ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
In this ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals course, I covered all the features of ASP.NET Core Identity. As you progress in this course, you will learn from the basic to advanced level features of ASP.NET Core Identity. Many new developers and students, as well as experienced software professionals, struggle to learn ASP.NET Core Identity quickly. To overcome this problem, I have prepared this course so you can understand it easily, quickly, and in depth.
What is ASP.NET Core Identity?
ASP.NET Core Identity is a robust and flexible authentication and authorization system built into ASP.NET Core applications. It provides everything needed to securely manage user accounts, roles, passwords, and permissions without having to write custom logic from scratch. By using ASP.NET Core Identity, developers can easily add essential features like registration, login, password recovery, and social login to their web applications, while ensuring best practices for security.
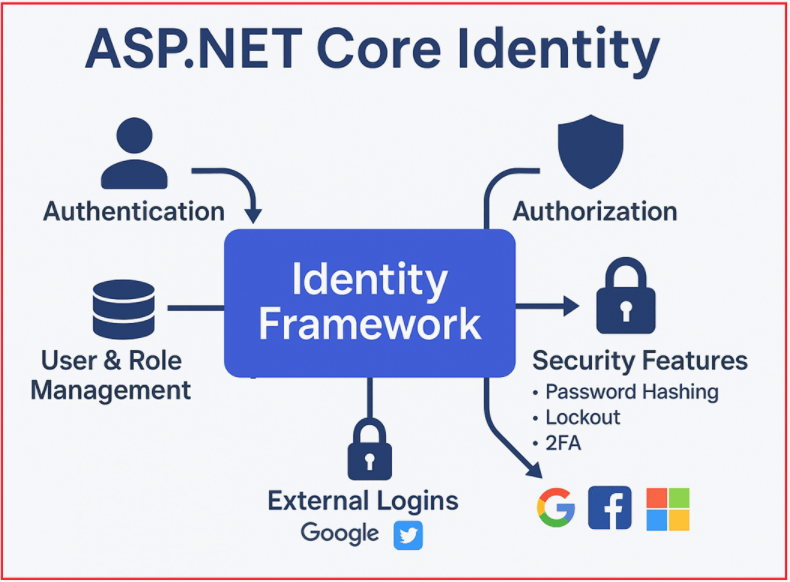
Think of it as a ready-made, highly customizable system that handles everything related to users: signing up, logging in, storing passwords securely, managing roles, enforcing security policies (like account lockout), verifying emails/phones, and supporting advanced features like two-factor authentication and role-based or claims-based authorization.
Additionally, ASP.NET Core Identity supports integration with external login providers such as Google, Facebook, Microsoft, or Twitter, allowing users to log in using those accounts.
In other words, instead of coding your own user table, login logic, password reset mechanism, and role checks from scratch (which is error-prone and risky), you get a complete, tested solution out of the box. You can use it as-is, or you can customize and extend it for more advanced scenarios.
Key Features of ASP.NET Core Identity
The following are some of the Key Features of ASP.NET Core Identity:

User Management:
- You can easily create, update, delete, and retrieve users. Every user’s basic data (like username, email, phone) is managed through a central user entity.
- Developers can extend this entity with custom fields, such as date of birth, address, and other relevant details.
Role Management:
- Roles are a way to group users based on their permissions or responsibilities (e.g., Admin, Manager, Moderator, Customer, etc.).
- With ASP.NET Core Identity, you can create and manage these roles, assign users to one or more roles, and then restrict or allow access to parts of your app based on the roles users belong to.
Password Management:
- Passwords are handled securely by hashing (converting the password into an irreversible encoded format).
- Identity enforces password policies, including minimum length and the requirement for digits/special characters.
- It also provides mechanisms for users to change or reset their passwords. It also supports password recovery via email links.
User Authentication and Authorization:
- This is the process of verifying who a user is when they try to log in. ASP.NET Core Identity manages this step to make sure that the user is legitimate.
- Once the user is authenticated, the system determines their permissions based on their assigned roles or claims (claims are detailed pieces of information about the user).
Role-Based Authentication:
- This means controlling access by assigning users to roles and then allowing or denying access to resources or features based on those roles.
Claims-Based Authentication:
- Beyond roles, claims provide more granular control. For example, a claim might indicate a user’s department, age, or subscription level, which can be used to control access to certain features.
Account Security:
Built-in features help protect accounts:
- Account Lockout: Temporarily disables an account after too many failed login attempts.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra security layer by requiring users to verify their identity with something they have (like a mobile app code or SMS) in addition to something they know (password).
- Email/Phone Verification: Users can be required to verify their email or phone before they can fully use their account.
External Login Providers:
- You can allow users to log in using their existing accounts from services like Google or Facebook, making the login process easier and more familiar to them.
Customizability:
- You can extend the built-in user and role classes to add your own fields, such as first name, last name, profile picture URL, or any other information your application needs.
