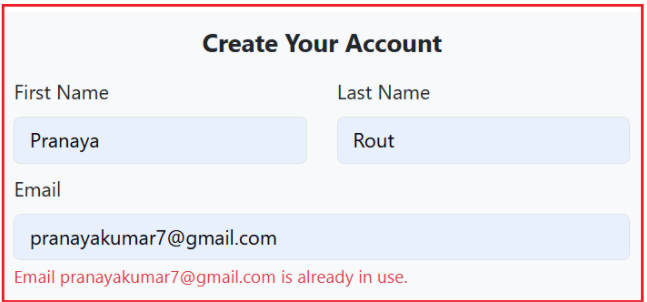
What Happens When You Use Remote Validation?
With Remote Validation in place:
- The user fills out the registration form.
- As soon as they leave the email field (or after a slight delay), the browser automatically sends an AJAX request to the IsEmailAvailable action.
- The server checks the database for existing users with that email.
- If the email is already taken, an error message appears next to the field immediately—no need to wait for full form submission.
- If the email is available, the user can continue filling out the rest of the form and submit it as normal.
Remote Validation in ASP.NET Core combines the best of client-side and server-side validation by making asynchronous calls to server methods during user input. It enhances user experience by providing instant feedback for validations that require server data, such as checking if an email is already in use, without waiting for form submission or page reload.
In the next article, I will discuss Roles Management in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain Remote Validation in an ASP.NET Core MVC Application. I hope you enjoy this Remote Validation in ASP.NET Core article.

nice blog
Prefer watching instead of reading?
I’ve recorded a step-by-step video covering Custom Password Policy, Remote Validation, and safe Redirect to ReturnUrl in ASP.NET Core MVC—with live demo. Watch here: https://youtu.be/EmOoDqa5R7M
If it helps, please like the video and subscribe to Dot Net Tutorials for more ASP.NET Core content.