ASP.NET Core Identity Key Components:
The following are the key components of ASP.NET Core Identity:

Core Identity Services:
The following three classes or services are responsible for managing different operations on the Identity database for users, allowing us to perform operations such as creating users, assigning roles, and managing sign-ins. That means, the following classes provide many methods that we can use to perform different operations on the Identity database.
UserManager Service:
UserManager is the core service responsible for managing user accounts within an ASP.NET Core Identity system. It acts as the central point for all user-related operations, such as creating new users, updating user information, deleting users, and managing their passwords. It abstracts away the complexity of handling user data securely by:
- Ensuring usernames and emails are unique.
- Enforcing password strength and validation policies.
- Hashing passwords before storing them ensures that plain-text passwords are never saved.
- Managing recovery options like password reset tokens and email confirmation tokens.
- Handling account security features, such as locking accounts after repeated failed login attempts.
In short, UserManager encapsulates all logic and best practices around user lifecycle management, security, and data integrity.
RoleManager Service
RoleManager is the service dedicated to managing roles within the identity system. Roles are a way to group users and assign permissions collectively. RoleManager is responsible for:
- Creating new roles (like “Admin,” “User,” or “Manager”).
- Updating or deleting roles as needed.
- Retrieving roles for administrative or authorization purposes.
Through roles, applications can implement role-based access control, meaning users’ access to different parts of the application or functionalities is controlled based on the roles assigned to them. RoleManager simplifies managing these roles and their lifecycle.
SignInManager Service
SignInManager focuses on the authentication aspect, specifically, how users log in and log out of the application. Its responsibilities include:
- Verifying user credentials (such as username and password) during the sign-in process.
- Managing the authentication session or cookie that keeps users signed in.
- Implementing additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), enhances protection.
- Supporting login via external providers like Google, Facebook, or Microsoft accounts.
- Managing the sign-out process to terminate user sessions securely.
SignInManager manages the entire sign-in workflow and ensures that only valid, authenticated users gain access to the system.
Identity Data Model in ASP.NET Core Identity:
Understanding these entities is key to seeing how ASP.NET Core Identity organizes and secures user and role data under the hood. The following are the entity models used in ASP.NET Core Identity. Together, the following models represent the relational structure that supports a flexible, secure, and extensible user authentication and authorization system in ASP.NET Core Identity.
IdentityUser Model
IdentityUser is the fundamental data model that represents a user in the ASP.NET Core Identity system. It stores all the core information about a user, such as:
- Username
- Email address
- Phone number
- Password hash (the encrypted password)
- Account lockout details (to prevent brute-force attacks)
- Other security and profile-related data
This model serves as the base class for users and can be extended with additional properties (like FirstName, LastName, DateOfBirth, LastLogin, etc.) to suit specific application needs. Essentially, every person who registers or is recognized in your application corresponds to one IdentityUser record.
IdentityRole Model
The IdentityRole represents a role within the application. Roles are logical groupings or categories of users, such as “Admin,” “Moderator,” “Customer,” or “Manager”. This model stores basic information about the role, including:
- Role name
- Role identifier (ID)
- Optionally, you can extend it to add descriptions or metadata about the role.
Roles help enforce role-based access control (RBAC) by grouping permissions and then assigning those roles to users.
IdentityUserRole Model
The IdentityUserRole represents the many-to-many relationship between users and roles. Since a user can have multiple roles and a role can be assigned to multiple users, this model acts as the linking table that associates users with their roles. It stores:
- User ID
- Role ID
This relationship allows ASP.NET Core Identity to determine which roles a particular user belongs to quickly.
IdentityUserLogin Model
The IdentityUserLogin stores information about external login providers linked to a user account. When users log in using third-party services like Google, Facebook, or Microsoft, this model keeps track of:
- The external login provider name (e.g., “Google”, “Facebook”, etc.)
- The unique provider key or user ID from the external provider
- The user in your system that this external login belongs to
This enables external authentication and linking multiple external logins to a single local user account.
IdentityUserClaim Model
The IdentityUserClaim represents a claim associated with a specific user. A claim is a piece of information about the user, such as their age, email address, membership level, or permission. Claims allow for more fine-grained control than just roles. This model stores:
- The claim type (e.g., “Department”, “Age”, “SubscriptionLevel”)
- The claim value (e.g., “HR”, “30”, “Gold”)
- The user to whom the claim belongs
Claims are useful for claims-based authorization, where access decisions depend on these user attributes.
IdentityRoleClaim Model
The IdentityRoleClaim represents claims that are assigned to a role rather than an individual user. Instead of assigning claims to users one by one, you can assign them to roles. Then, all users in that role inherit the claims. This is useful when you want role-based claims, where permissions or attributes are granted to an entire role group. It stores:
- The role ID
- The claim type and claim value associated with that role
IdentityUserToken Model
The IdentityUserToken stores tokens related to a user that are used for security purposes. Tokens can be things like:
- Password reset tokens
- Authentication tokens for two-factor authentication
- Refresh tokens for persistent logins
These tokens are stored securely and linked to the user to help manage authentication flows and security operations that require temporary or revocable tokens.
IdentityDbContext
IdentityDbContext is a special Entity Framework Core database context class designed to handle all identity-related data in an ASP.NET Core application. Think of it as the central manager that connects your user and role information with your database.
It defines the necessary tables, relationships, and database structure for the Identity system. Using IdentityDbContext, you can easily interact with identity data, like users, roles, claims, and tokens, through Entity Framework Core.
Imagine your application as a hotel, and IdentityDbContext is the front desk manager. Whenever you need to register a guest, assign rooms, handle keys, or check out, the manager knows how to update all the right records (database tables) efficiently.
Why is IdentityDbContext Important?
- Predefined Identity Tables: It provides DbSet properties for all the standard identity tables, such as users (IdentityUser), roles (IdentityRole), and their relationships (IdentityUserRole).
- Database Schema Management: When you apply Entity Framework migrations, IdentityDbContext creates all the required tables like AspNetUsers, AspNetRoles, and AspNetUserRoles.
- Customizable: You can extend IdentityDbContext to add custom fields or relationships to users and roles. You can also add extra tables (DbSets) to support your app’s specific needs.
How IdentityDbContext Works in the Application
- When we perform operations like creating a user, assigning roles, or validating credentials, the ASP.NET Core Identity services internally use IdentityDbContext to persist and retrieve data.
- IdentityDbContext abstracts database details and lets you work with identity data using Entity Framework Core.
- You can configure IdentityDbContext with your database connection string, migrations, and other EF Core options.
How Does IdentityDbContext Work in Your Application?
- When your application creates users, assigns roles, or checks credentials, the Identity services use IdentityDbContext behind the scenes to save and retrieve this information from the database.
- It hides the complexity of raw database access, letting you work with identity data easily using Identity service classes.
So, ASP.NET Core Identity streamlines the process of implementing secure user authentication and authorization in modern web applications. With its customizable models, comprehensive management services, and support for both local and external login providers, it enables developers to build feature-rich, secure, and scalable user management systems efficiently.
For whom are these ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials?
These ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials are designed for Students, Beginners, intermediates, and Professional Software Developers who want to learn ASP.NET Core Identity step by step. We will provide a hands-on approach to the subject with step-by-step program examples that will assist you in learning and putting the acquired knowledge into practice.
Important Note: To fully take advantage of this course, please read all the articles in the sequence we added to it. Each article is linked to its previous articles, so if you miss any article, you will find it challenging to understand the concepts. I will explain all the ASP.NET Core Identity concepts using a Single ASP.NET Core MVC Application.
Prerequisites to Learn ASP.NET Core Identity
To learn ASP.NET Core Identity effectively, the following are the prerequisites:
- Basic Understanding of ASP.NET Core: Basic understanding of ASP.NET Core, including MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture. Knowledge of how to create Web APIs using ASP.NET Core.
- C# Programming Language: Good understanding of the C# Language. This is the primary language used for developing ASP.NET Core applications.
- Entity Framework Core: Understanding the Entity Framework Core is Mandatory. EF Core is commonly used for database operations in ASP.NET Core applications. ASP.NET Core Identity uses EF Core to perform database operations.
Note: If we missed any topics in this ASP.NET Core Identity Course, please let us know by leaving a comment in the Comment Box, and we promise that we will publish articles on that topic as soon as possible.
Lastly, your valuable feedback is essential and means a lot to us. So, if you have a few minutes, please let us know your thoughts and feedback on this ASP.NET Core Identity course.
ASP.NET Core Identity
ASP.NET Core Identity – External Providers
ASP.NET Core Identity – Advanced
ASP.NET Core Identity – Interview Questions & Answers
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group


Best tutorial to learn ASP.NET Core Identity
Thank you for this valuable information.
please update your tutorial with Blasor webassembly+asp.net web api, because mostly we use web api + some spa frameworks (Teact, Angular) and for beginners it Will be easy to understand how to use Identity with spa.
please update your tutorials of Identity with Blazor webassembly+asp.net web api, because mostly we use web api + some spa frameworks (React, Angular) and for beginners it Will be easy to understand how to use Identity with spa.
Want to master ASP.NET Core Identity?
Check out our latest video: ASP.NET Core Identity Introduction, Setup, and Customization
Learn step-by-step how to set up and customize ASP.NET Core Identity for secure login, role management, and more.
Watch now 👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WGd9nyoQMjg
Boost your .NET skills with practical, easy-to-follow tutorials from Dot Net Tutorials! Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe for more .NET tutorials and videos!
Such a gem